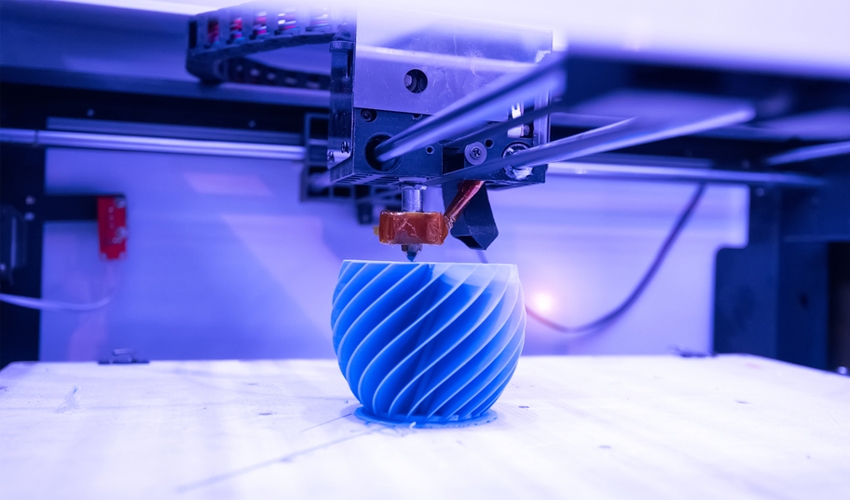
FDM 3D Printing Services
Source high-performing parts for rapid prototyping and low-volume industrial production with FDM 3D printing.
What is FDM 3D Prining?
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D printing revolutionizes manufacturing by employing precise layer-by-layer