- Capabilities
-

CNC Machining
Tight tolerance and 20+ finishes 3, 4 , 5 axis, as fast as 2 days -
Sheet Metal Fabrication
High-precision, on-demand sheet metal cutting and bending. -

3D Printing
SLA, SLS,MJF,SLM, FDM 3d printing with post treatment. -

Vacuum Casting
Production quality parts without the tooling investment.
-
- Solutions
Rapid Prototyping
Fastest lead time of high-quality prototypes at minimal cost.
Low Volume Production
From one-off prototyping to low-volume production.

Mechanical Assembly
Custom assembly for project-specific needs.

Custom Package
Ready to help you prompt your brand.
- Sources

Materials
Select from 100 more types of metals and plastics.

Finishes
Select from 20 more types of surface fishes.
Industries
Providing precision machining and manufacturing solutions.

Cases
How we assist our clients in bringing their projects to fruition.
- Company

Quality Assurance
Consistent quality, every time.

About Us
Your go-to manufacturer for custom parts.

Newsroom
Learn updated news about ECOREPRAP.
How Does CNC Machining Work? An Operation Guide
Updated: June 08, 2024

Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining is a manufacturing process in which pre-programmed computer software controls the movement of factory tools and machinery. This advanced technology allows for precise control of a range of complex machinery, including grinders, lathes, milling machines, and CNC routers.
In this guide, we’ll explore the intricacies of CNC machining, including its types, terminology, and stages of operation, to gain a comprehensive understanding of how this process works.
What is CNC Machining?
CNC machining is a manufacturing process where computer software controls factory tools and machinery. It can manage various complex machines like grinders, lathes, milling machines, and routers. With CNC machining, you can perform three-dimensional cutting tasks using a single set of commands.
The process transforms raw materials into finished products through automated control. It starts with creating a CAD (computer-aided design) model, a digital blueprint of the part. This CAD model converts into a CNC program via CAM (computer-aided manufacturing) software. The program generates precise instructions, called G-codes, which the CNC machine follows.
These G-codes detail every movement, speed, and feed rate of the tool, ensuring precise execution of cuts, drills, and mills. The CNC machine interprets these instructions and moves the tool along multiple axes (usually 3, but sometimes 4 axes or more) to shape the material.
CNC machining works with various materials, including metals like aluminum, steel, and titanium, as well as plastics, composites, and wood. This versatility makes it essential in industries such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, and medical devices.
Types Of CNC Machining
CNC machining encompasses a variety of methods, each of which is suited to specific tasks and materials. There are two main types: CNC milling and CNC turning. Let’s explore these methods in detail.
CNC Milling
CNC milling is a cutting process that uses a rotating tool to remove material from a workpiece. It is ideal for producing parts with complex shapes and intricate details. In CNC milling, the workpiece remains stationary while the cutting tool moves in multiple axes (X, Y, and Z) to precisely shape the material.
It is highly accurate, can machine a wide range of materials, and can increase productivity and reduce time and labor costs. Ideal for automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and prototyping delicate parts.
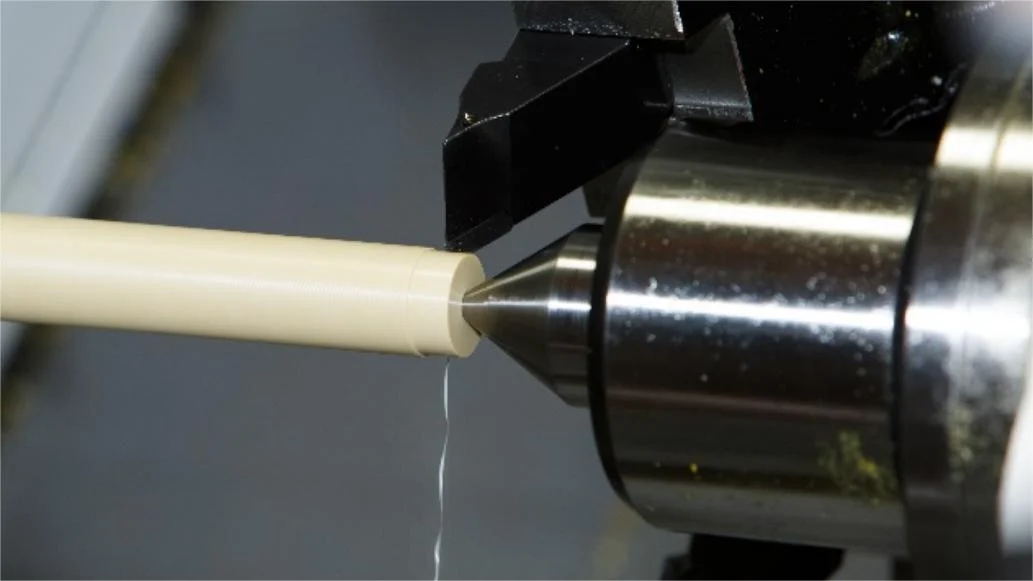
CNC Turning
CNC turning uses a cutting tool to remove material from a rotating workpiece, making it ideal for manufacturing cylindrical and symmetrical parts. There are many types of lathe tools for CNC turning and different tools produce different types.
It’s commonly used to produce shafts, rods, fasteners, bushings, bearings, and medical implants. Benefits include high accuracy, efficient material removal, and cost savings through less waste and reduced labor costs.
CNC Machining Terminology
Computer-Aided Design (CAD): CAD software allows engineers and designers to precisely define the geometry, dimensions, and specifications of a desired part.
Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM): CAM generates tool paths and machining strategies based on design specifications, ensuring efficient and accurate production.
Distributed Numerical Control (DNC): DNC allows centralized program storage, editing and retrieval, ensuring consistency and synchronization between different machine tools in a production facility.
Manufacturing Data Collection (MDC): MDC Capture collects and analyses real-time data from CNC machines during the manufacturing process. This data includes information such as cycle times, machine utilization, tool life, and production quantities.
G Code: Short for geometric code, G code is an alphanumeric language that tells a CNC machine tool how to move and operate. Each line of G code contains instructions for a specific movement, such as positioning a tool or controlling a spindle, and the X, Y, and Z parameters represent the different axes of movement, determining the exact position or distance of the movement.
M Code: M code commands are used to control auxiliary functions and operations of CNC machine tools, such as tool change, coolant activation, spindle control, and machine positioning.
How Does CNC Machining Work?
CNC machining is a precise and efficient manufacturing process that involves several detailed steps. If you are a CNC machine operator, I think you need to know about the steps of CNC machining. Here are the detailed steps of CNC machining:
Stage 1: Create A CAD Model
The first step in CNC machining is to create a CAD (Computer-Aided Design) model. This digital blueprint defines the geometry, dimensions, and specifications of the part to be manufactured.
- Choose CAD Software: Select appropriate CAD software like AutoCAD, SolidWorks, or Fusion 360.
- Design the Part: Use the software to draw the part, specifying all the necessary dimensions, shapes, and features.
- Optimize the Design: Ensure the design is optimized for manufacturability, considering factors like material properties and machining capabilities.
- Save the File: Save the completed design in a format compatible with CAM software, typically in formats like.STEP or.IGES.
Stage 2: Convert CAD Model To CNC File
The next step is to convert the CAD model into a CNC program that the machine can understand. This involves using CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software.
- Import CAD File into CAM Software: Load the saved CAD model into CAM software.
- Define Machining Parameters: Specify the cutting tools, material properties, and machining strategies. This includes tool paths, feed rates, and cutting speeds.
- Generate Toolpaths: The CAM software calculates the optimal toolpaths based on the machining parameters.
- Simulate the Process: Run a simulation to ensure that the toolpaths are correct and the machining process will not cause collisions or errors.
- Generate G-code: Convert the toolpaths into G-code, the language used by CNC machines to control their movements.
- Save the CNC File: Save the generated G-code file for use in the CNC machine.

