- Capabilities
-

CNC Machining
Tight tolerance and 20+ finishes 3, 4 , 5 axis, as fast as 2 days -
Sheet Metal Fabrication
High-precision, on-demand sheet metal cutting and bending. -

3D Printing
SLA, SLS,MJF,SLM, FDM 3d printing with post treatment. -

Vacuum Casting
Production quality parts without the tooling investment.
-
- Solutions
Rapid Prototyping
Fastest lead time of high-quality prototypes at minimal cost.
Low Volume Production
From one-off prototyping to low-volume production.

Mechanical Assembly
Custom assembly for project-specific needs.

Custom Package
Ready to help you prompt your brand.
- Sources

Materials
Select from 100 more types of metals and plastics.

Finishes
Select from 20 more types of surface fishes.
Industries
Providing precision machining and manufacturing solutions.

Cases
How we assist our clients in bringing their projects to fruition.
- Company

Quality Assurance
Consistent quality, every time.

About Us
Your go-to manufacturer for custom parts.

Newsroom
Learn updated news about ECOREPRAP.
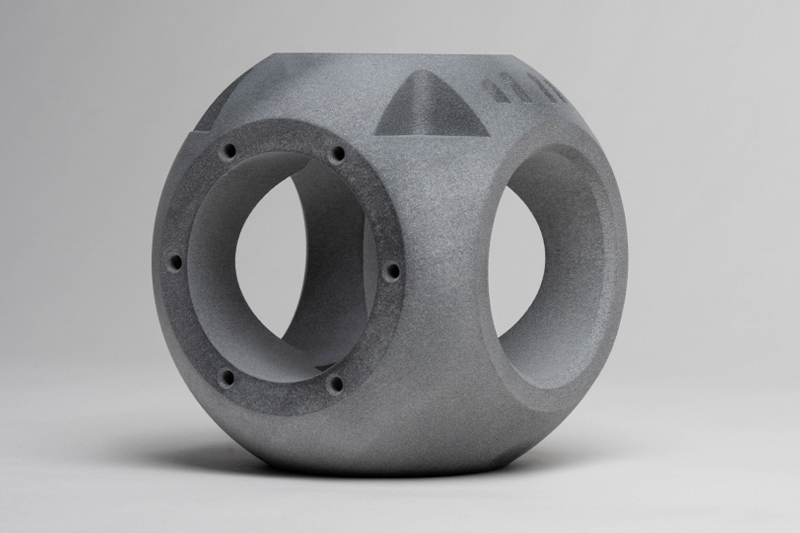
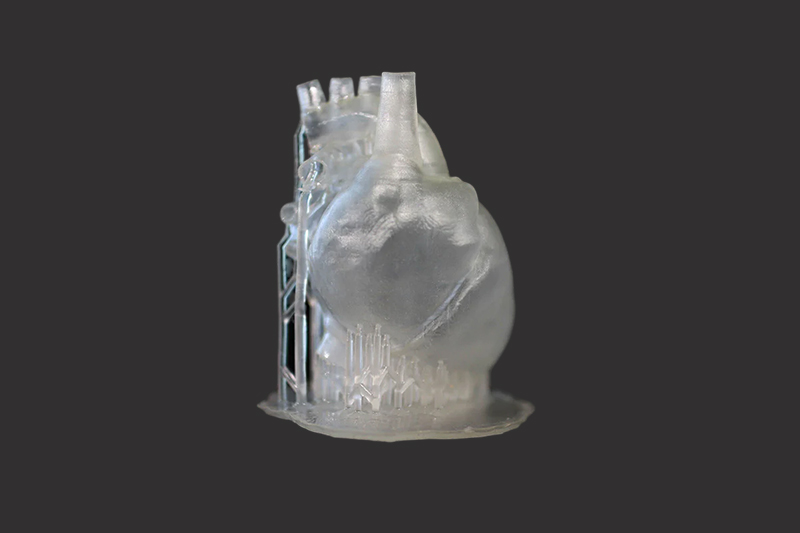
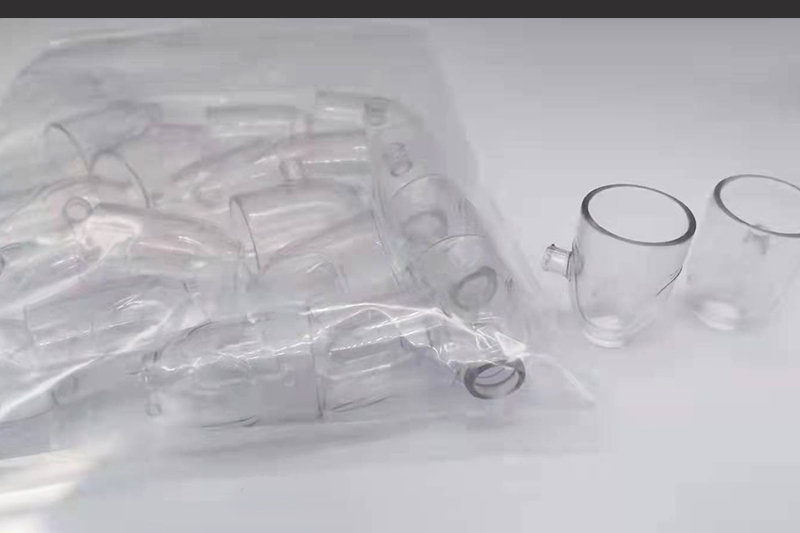
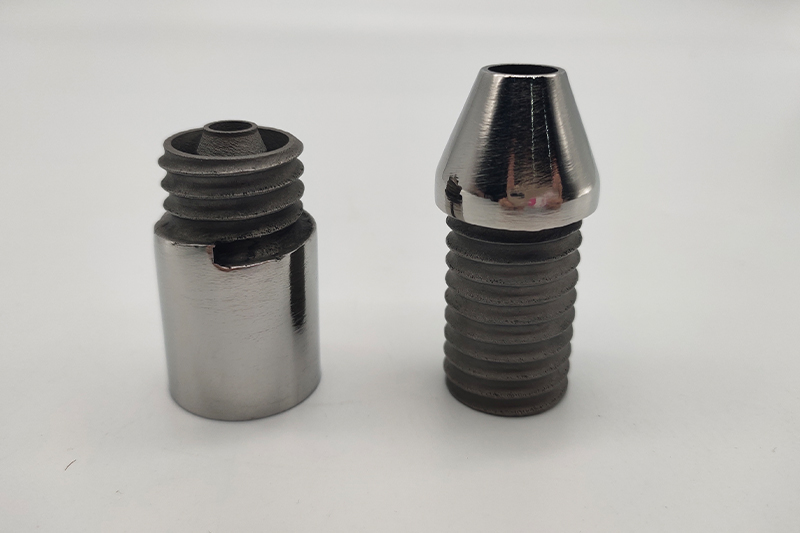
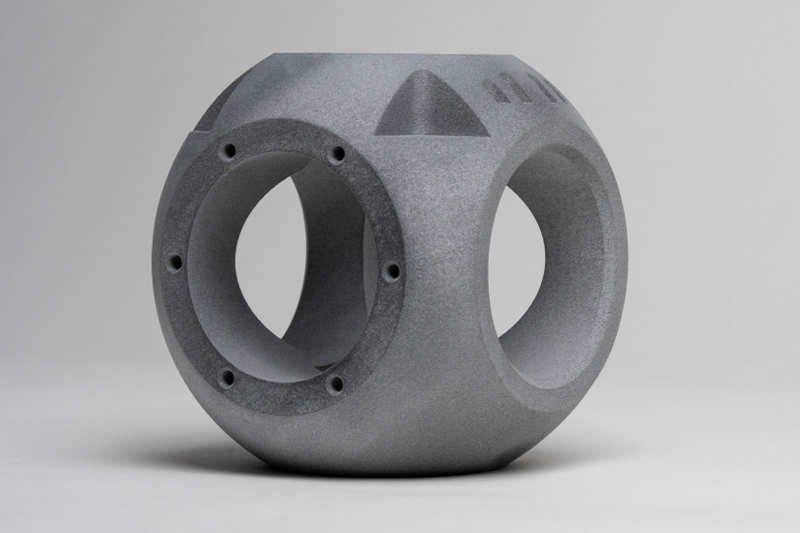
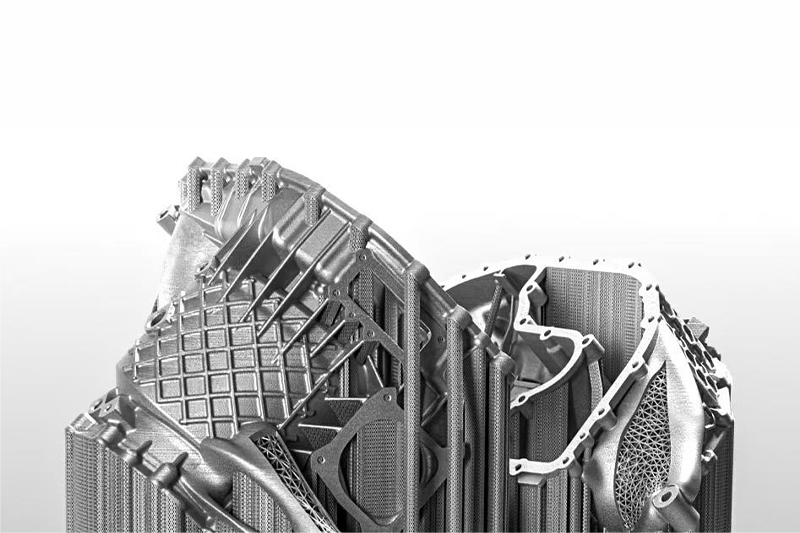
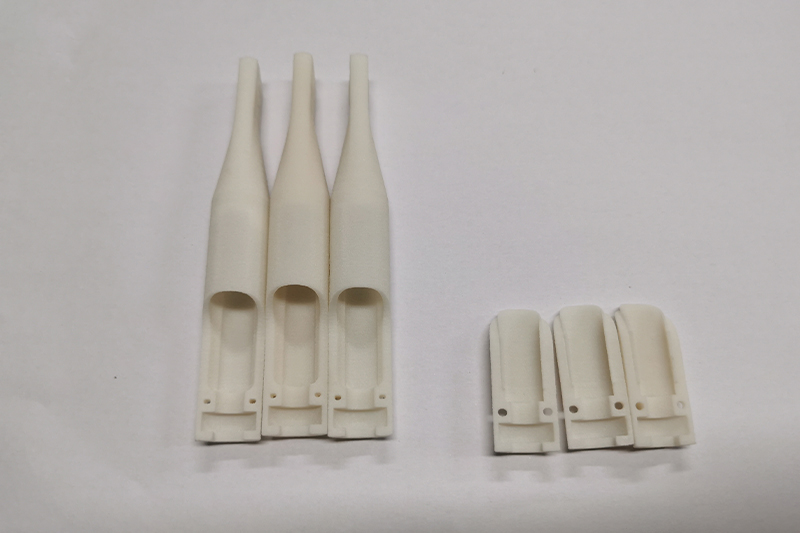
SLM 3D Printing Services
High-quality metal parts for prototyping and production easily using selective laser melting (SLM) 3D printing as fast as 3 days.
All your designs are secure and confidential
What is selective laser melting?
Selective laser melting (SLM) is one of many proprietary names for metal additive manufacturing (AM) technology that uses a bed of powder with a source of heat to create metal parts. Also known as direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) and laser powder bed fusion (LPBF), the ASTM standard term is powder bed fusion (PBF). Selective laser melting is a rapid prototyping, or additive manufacturing technique designed to use a high-power-density laser to melt and fuse metallic powders.

