What is the meaning of 1G 2G 3G 4G 5G 6G in sheet metal welding?
Updated: Mar. 24, 2024
Welding is very common in sheet metal fabrication. In the drawings, there are always welding indicators like 1G 2G 3G 4G 5G 6G. What is the meaning of 1G 2G 3G 4G 5G 6G?
1G 2G 3G 4G 5G 6G are the welding positions in AWS and ASME standards, which is mostly used in USA and Canada. In our blog Welding Positions Standards to DIN EN ISO 6947/AWS/ASME, you can get the difference between the 3 standards.
1. What is a 1G weld?
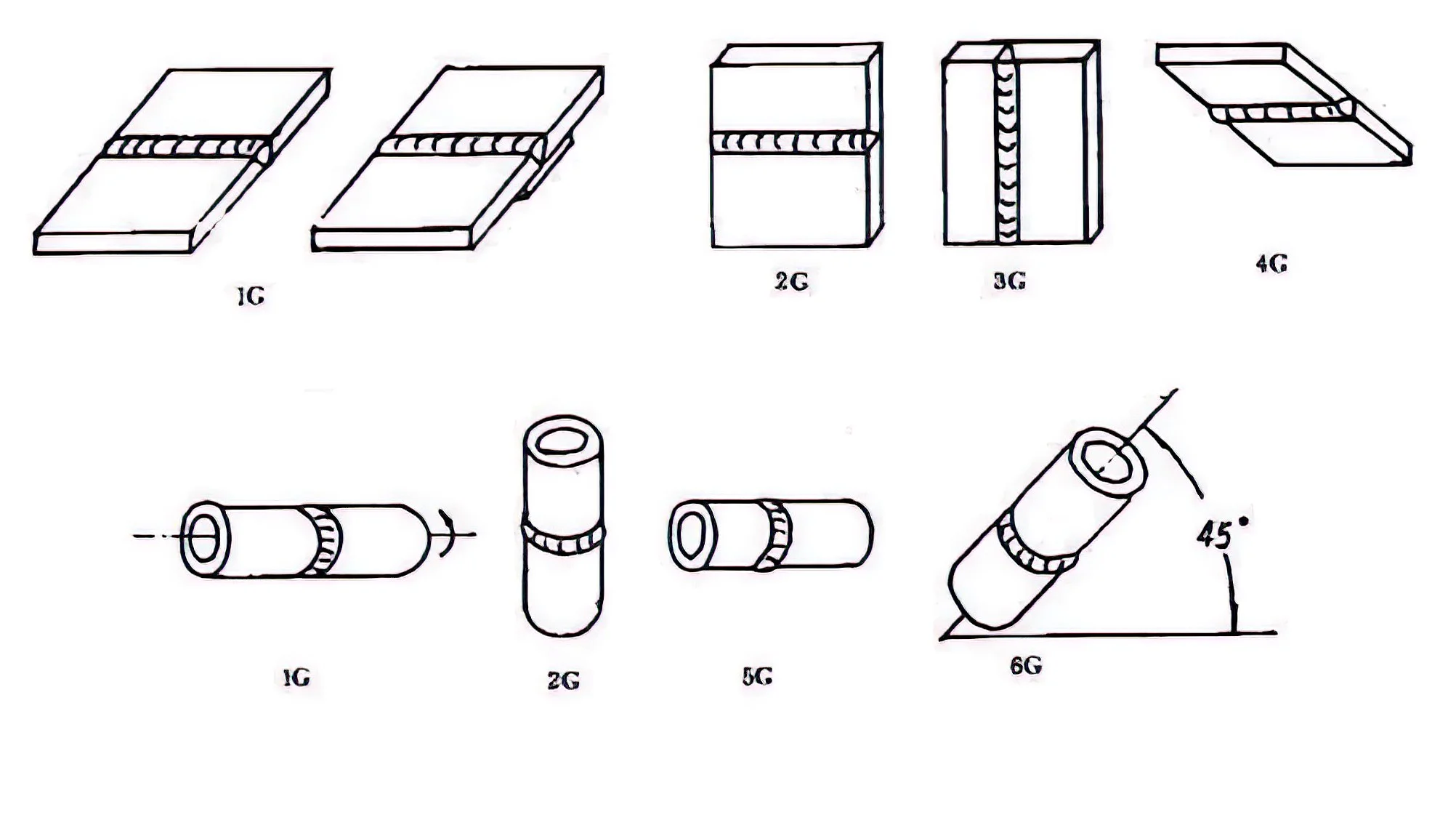
1G welding is flat welding. A 1G flat weld is a welding position in which the workpiece is in a horizontal position during the welding process and the welder is welding from the top down. In 1G flat welding, the welded joint is on a horizontal plane and the welder usually stands on top of the workpiece and welds the joint from above with a torch or wire rod. This welding position is usually used for larger or heavier workpieces and makes the welding operation easier and more stable.
What is 1G flat welding characteristics?
1 . The molten weld metal mainly relies on self-weight to the molten pool excess.
2. The shape of the molten pool and the molten metal are easy to maintain and control.
3. Welding the same plate thickness of metal, flat welding position of the welding current than other welding position of the current, high productivity.
4. The slag and the molten pool are easy to be mixed, especially when welding flat fillet welds, the slag is easy to overrun and form slag inclusions.
*Acid electrode slag and molten pool is not easy to distinguish; alkaline electrodes are clearer;
Welding parameters and improper operation, easy to form weld tumor, biting edge, welding deformation and other defects.
5. Single-sided welding back free molding, the first weld is prone to produce uneven weld penetration procedures, the back of the poor molding and other images.
What are 1G flat welding key points?
- According to the thickness of the plate can choose a larger diameter welding rod and larger welding current welding.
- Welding rod and weldments into 60 ~ 80 ° angle, control the slag and liquid metal separation, to prevent the slag from appearing ahead of the phenomenon.
- When the plate thickness ≤ 6mm, butt-flat welding generally open Ⅰ bevel, front weld should be φ2 ~ 4 of the electrode short-arc welding, depth of fusion up to 2 / 3 of the thickness of the plate; the back of the back cover before the bottom, you can not clear the root (except for the important structure), but the slag should be cleaned up, the current can be larger.
- butt flat welding if there is slag and pool metal mixing phenomenon, you can lengthen the arc, welding rod forward, and do to the back of the pool to push the slag action to prevent slag generation.
- When welding horizontal inclined weld, it is appropriate to use uphill welding to prevent slag and molten pool to the front to avoid slag.
- When using multi-layer multi-channel welding, attention should be paid to the number of weld channels and welding order, each layer should not exceed 4~5mm.
- T-type, angle, lap joints, flat angle welding joints, if the thickness of the two boards are different, you should adjust the angle of the electrode will be biased towards the thicker side of the arc, so that the two boards are heated evenly.
- The correct choice of transport method
(1) welding thickness ≤ 6mm, Ⅰ type bevel butt welding, double-sided welding, the front weld using straight-line transport, slightly slow; back weld also use straight-line transport, welding current is slightly larger, faster.
(2) plate thickness ≤ 6mm, open other forms of beveling, can be used for multi-layer welding or multi-layer multi-channel welding, the first layer of bottoming welding should be used for small current electrodes, small specification current, linear electrode or sawtooth shaped electrode welding. Filler layer welding, can choose a larger diameter electrode and larger welding current short arc welding.
(3) T-type joints, flat angle welding foot size <6mm, you can choose a single layer of welding, with a straight line, diagonal ring or serrated rod method; foot size is larger, it is appropriate to use multi-layer welding or multi-layer multi-channel welding, bottoming weld with a straight line rod method, the filler layer can be used to select the diagonal sawtooth, diagonal ring rod.
(4)Multi-layer multi-pass welding is generally preferred to use linear welding rod method.