Phase 3: Configuration Of CNC Machines
Before starting the machining process, the CNC machine must be properly configured to ensure accurate and efficient operation.
- Setup the Machine: Install the necessary cutting tools and ensure they are properly aligned and secured.
- Load the Material: Place the raw material (workpiece) onto the machine’s worktable and secure it using clamps or a vice.
- Upload the CNC Program: Transfer the G-code file to the CNC machine’s computer, either through a network connection or a USB drive.
- Set Zero Points: Define the starting point (zero point) for the machine’s coordinate system on the workpiece.
- Check Machine Settings: Verify that all machine settings, such as spindle speed and coolant flow, are correctly set according to the CNC program.
Stage 4: Execution Of Processing Operations
With the machine configured, the actual machining process can begin, transforming the raw material into the finished part.
- Start the Machine: Begin the CNC program to start the machining process.
- Monitor the Operation: Keep an eye on the machine to ensure it’s operating correctly. Watch for any issues like tool wear or material movement.
- Perform Quality Checks: Periodically pause the machine to inspect the part for accuracy and quality, ensuring it meets the specified tolerances.
- Complete the Machining: Allow the CNC machine to finish all programmed operations, which may include cutting, drilling, milling, or turning.
- Remove the Part: Once machining is complete, safely remove the finished part from the machine.
- Final Inspection: Conduct a thorough inspection of the finished part to ensure it meets all design specifications and quality standards.
Conclusion
If you need CNC machining, you can choose to trust us. ECOREPREP offers a wide range of CNC machining services, and we will let our team of expert application engineers help you choose the right one for your project. To use and consult your project, please contact us.
Let's get your projects started, together!
Get custom parts machined in high quality, delivery on time.