CNC Machining for Rapid Prototyping: How to Choose the Right Solution for Fast, Accurate Results
Published on: Apr 27, 2024
Updated: Dec 05, 2025
Table of Contents
- 1. What is prototyping?
- 2. Why Choose CNC Machining for Rapid Prototyping?
- 3. Limitations of Rapid CNC Machined Prototypes
- 4. What are the applications of CNC machining prototyping?
- 5. How to make CNC machining prototypes?
- 6. What materials are used in CNC prototype?
- 7. Types Of CNC machines used for prototyping
- 8. Which is better for prototyping? CNC machining VS 3D printing?
- 9. 5 Tips for making prototypes via CNC machining
- 10. How to choose a reliable prototype CNC machining manufacturers?
In modern product development, rapid prototyping is an essential step to validate designs, test functionality and reduce production risks.
Companies looking for CNC machining solutions often face critical questions: how to turn a design into a high-precision physical part efficiently, how CNC compares with alternative prototyping methods, and how to select a supplier that can provide reliable guidance.
Choosing the right approach can save weeks in the development cycle, reduce costs, and ensure that prototypes accurately reflect the intended design.
CNC machining for rapid prototyping is particularly valued for its ability to work with both metals and engineering plastics, providing precise tolerances and consistent repeatability.
It is especially suited for functional parts where strength, surface finish, and material properties matter.
Suppliers with deep experience in CNC machining can offer practical advice on design adjustments, material selection, and finishing processes, helping teams avoid costly iterations.
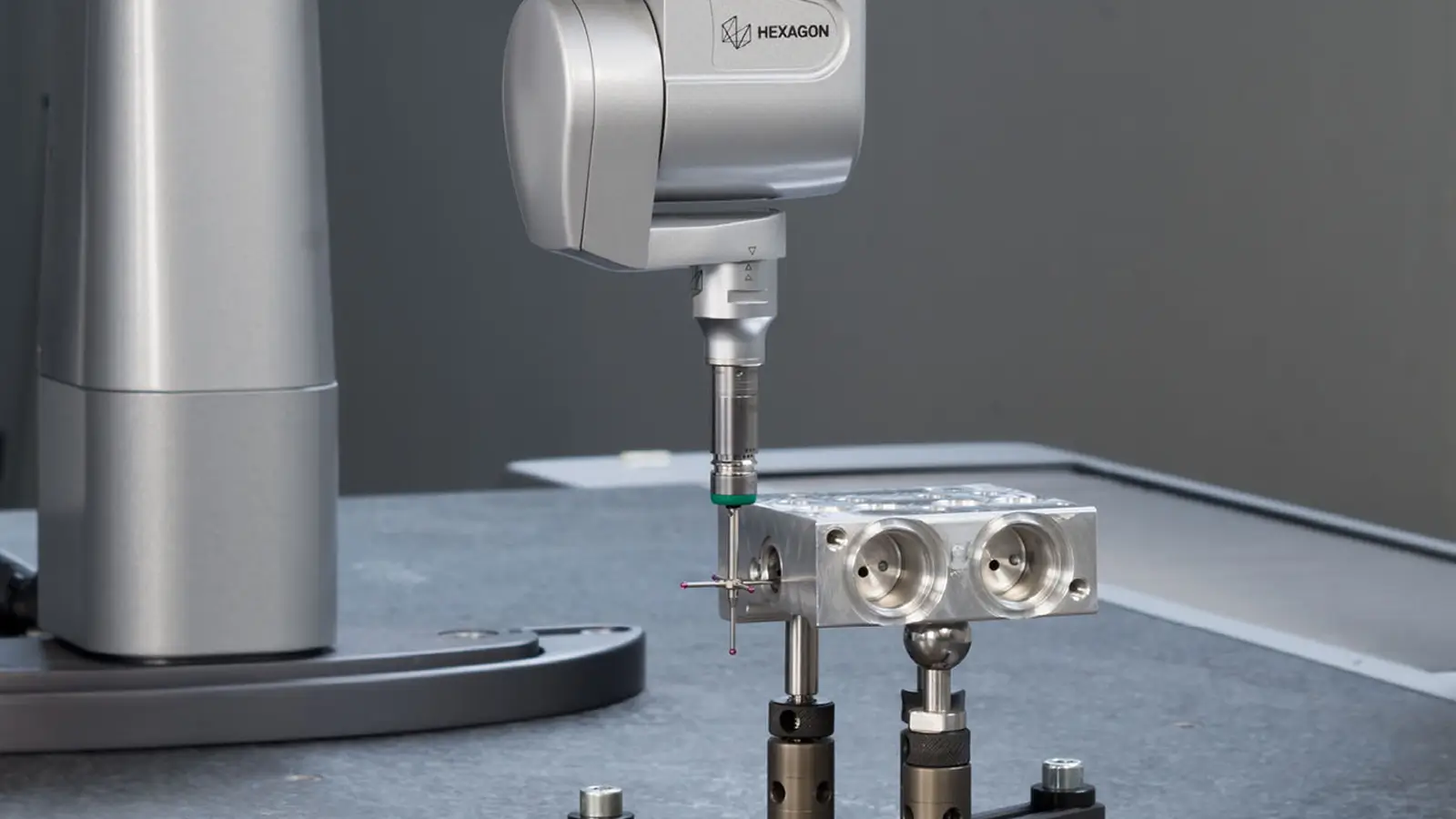

Key Questions to Consider When Choosing CNC Machining
Selecting a CNC prototyping service requires careful consideration of several technical and operational factors.
