- Capabilities
-

CNC Machining
Tight tolerance and 20+ finishes 3, 4 , 5 axis, as fast as 2 days -
Sheet Metal Fabrication
High-precision, on-demand sheet metal cutting and bending. -

3D Printing
SLA, SLS,MJF,SLM, FDM 3d printing with post treatment. -

Vacuum Casting
Production quality parts without the tooling investment.
-
- Solutions
Rapid Prototyping
Fastest lead time of high-quality prototypes at minimal cost.
Low Volume Production
From one-off prototyping to low-volume production.

Mechanical Assembly
Custom assembly for project-specific needs.

Custom Package
Ready to help you prompt your brand.
- Sources

Materials
Select from 100 more types of metals and plastics.

Finishes
Select from 20 more types of surface fishes.
Industries
Providing precision machining and manufacturing solutions.

Cases
How we assist our clients in bringing their projects to fruition.
- Company

Quality Assurance
Consistent quality, every time.

About Us
Your go-to manufacturer for custom parts.

Newsroom
Learn updated news about ECOREPRAP.
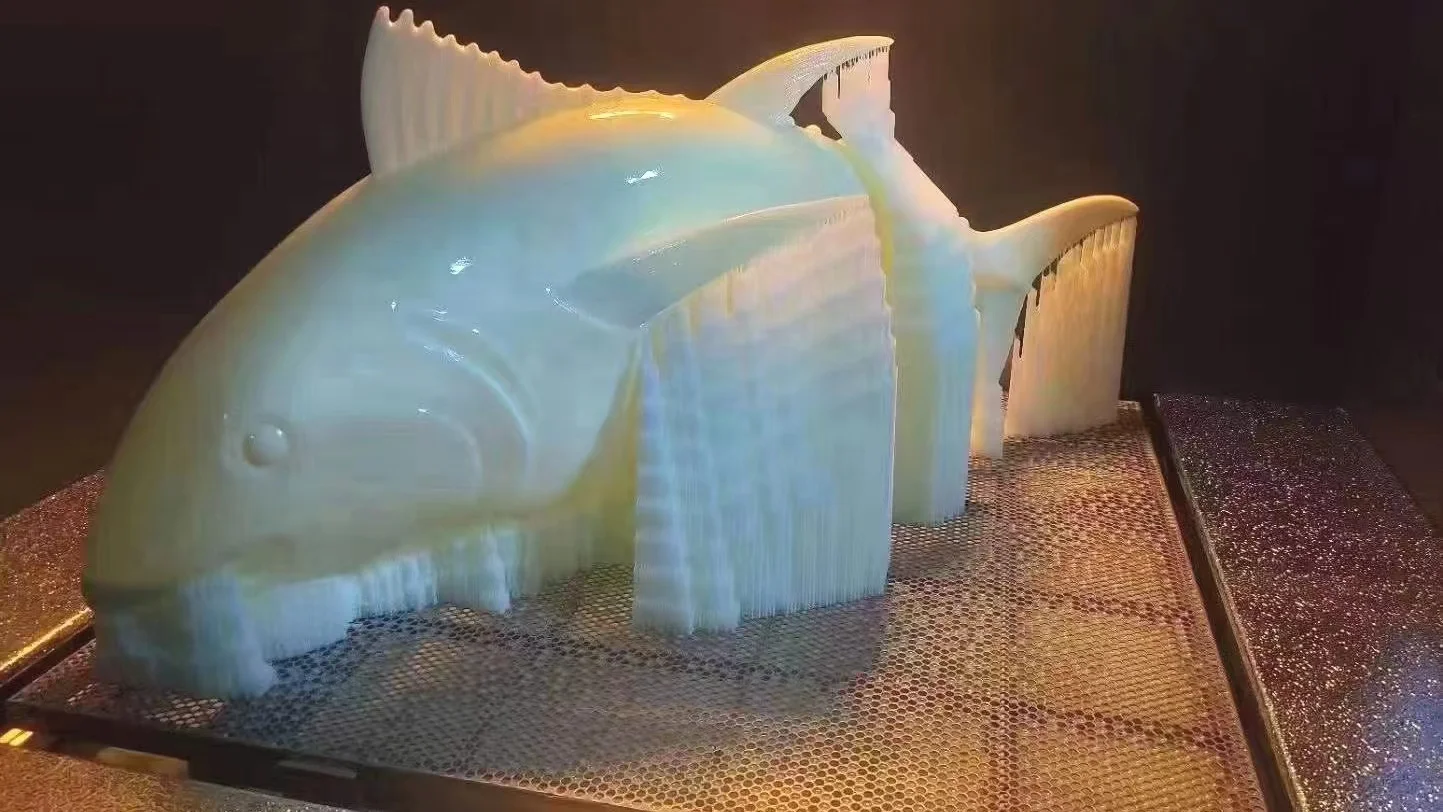
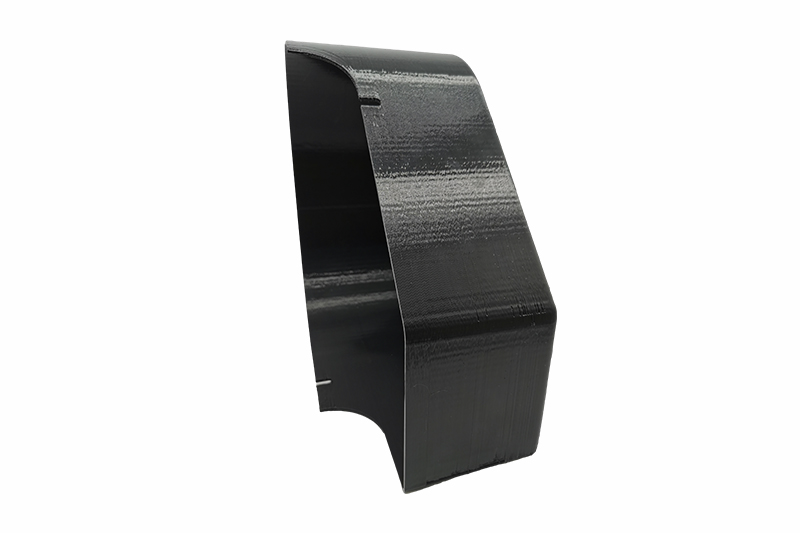
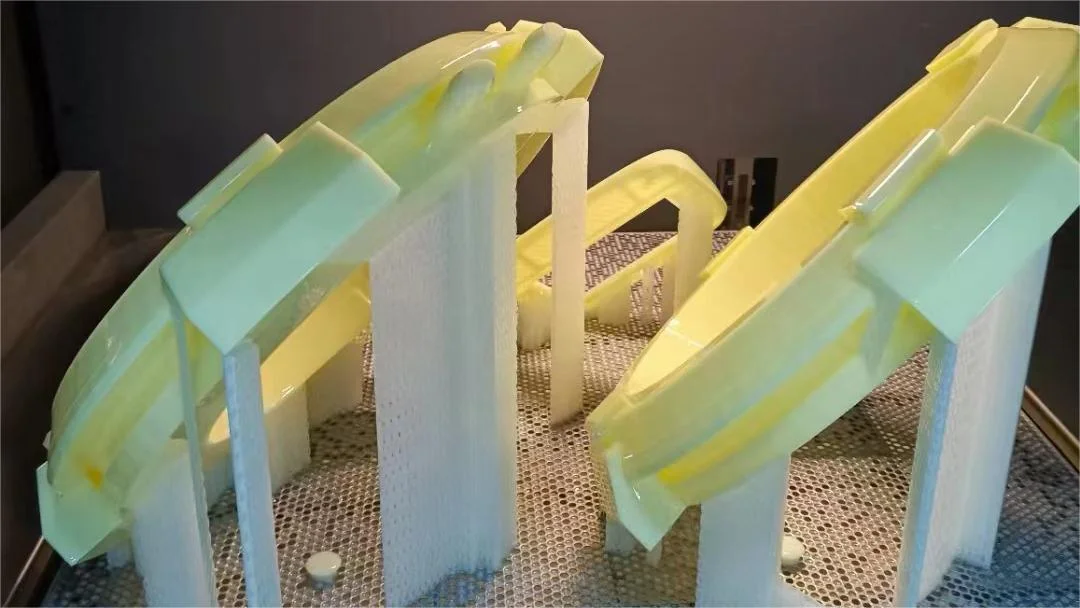
SLA 3D Printing Services
China online SLA 3d printing services for high-performance parts for rapid prototyping and low-volume production. As fast as in 1 day.
All your designs are secure and confidential
What is SLA 3D printing?