2. What is a 2G weld?
A 2G weld is horizontal welding. 2G weld is a welding position in which the workpiece is held vertically during the welding process and the welder performs the weld from the side. In 2G cross welding, the welded joint is on a horizontal plane, but the workpiece is placed in a vertical orientation. The welder usually stands on one side of the workpiece and welds in the horizontal direction. This welding position is often used for larger or heavier workpieces, making the welding operation easier and more efficient.
What are 2G horizontal welding characteristics?
- The molten metal is easy to fall on the bevel due to self-weight, resulting in the upper side of the biting defects, the lower side of the formation of tear-drop type weld bead or weld defects.
- The molten metal and slag are easy to separate, slightly like standing welding.
What are 2G horizontal welding key points?
- Docking cross weld beveling is generally V-type or K-type, plate thickness of 3 ~ 4mm butt joints available Ⅰ bevel double-sided welding.
- Choose a small diameter welding rod, welding current is smaller than the flat welding, short arc operation, better control of molten metal flow.
- thick plate welding, in addition to the bottom weld, it is appropriate to use multi-layer multi-channel welding.
- multi-layer multi-channel welding, pay special attention to the control of the overlap distance between the welding channel. Each overlap welding, should be in the previous weld 1 / 3 of the beginning of welding, in order to prevent the production of unevenness.
- According to the specific conditions, maintain the appropriate welding rod angle, welding speed should be slightly block and uniform.
- Use the correct method of transporting the electrode.
(1) Ⅰ type butt cross welding, the front weld using reciprocating straight line welding method is better; slightly thicker parts should be used linear or small oblique ring shaped welding rod, the back of the straight line welding rod, the welding current can be increased appropriately.
(2)the use of other bevel butt cross weld, the gap is small, bottom welding can be used straight transport; gap is large, the bottom layer using reciprocating straight transport, the other layers when the multi-layer welding, can be used oblique ring transport, multi-layer multi-channel welding, should be used in a straight transport.