Understanding these factors helps ensure that the prototype not only looks like the final product but also performs as expected in real-world conditions.
Machining Accuracy and Material Compatibility
CNC machining is capable of producing high-precision parts in metals such as aluminum, steel, and copper, as well as engineering plastics including ABS, PC, and Nylon. Typical tolerances range from ±0.01 to ±0.05 mm, depending on the complexity of the part and the capabilities of the machinery.
For intricate geometries, 5-axis CNC machines are often required, while simpler shapes can be effectively produced on 3-axis equipment.
Material selection has a direct impact on the machining process.
Harder metals require higher cutting forces, while certain plastics may be prone to warping under heat or cutting stress. Experienced suppliers can recommend suitable materials and machining strategies to ensure dimensional accuracy and repeatability.
For prototypes requiring multiple iterations or batch production, maintaining consistent tolerances across all units is essential to avoid time-consuming rework.

Cost Considerations and Lead Time
While CNC machining provides high accuracy and functional fidelity, it is important to balance cost with project timelines.
Small-batch functional prototypes are often more expensive than models produced via 3D printing but allow testing with the actual material, which is crucial for parts under mechanical stress or thermal load.
3D printing can be a cost-effective alternative when the prototype is primarily for visual inspection or concept validation.
Lead times for CNC-machined prototypes typically range from three to ten days, depending on the material, complexity, and workload of the supplier.
Requesting a detailed cost breakdown that includes setup, machining, and finishing can prevent unexpected charges and help align the project with the overall development schedule.
Surface Finishing and Post-Processing
Many prototypes require post-processing to achieve the desired functionality or appearance.
This can include polishing, anodizing, plating, or coating. The choice of post-processing affects both the part’s durability and aesthetic qualities.
Suppliers that offer integrated finishing services reduce the need for multiple vendors and shorten delivery timelines.
It is also important to discuss surface finish tolerances upfront. Certain functional components, such as sliding mechanisms or sealing interfaces, require precise surface qualities to perform correctly.
Experienced CNC prototyping providers often advise on design adjustments that simplify post-processing while maintaining functional requirements.
Supplier Expertise and Technical Support
A CNC prototype’s quality depends not only on the machinery but also on the operator’s experience and the supplier’s process knowledge.
Effective suppliers provide guidance on design-for-manufacturability, suggesting modifications that reduce machining complexity or potential errors.
They also assist with toolpath optimization, tolerance assessment, and material handling strategies.
Engaging a supplier with broad experience across materials and prototyping scenarios ensures that potential issues are identified early, reducing iteration cycles and improving the reliability of the final prototype.
Technical support extends beyond machining itself, encompassing post-processing, inspection, and recommendations for testing or validation.
Prototype Verification and Testing
Reliable rapid prototyping services offer structured verification processes.
Dimensional inspections and measurement reports provide confidence that parts meet design specifications. In cases where functionality is critical, some suppliers support stress testing, thermal testing, or assembly verification.
Quick iteration based on initial feedback allows product teams to refine the design before committing to full-scale production.
Such structured verification not only ensures prototype quality but also accelerates development.
Suppliers who can combine accurate machining with practical guidance on testing and iteration reduce project risk significantly.