extrusion of thermoplastics to craft tailor-made components. FDM proves versatile, catering to initial and functional prototyping, as well as low-volume production across an array of robust plastic materials. Recognized for its affordability, FDM extends beyond small-scale manufacturing, offering accessibility to an assortment of thermoplastics, including PLA and PETG, with a commendable dimensional accuracy of ±0.5% and a minimum limit of ±0.5 mm.
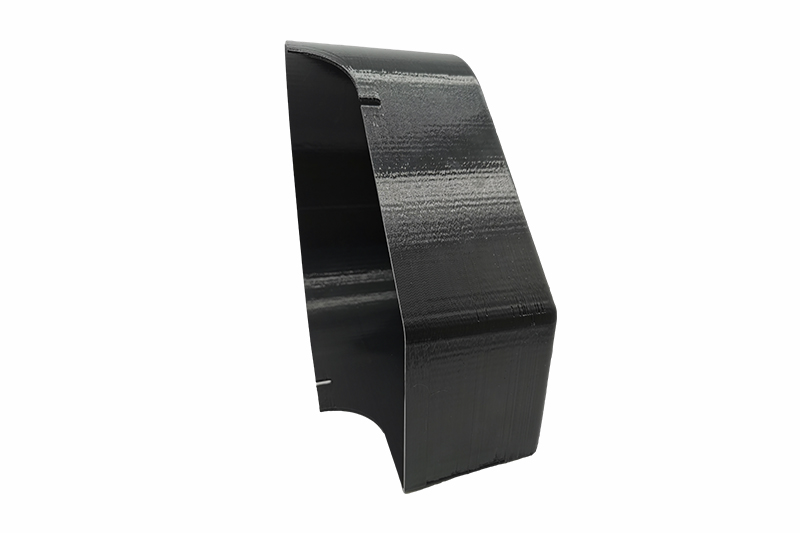
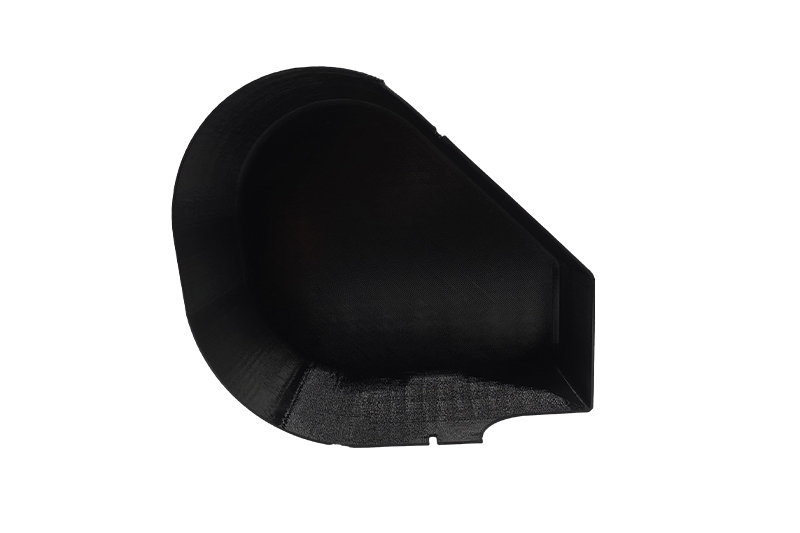
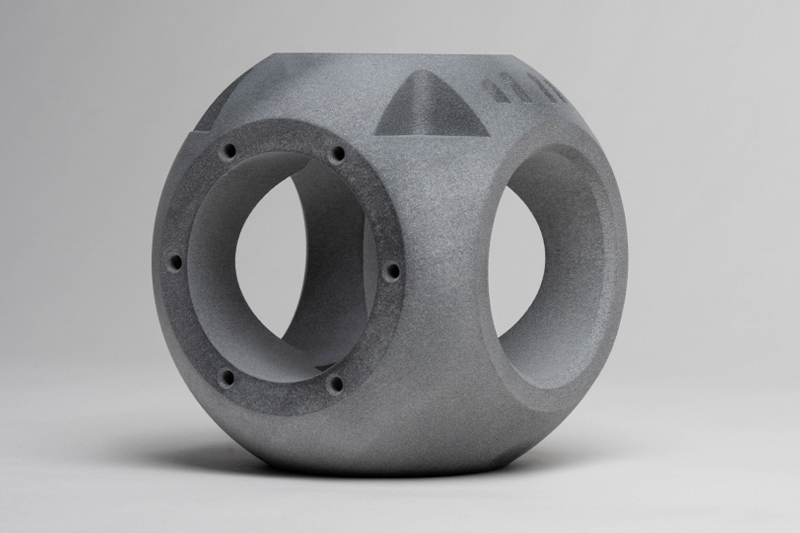
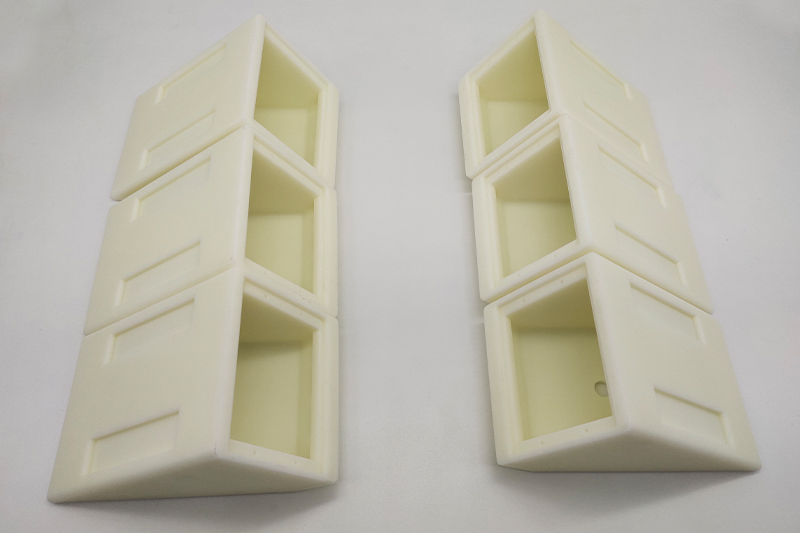
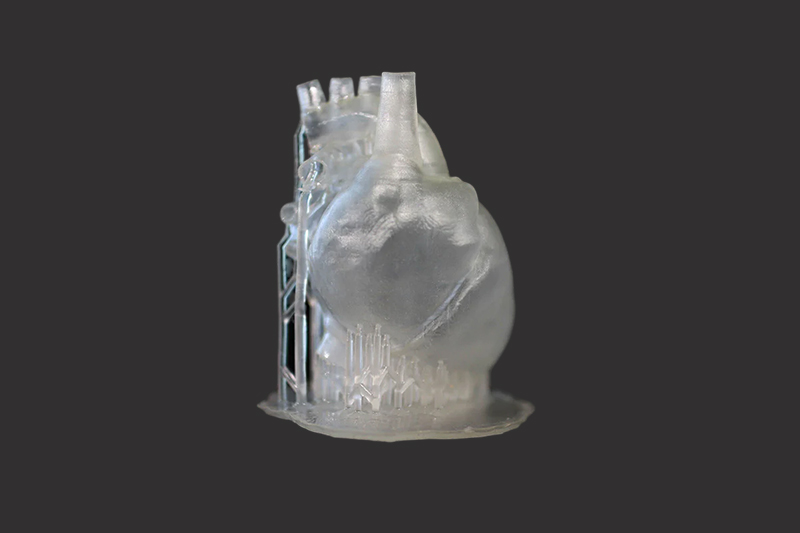