Stereolithography, also named resin 3D printing or vat photopolymerization, is an additive manufacturing technique in which a light source hardens liquid resin into solid plastic. With the light source hardening the liquid resin, the SLA 3d printer can turn the liquid resin into 3d objects.
With the SLA 3d printing services provided by ECOREPRAP, you can get high accuracy and high resolution and end-use parts with fine details and smooth surfaces. The SLA-printed parts can be used for end-use, low-volume manufacturing, or rapid prototyping.
We have standard, tough, and transparent resin for SLA resins to meet your on-demand manufacturing.
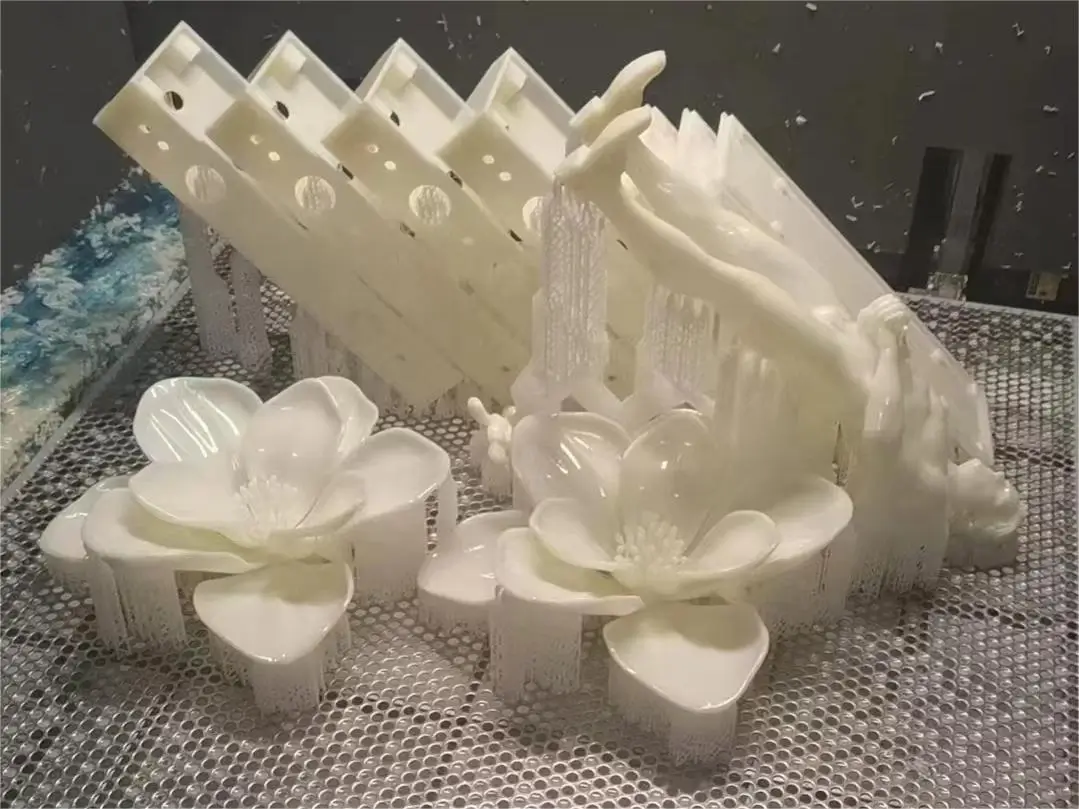

SLA 3D Printing Materials
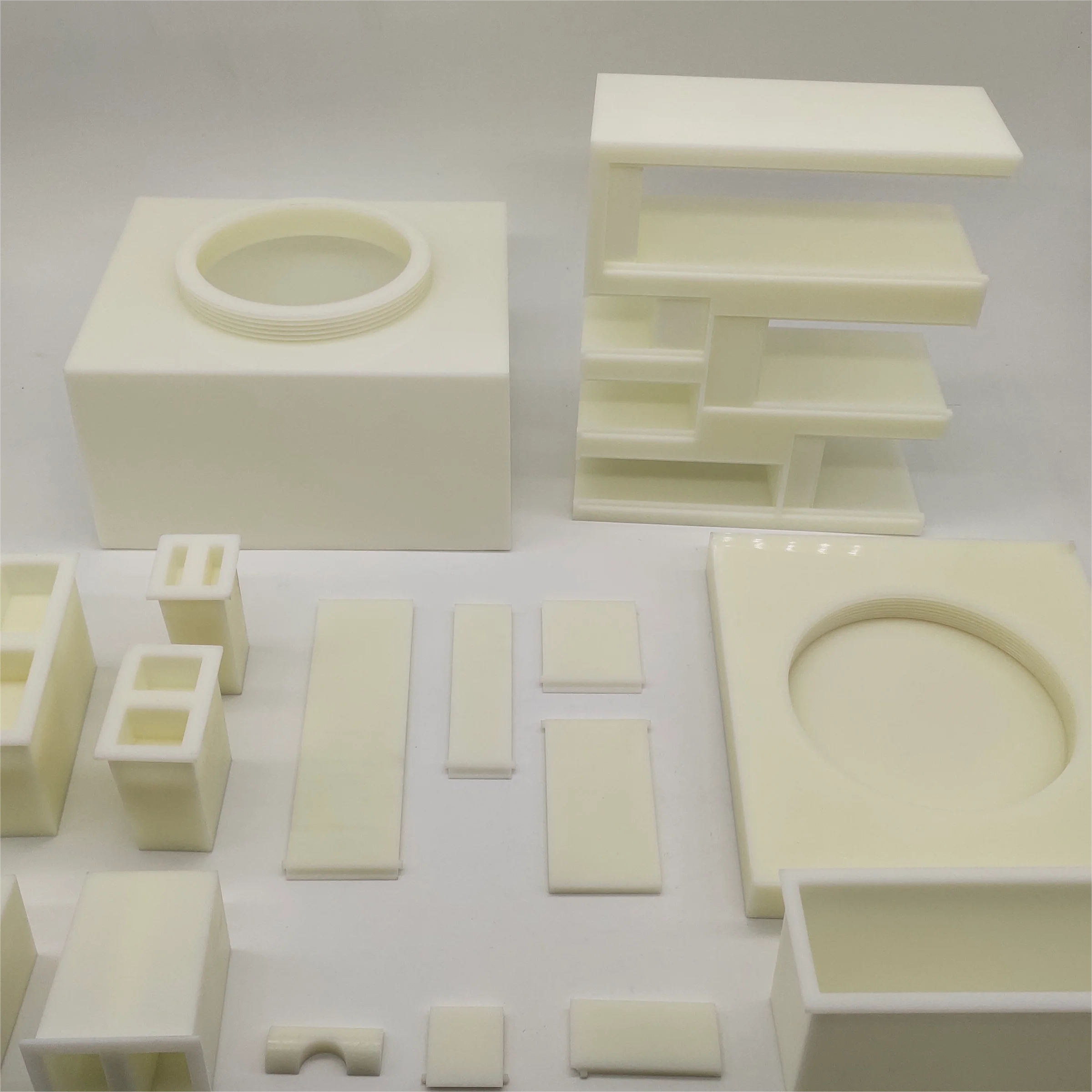
Standard SLA Resin Material