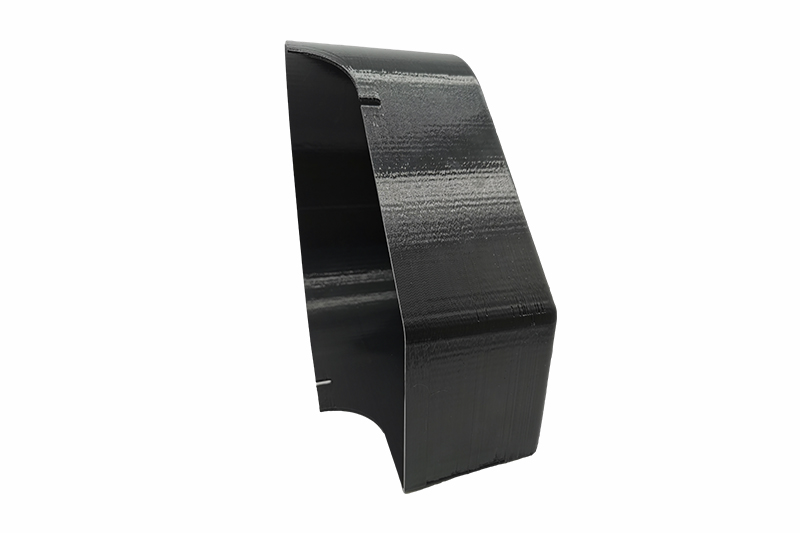
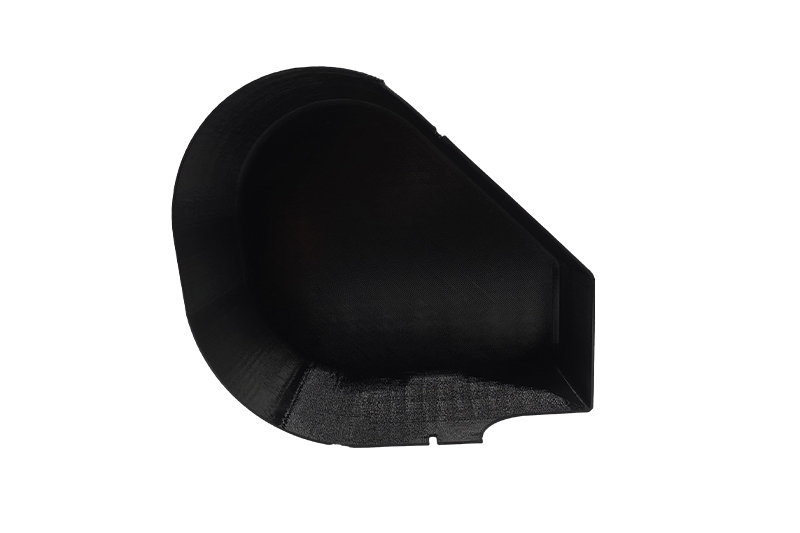
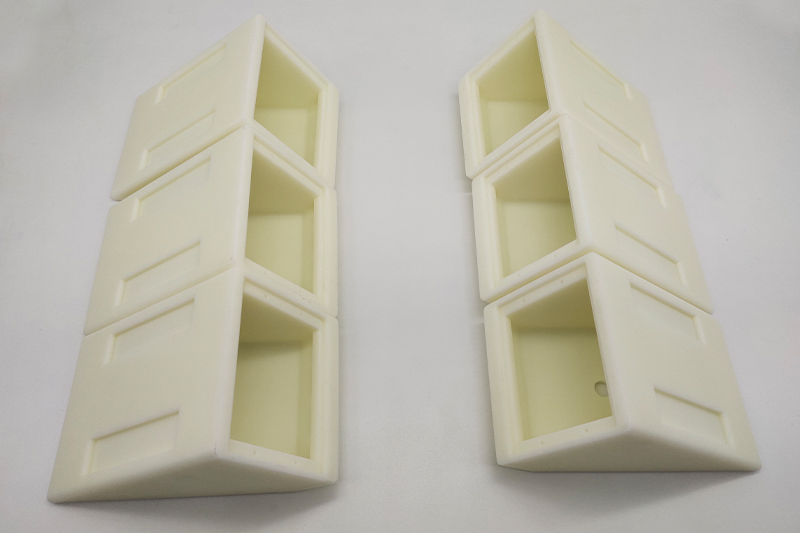