Comparing CNC Machining with Other Rapid Prototyping Methods
Understanding how CNC machining compares with other methods helps teams select the most appropriate approach:
| Feature | CNC Machining | 3D Printing | Rapid Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Accuracy | High | Medium | High |
| Surface Finish | High | Low | High |
| Part Strength | High | Low | High |
| Lead Time | Medium | Fast | Medium–Slow |
| Ideal Use Case | Functional and structural prototypes | Concept models, visual inspection | Small-batch pre-production |
CNC machining excels when functional testing and material fidelity are required.
3D printing is ideal for quick visual models or initial concept validation. Rapid injection molding works well for small-batch pre-production that also tests manufacturing processes.
Choosing the right method depends on prototype goals, required properties, and project timelines.
Common Mistakes and Risks
Even experienced teams encounter pitfalls when procuring rapid prototyping services. Common mistakes include:
- Selecting suppliers based solely on price, which may compromise material quality or machining accuracy.
- Neglecting post-processing needs, resulting in delays or higher costs due to outsourcing finishing work.
- Failing to optimize designs for manufacturability, leading to increased machining time or errors.
- Engaging suppliers without relevant experience, risking missed deadlines or unusable prototypes.
Avoiding these mistakes ensures faster validation, fewer iterations, and adherence to project timelines.
Practical Guidelines for Selecting a CNC Prototyping Service
Effective selection involves evaluating several key factors:
- Confirm the supplier has experience with both the materials and the complexity required.
- Request customized prototyping plans that detail material choice, tolerances, machining strategy, and finishing options.
- Ensure technical support is available for design-for-manufacturability guidance, risk mitigation, and post-processing advice.
- Verify that the supplier can maintain consistent tolerances across batches.
- Review lead times and cost breakdowns upfront to align with your project schedule and budget.
Integrated services that combine precision machining, optional finishing, and technical guidance enable teams to reduce risk, improve prototype reliability, and accelerate time-to-market.
Practical Examples and Tips
A manufacturer needed a high-strength aluminum bracket for structural testing.
By using multi-axis CNC machining, tolerances of ±0.02 mm were achieved, and anodizing was applied for corrosion resistance.
The prototype was delivered within a week, enabling timely functional testing.
In another case, a client required a complex ABS plastic enclosure.
The supplier provided 3-axis CNC machining with light sanding to achieve the required surface finish.
Design adjustments suggested by the supplier simplified machining and reduced production time by approximately 15%.
For best results, provide clear 3D CAD files and specifications, including tolerances, materials, and desired surface finishes.
Early discussion of post-processing and inspection requirements can prevent revisions and avoid delays.
Next Steps for Reliable Prototyping
To move from concept to functional prototype efficiently, consider these actions:
- Submit design files to receive a tailored CNC prototyping plan detailing materials, machining strategy, and delivery timelines.
- Review case studies and technical documentation from experienced suppliers to understand practical results and performance metrics.
- Request a quote and expert consultation to ensure that prototypes meet functional, aesthetic, and budgetary requirements.

Following these steps enables teams to select the right prototyping approach, reduce iteration costs, and accelerate product development, leveraging suppliers with proven experience and integrated services.
Rapid Prototyping Knowledge Hub
1.Understanding CNC Rapid Prototyping
- What is CNC Rapid Prototyping? Complete Guide for 2025
- What are the Benefits of CNC for Rapid Prototyping?
- CNC Machining for Rapid Prototyping: How to Choose the Right Solution
- 3 Types of Prototyping Services for Fast and Cost-Effective Prototypes
2.CNC vs Other Prototyping Methods
- CNC Rapid Prototyping vs 3D Printing: Which to Choose in 2025?
- 3D Printing vs CNC Machining: Which Is Right for You?
- CNC Milling vs CNC Turning: Which Is Better for Prototyping?
3.Engineering & DFM Considerations
- CNC Prototype Tolerances Explained
- How to Optimize CAD Files for CNC Prototyping
- How Material Selection Affects CNC Prototype Performance
- ABS vs Aluminum: Which is Better for CNC Prototypes?
- Why Production Time Matters in Prototype CNC Parts Manufacturing?
4.From Prototype to Production
- CNC Machining for Small Batch Prototyping
- From Prototype to Production: How CNC Companies Support Scalability
5.CNC Prototyping Services in China
- CNC Prototyping Services China (Complete Buying Guide)
- Key Factors to Consider When Sourcing CNC Prototypes from China
- Top 5 Prototype Manufacturers in China
- 5 Key Benefits of Using Chinese Prototyping Services