Standard resin is the most commonly used resin in SLA 3D printing. It is white. SLA 3d printed parts with standard resin have smooth surfaces, strong detail performance, stable dimensions, and high cost-effectiveness. With good overall performance, the standard resin can be applied in various industrial fields such as automotive, medical, and consumer electronics to produce master molds, concept models, general parts, and functional components.
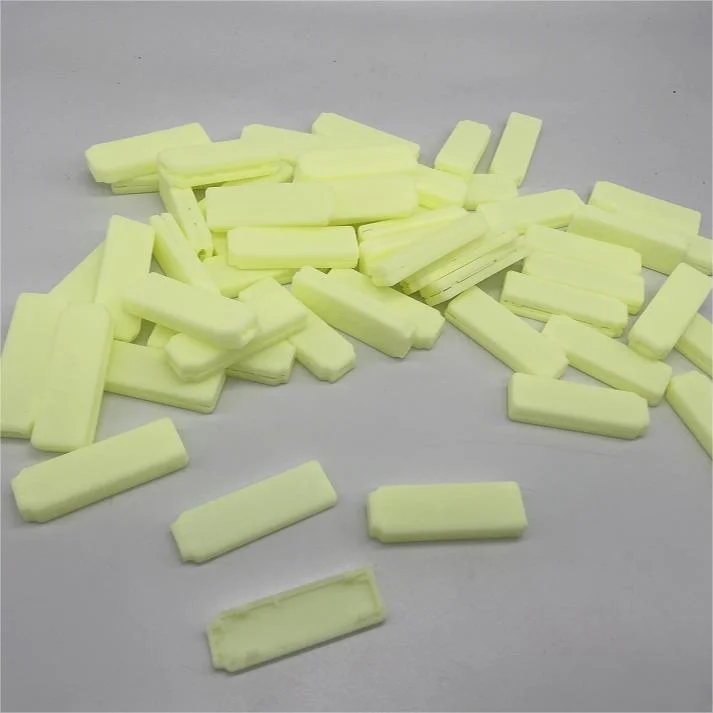

Tough SLA Resin Material
Tough resin is light yellow. Compared with standard resin, tough resin has better toughness. Tough resin and standard resin are almost identical for other properties like surface smoothness, detail representation, and dimensional stability. Thus, tough resin is a better choice if the parts have special requirements for toughness, for industries like aerospace, prototyping, and electronics, parts printed with tough resin are usually used.