3. What is a 3G weld?
A 3G weld is vertical welding. 3G vertical welding is a welding position in which the workpiece is placed vertically and the welder welds from the side. In 3G Vertical Welding, the welded joints are located in the vertical direction and the welder usually stands on one side of the workpiece to perform the welding. This welding position is usually used for welding joints in the vertical direction and can effectively accomplish such welding configurations.
What are 3G vertical welding characteristics?
- The molten pool metal and slag are easy to separate due to the fall of self-weight.
- When the molten pool temperature is too high, the molten pool metal is easy to flow down to form weld tumor, biting edge, slag and other defects, and the weld is not flat.
- The root of the T-joint weld is easy to form a non-welded-through.
- The degree of penetration is easy tocontrol.
- Compared with fat welding, vertical welding productivity is lower.
What are 3G vertical welding key points?
- Maintain the correct welding rod angle;
- Commonly used in the production of upward vertical welding, downward vertical welding to use a special electrode to ensure the quality of the weld. Upward vertical welding welding current is smaller than the flat welding 10 ~ 15%, and should use a smaller electrode diameter (<φ4mm)
- Use short arc welding to shorten the distance from the molten drop to the molten pool.
- Use the correct method of transporting the rod.
(1) T-bevel butt (commonly used in thin plate) upward vertical welding, commonly used linear, sawtooth, crescent-shaped transport method of welding, the maximum arc length is not less than 6mm.
(2) open other forms of bevel butt vertical welding, the first layer of weld is often used to break the welding, the swing is not large crescent-shaped, triangular transport welding. Subsequent layers can be crescent-shaped or sawtooth-shaped transport method.
(3) T-joint vertical welding, the welding rod should be in the weld on both sides and the top corner of the appropriate residence time, the welding rod swing should not be greater than the width of the weld, the operation of transporting strips and other forms of beveling similar to the vertical welding.
(4)When welding the cover layer, the shape of the weld surface is determined by the method of transporting the electrode. Weld surface requirements are slightly higher can choose crescent-shaped transport bar; surface flat can be used serrated transport bar (the middle concave shape and pause time).

4. What is a 4G weld?
A 4G back weld is overhead welding. 4G overhead welding is a welding position in which the workpiece is placed upside down during the welding process and the welder welds from the bottom. In 4G back welding, the welded joint is located on the bottom, and the welder is usually positioned on the top or side of the workpiece, welding the joint from the bottom. This welding position is often used when welding from below, making the welding operation easier and more efficient.
What are 4G overhead welding characteristics?
- The molten metal falls down due to gravity, and the shape and size of the molten pool should not be controlled.
- It is difficult to transport the rod, and the surface of the weldment should not be welded flat.
- Easy to slag, not welded through, weld tumor and weld molding defects.
- Molten weld metal spatter spreads, easy to cause scalding accidents.
- The efficiency of back welding is lower than other position welding.
What are 4G overhead welding key points?
- Butt weld back weld, when the thickness of the weldment ≤ 4mm, use Ⅰ type bevel, choose φ3.2mm electrode, welding current should be moderate; Welding thickness ≥ 5mm, should be used multi-layer multi-channel welding.
- T-joint weld back welding, when the welding foot is less than 8mm, should be used for single layer welding, welding foot is greater than 8mm when using multi-layer multi-pass welding.
- According to the specific circumstances, using the correct method of transportation:
(1) welding foot size is small, the use of linear or linear reciprocating type transport bar, single layer welding is completed; welding foot size is large, can be used for multi-layer welding or multi-layer multi-channel welding transport bar, the first layer should be used for linear transport bar, the rest of the layers can be used to select the oblique triangular type or oblique ring type transport bar method.
(2)No matter what kind of transport method, each time to the molten pool excessive weld metal should not be too much.

5. What is a 5G weld?
A 5G welding is for pipe welding. This type of welding requires the pipe to be fixed horizontally at the mouth. Its welding is more complex. Pipe welding must be done around the circumference of the pipe, it goes through flat, vertical and horizontal overhead positions. The difference between uphill and downhill is the starting position; uphill starts at the bottom and ends up in the overhead position, while downhill is the opposite.



6. What is a 6G weld?
6G welding is another type of pipe welding where the pipe is placed at an angle of 45 degrees to be welded. This type of welding is more difficult than 5G welding, and 6G welding is considered a test of the welder’s skills. This type of welding position is often used when welding needs to be done in a variety of angles and directions, and requires a high level of technical skill and all-around welding skills from the welder.


1G 2G 3G 4G 5G 6G welding are mostly used in AWS documentation. ISO standards use different names for the same processes, sometimes with additional granularity.