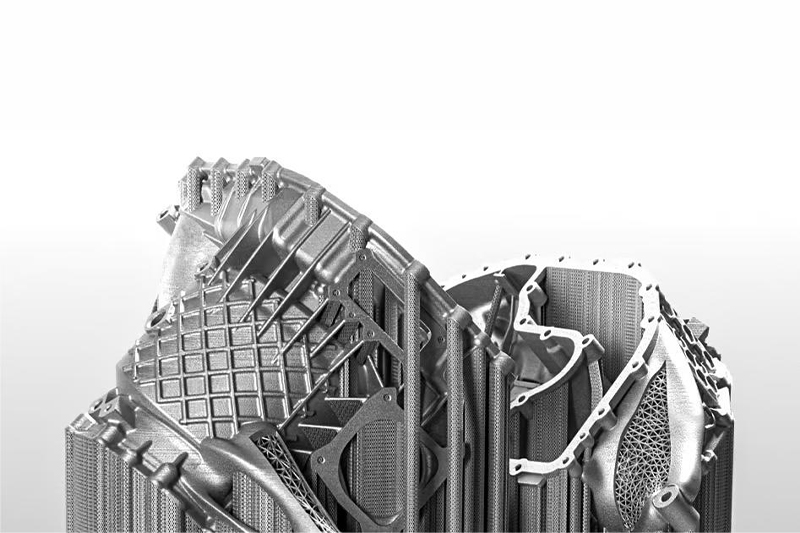
Gallery
SLM 3D Printing Materials
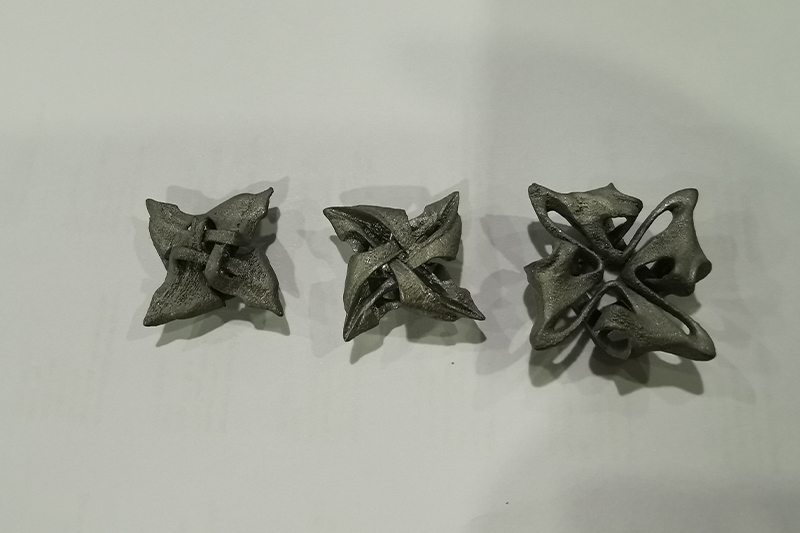