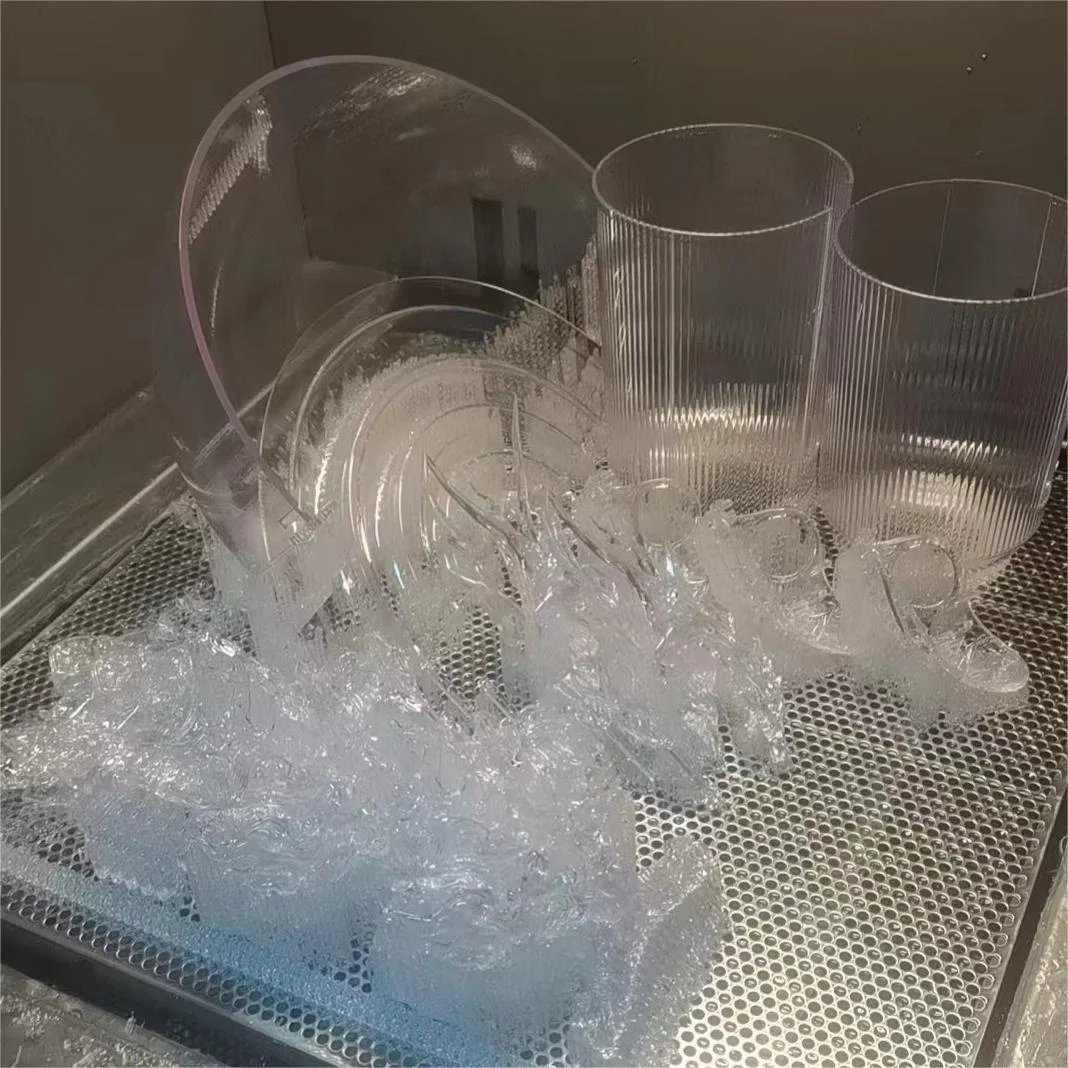

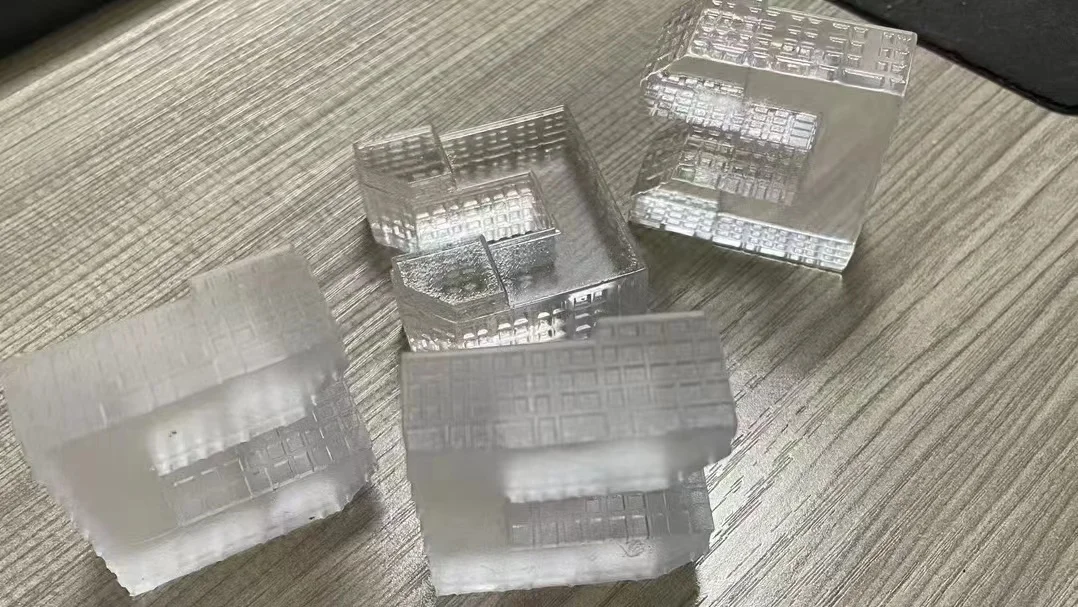
Transparent SLA Resin Material
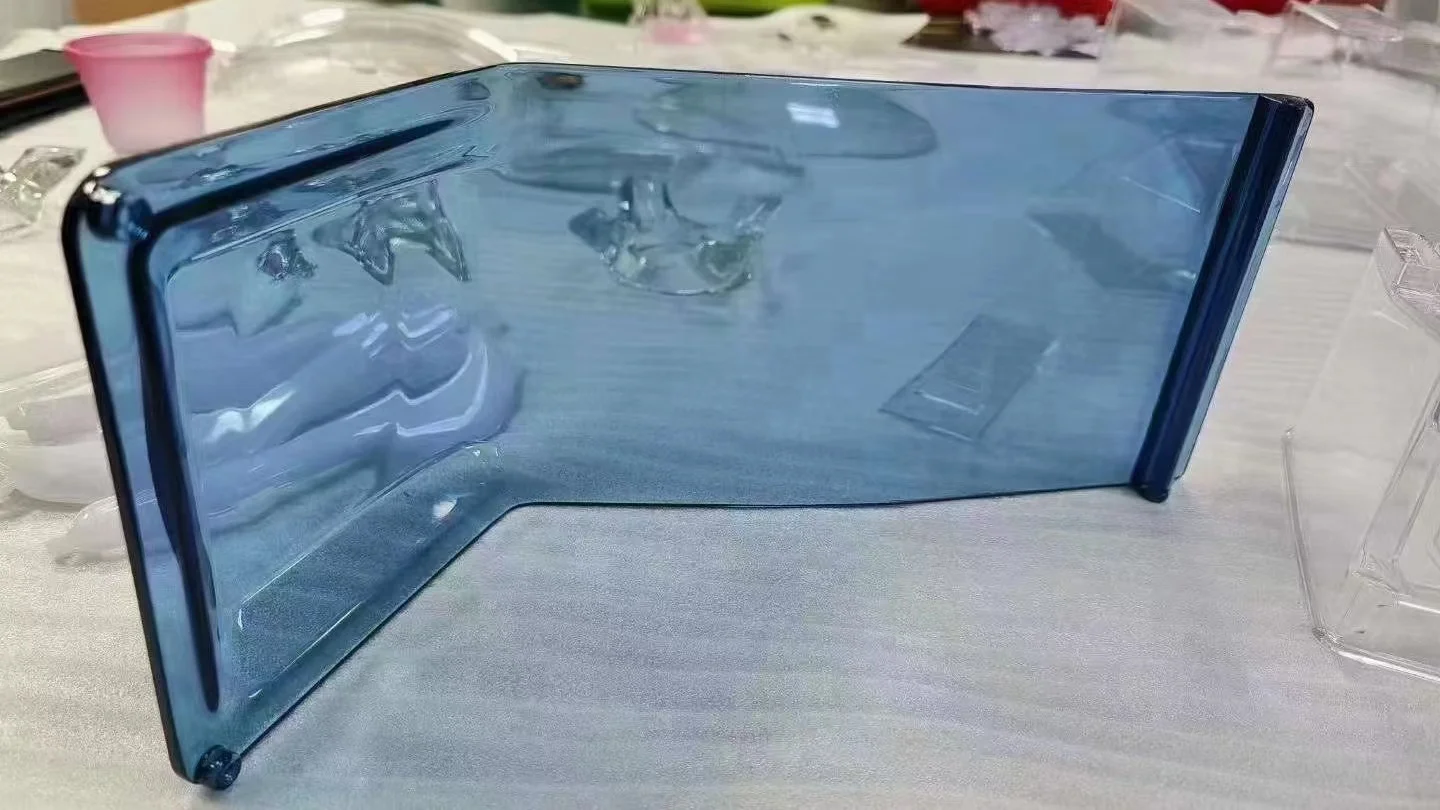
Transparent resin is specially designed to produce translucent and transparent 3d printed parts. Parts pointed with the transparent resin have a smooth surface, offer detailed presentation, and are with good dimensions. Parts printed with transparent resin are nearly colorless. Without surface treatment, the parts printed with transparent resin initially appear translucent. To achieve high transparency, vapor polishing can be applied.
SLA 3D Printing Post-processing
Standard
All support material is removed and support nibs are sanded smooth.
Standard Sandblasting
Parts can be media blasted for a uniform matte finish.
Polishing
For transparent and translucent SLA parts, they will be polished manually before vapor polishing.
Painting