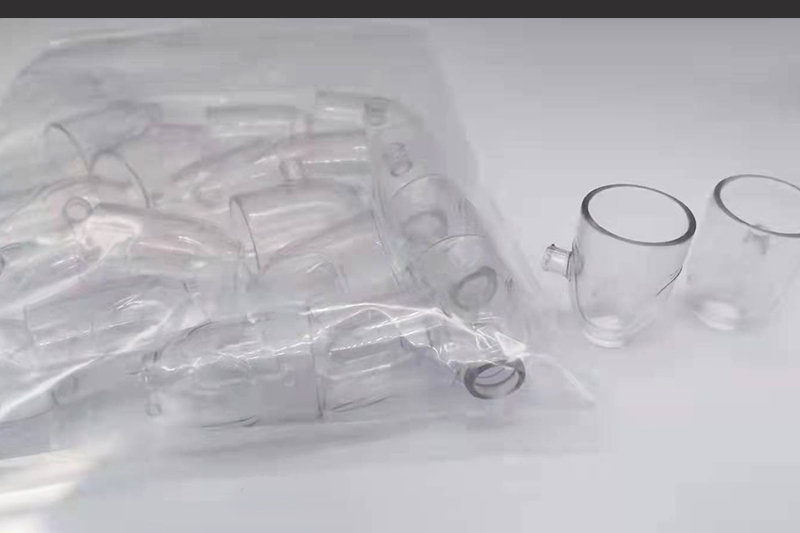
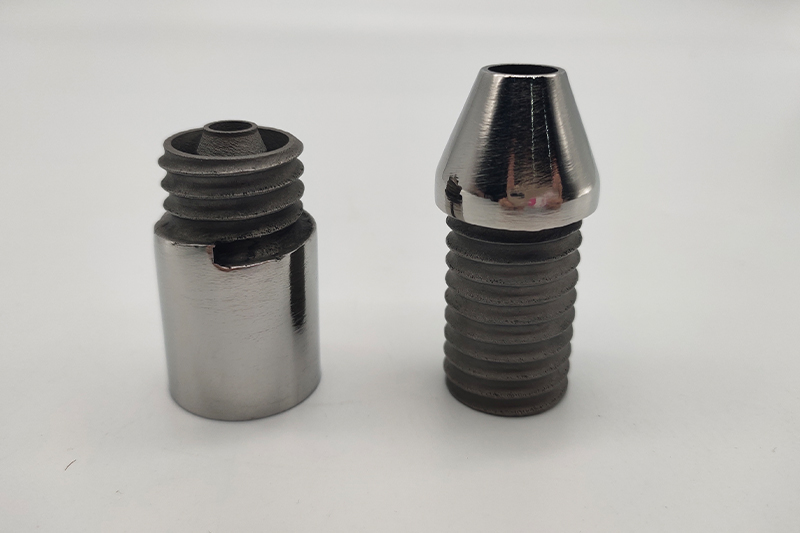
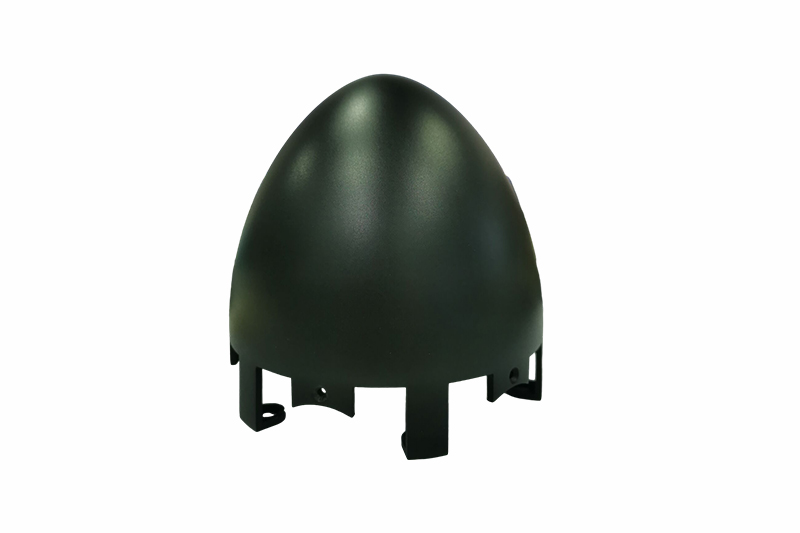
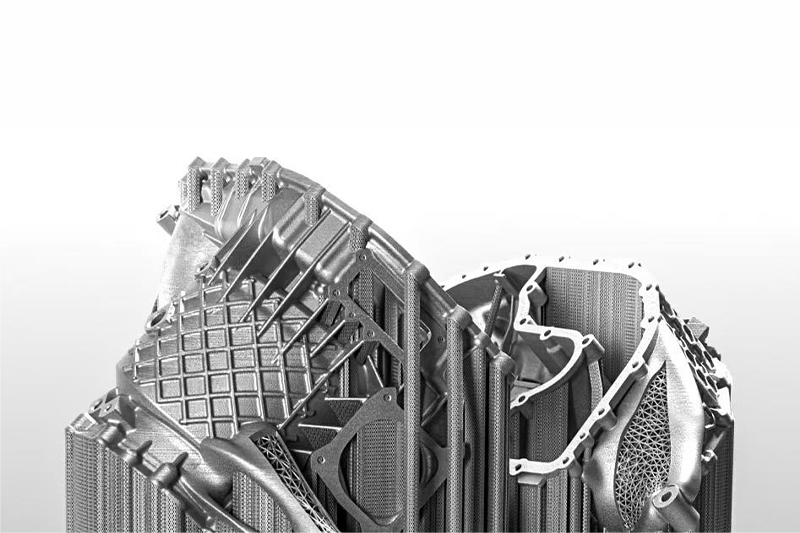
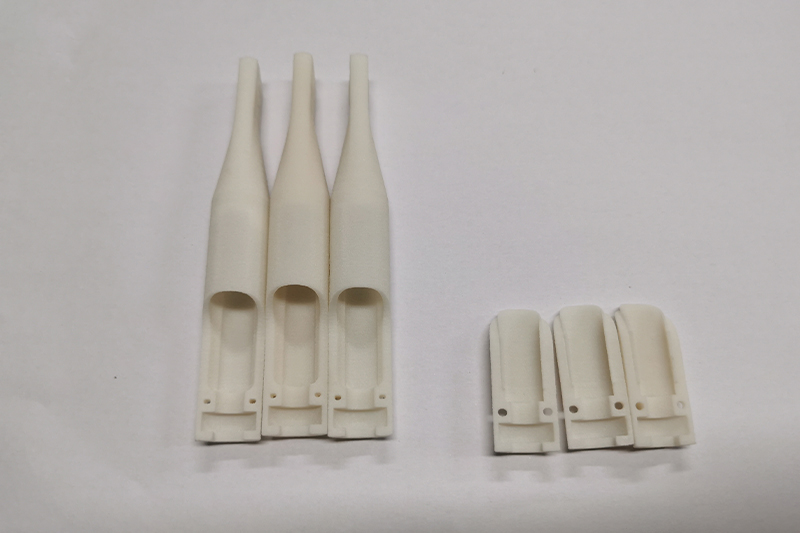
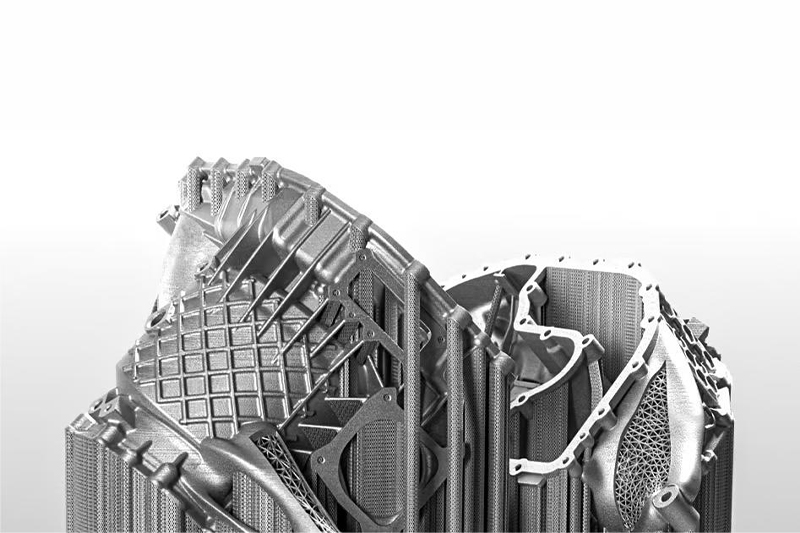
Gallery
FDM 3D Printing Materials

PLA
Black,white.Environment friendly materials.