Aluminum
AISi10Mg
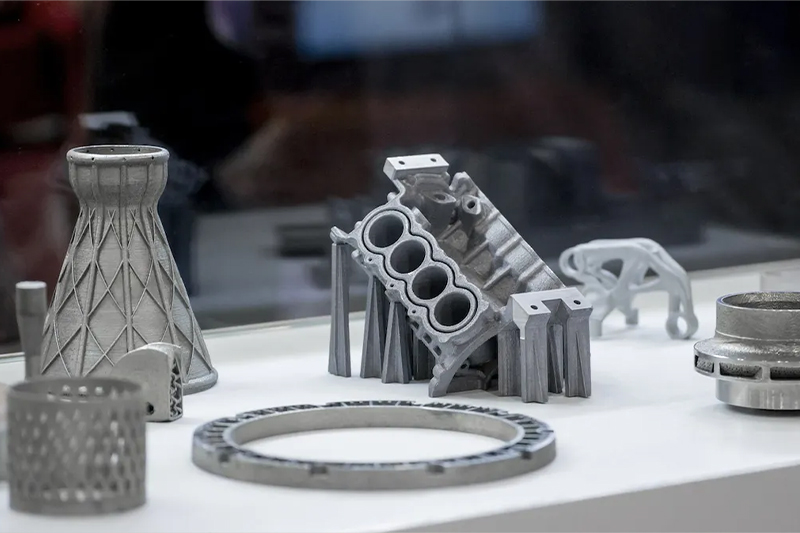

Stainless Steel
316L
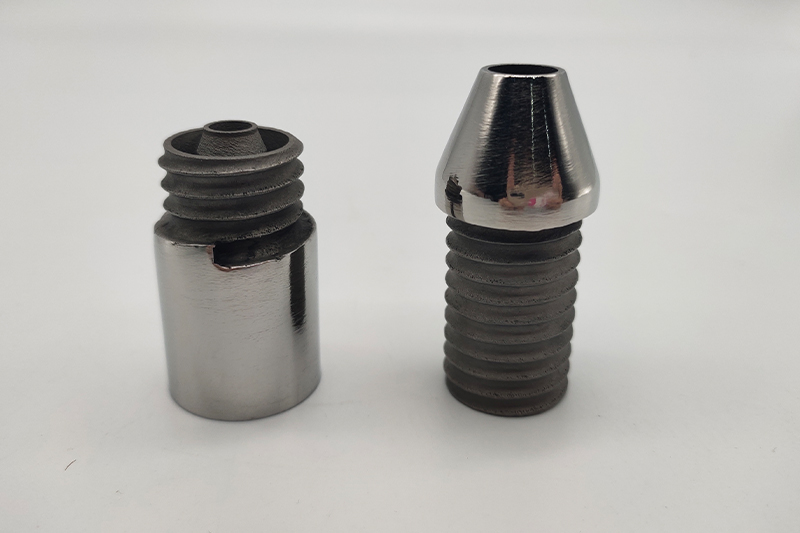

Die Steel
MS1
Titanium
TC4
Copper
SLM 3D Printing Finishes
Standard
The surface finish of the final melted part is rough.
Sandblasting
Parts can be media blasted for a uniform matte finish.
Polishing
The rough surface can be polished
Custom
CNC machining of features and polishing is evaluated on a case-by-case basis and can be requested for quoting.
SLM 3D Printing Tolerance
| Maximum Build Size | Standard Lead Time | Dimensional Accuracy | Layer Thickness | Minimum Feature Size |
| 320x320x400mm | 7 business days | ± 200μm or 0.2%mm | 200μm | 1 mm |
SLM 3D Printing Application
Aerospace Landing Gear
Safran Landing Systems and SLM Solutions worked together to improve a previously forged nose landing gear part for private jets.
Automotive Tools
Audi uses the EOS M 400 printer to manufacture hot forming segments and high-pressure die casting tool inserts.
Medical Titanium Implants
GE Additive produces an additively manufactured option made from titanium powder using LPBF printing.
Energy Steam Distribution Block
Orano and AddUp created several copies of a 3D printed material transfer bridge and a steam distribution block.
3D Printing Technologies Comparision
| Materials | Dimensional accuracy | Strengths | Build Volume | Layer Thickness | Min. Feature Size | |
| FDM | 3 | ± 0.5% with a lower limit on ± 0.5 mm | Low cost, wide range of materials | 500 x 500 x 500 mm | 100-300μm | 2.0 mm |
| SLA | 3 | ± 0.2% with a lower limit of ± 0.127 mm | Smooth surface finish, fine feature details, big print area | 500 x 500 x 500 mm | 50-100μm | 0.2 mm |
| SLS | 2 | ± 0.3% with a lower limit of ± 0.3 mm | Design flexibility, supports not required | 395 x 500 x 395 mm | 100μm | 0.5 mm |
| MJF | 3 | ± 0.3% with a lower limit on ± 0.3 | Design flexibility, supports not required | 380 x 285 x 380 mm | 80μm | 0.5 mm |
| SLM | 5 | ± 0.2% with a lower limit of ± 0.127 mm | Metal parts | 320x320x400mm | 200μm | 1 mm |
3D Printing Technologies
SLA 3D Printing FAQs
SLM,DMLS,PBF,LPM all refer to the same 3d printing technology, which uses a bed of powder with a source of heat to create metal parts. Selective laser melting (SLM) is one of many proprietary names for a metal additive manufacturing (AM) technology that uses a bed of powder with a source of heat to create metal parts. Also known as direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) and laser powder bed fusion (LPBF), the ASTM standard term is powder bed fusion (PBF). PBF is a rapid prototyping, 3D printing, or additive manufacturing technique designed to use a high power-density laser to melt and fuse metallic powders together.
SLM 3D printers use high-powered lasers to selectively melt a metal powder. The melted parts fuse together layer-by-layer on a molecular basis until the homogenous model is complete.