Painting is avalible for SLA parts with different color based on pantone number.
Plating
Painting is avalible for SLA parts.
SLA 3D Printing Tolerance
| Maximum Build Size | Standard Lead Time | Dimensional Accuracy | Layer Thickness | Minimum Feature Size | |
| SLA 3D Printing | 500 x 500 x 500 mm | From 1 business days | ± 0.2% with a lower limit of ± 0.127 mm | 50-100 μm | 0.2 mm |
SLA 3D Printing Guidelines
This table summarizes the recommended and technically viable values for the most usual attributes of 3D-printed components.
Browse SLA 3d printing guidelines
Feature
Recommended Size
Unsupported Walls
1.0 mm
Supported Walls
0.5 mm
Minimum Feature Size
0.2 mm
Minimum Hole Diameter
Minimum Hole Diameter
Minimum Escape Hole Diameter
4.0 mm
SLA 3D Printing Advantages And Drawbacks
Advantages
•SLA 3d printing can create parts with very high dimensional precision and intricate information.
•SLA printed parts have a smooth surface area finish, making them optimal for aesthetic models.
•Speciality SLA materials are available, such as clear, adaptable, and castable resins.
Drawbacks
• SLA parts are generally brittle and not suitable for functional prototypes, though industrial SLA can produce more functional components for this stage.
• The mechanical properties and visual appearance of SLA parts will degrade over time when the parts are exposed to sunlight.
• Support structures are always required and post-processing is necessary to remove the visual marks left on the SLA part.
SLA 3D Printing Application
Engineering and Product Design
3D printing offers engineering and design unparalleled versatility and efficiency. In engineering, it speeds up rapid prototyping and iterative design processes so the engineers can refine concepts quickly and cost-effectively.