PETG
Black,white.Good shock resistance and flexibility.

ABS
Blue,white. Engineering plastic, strong.
FDM Infill Options
For prototyping with FDM, customization thrives with infill options of 20%, 30%, 40%, 60%, and 80%.
FDM 3D Printing Finishes
FDM constructs parts with temporary support materials, facilitating their removal during post-processing, though fine layer lines remain on part surfaces.
FDM 3D Printing Tolerance
| Maximum build size | Standard lead time | Dimensional accuracy | Layer height | Infill | |
| Prototyping FDM | 500 x 500 x 500 mm | From 2 business days | ±0.5% with a lower limit on ± 0.5 mm | 100-300 μm | 20-80% |
FDM 3D Printing Guidelines
The table below summarizes the recommended and technically feasible values for the most common features encountered in FDM 3D printed parts.
Browse FDM 3d printing guidelines
Feature
Recommended Size
Unsupported Walls
0.8 mm
Supported Walls
0.8 mm
Minimum Feature Size
2.0 mm
Minimum Hole Size
2.0 mm
FDM 3D Printing Advantages And Drawbacks
Advantages
• FDM ranks as the most cost-effective avenue for crafting custom thermoplastic prototypes and parts.
• Impressively brief lead times, typically spanning just a few days.
• A diverse material selection caters to both prototyping and industrial applications.
Drawbacks
• FDM’s suitability diminishes for intricately detailed parts due to its lower resolution.
• Post-processing becomes essential to achieve a polished finish, as FDM parts may exhibit visible layer lines.
• Inherent anisotropy characterizes FDM parts, owing to the layer adhesion mechanism.
FDM 3D Printing Application
Concept Models
The speed and versatility of FDM lets engineers create physical snapshots of their designs.
Rapid Prototyping
An FDM machine can be used to create durable prototypes that withstand thermal, chemical, and mechanical stress.
Direct Digital Manufacturing
High-performance materials make FDM ideal for producing jigs, fixtures, and production tooling.
3D Printing Technologies Comparision
| Materials | Dimensional accuracy | Strengths | Build Volume | Layer Thickness | Min. Feature Size | |
| FDM | 3 | ± 0.5% with a lower limit on ± 0.5 mm | Low cost, wide range of materials | 500 x 500 x 500 mm | 100-300μm | 2.0 mm |
| SLA | 3 | ± 0.2% with a lower limit of ± 0.127 mm | Smooth surface finish, fine feature details, big print area | 500 x 500 x 500 mm | 50-100μm | 0.2 mm |
| SLS | 2 | ± 0.3% with a lower limit of ± 0.3 mm | Design flexibility, supports not required | 395 x 500 x 395 mm | 100μm | 0.5 mm |
| MJF | 3 | ± 0.3% with a lower limit on ± 0.3 | Design flexibility, supports not required | 380 x 285 x 380 mm | 80μm | 0.5 mm |
| SLM | 5 | ± 0.2% with a lower limit of ± 0.127 mm | Metal parts | 320x320x400mm | 200μm | 1 mm |
3D Printing Technologies
SLA 3D Printing FAQs
In general, part accuracy depends on how you’ve calibrated your FDM printer and the complexity of your model.
FDM printers produce high-quality parts from durable materials, able to retain sound mechanical properties. Both types of FDM machines offer high dimensional accuracy, and even at the industrial level, FDM tends to be more cost-efficient than other AM processes.