3D printing makes complex geometries and customized components accessible, revolutionizing industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. Designers can use 3d printing to explore innovative shapes, materials, and manufacturing techniques in product design. 3D printing can accelerate product development with highly detailed prototypes for visual and functional evaluation.
On Demand Manufacturing
3D printing can make complex parts directly from digital designs for many industries. For prototyping processes, 3D printing allows for rapid iteration and testing of designs, reducing time-to-market time.
It provides on-demand manufacturing services so customers can get the correct quantity and do not need to have a lot of inventory. Customization and small bath production are available with 3d printing.
Whether it is only one piece, or small batch, even high-volume parts, 3D printing is a nice try for on demand manufacturing.
Specific Industrial Application
Nowadays, 3d printing is widely used by designers, manufacturers, and engineers in different industries. In the automotive sector, 3d printing creates concept models and produces after-market parts, such as gaskets, engines, and transmission. In the aerospace sector, it is used to make different parts like fixtures. These parts can be used for testing, prototyping, and manufacturing.
3D printing is also widely used in education, dental, medical, electronics, jewelry, and audiology sectors. Its low cost and time efficiency make printing more and more popular.
3D Printing Technologies Comparision
| Materials | Dimensional accuracy | Strengths | Build Volume | Layer Thickness | Min. Feature Size | |
| FDM | 3 | ± 0.5% with a lower limit on ± 0.5 mm | Low cost, wide range of materials | 500 x 500 x 500 mm | 100-300μm | 2.0 mm |
| SLA | 3 | ± 0.2% with a lower limit of ± 0.127 mm | Smooth surface finish, fine feature details, big print area | 500 x 500 x 500 mm | 50-100μm | 0.2 mm |
| SLS | 2 | ± 0.3% with a lower limit of ± 0.3 mm | Design flexibility, supports not required | 395 x 500 x 395 mm | 100μm | 0.5 mm |
| MJF | 3 | ± 0.3% with a lower limit on ± 0.3 | Design flexibility, supports not required | 380 x 285 x 380 mm | 80μm | 0.5 mm |
| SLM | 5 | ± 0.2% with a lower limit of ± 0.127 mm | Metal parts | 320x320x400mm | 200μm | 1 mm |
3D Printing Technologies
SLA 3D Printing FAQs
SLA is short for Stereolithography. SLA 3d printing is one type of 3d printing technology. In SLA printing, a light source, typically a UV laser, selectively hardens liquid resin layer by layer, making it a desired shape.
There is a vat or tank to contain the liquid resin. The liquid photosensitive SLA resin is poured into the tank of the 3d printer; the UV light source will interact with the resin and selectively cure it by layer. As each layer gets solid, the build platform moves downward, exposing the next resin layer to the UV laser and cured. SAL 3D printing is widely used for its high-detail presentation, smooth surface finish, and ability to manufacture complicated parts.
The liquid material used for SLA 3d printing is called SLA resin, which typically consists of photosensitive monomers, photoinitiators, and other auxiliary components. As the main components of the resin, photosensitive monomers have unique chemical structures and undergo polymerization reactions when exposed to UV light. Photosensitive monomers are usually acrylic resins. Standard SLA resin are typical acrylic esters. Tough SLA resin and high-temperature resin may be acrylic polyamide, while transparent SLA resin is acrylic light-cured resin. The specific compositions may be different between manufacturers.
We recommend that you choose standard resin for prototypes with a smooth injection molding-like surface finish.
The unit price per liter of SLA resin vary from 50usd to 200usd, depending on different suppliers. Compared with FDM printing, SLA printing is more expensive. But SLA printing is cheaper if compared to SLS, MJF and SLM. The SLA printing price per gram is about 0.7g/usd-1.5g/usd.
SLA and FDM are two popular 3d printing technologies. SLA 3d printer uses a UV light source to cure liquid resin to build solid objects. FDM 3d printer extrudes thermoplastic filaments layer by layer to form objects.
Generally speaking, FDM prints faster than SLA printer. Because FDM printer can deposit material more quickly, especially when printing larger objects, or objects with simple design.
The strength comparison between SLA resin and FDM filament depends on the materials used in FDM printing. PLA, ABS, PETG, PC, and TPU are the common FDM printing filaments. SLA resin typically offers similar properties to ABS. Compared with FDM PLA filament, SLA resin is stronger. While compared with other filaments like ABS, PETG, PC and TPU, SLA resin is weaker.