- Capabilities
-

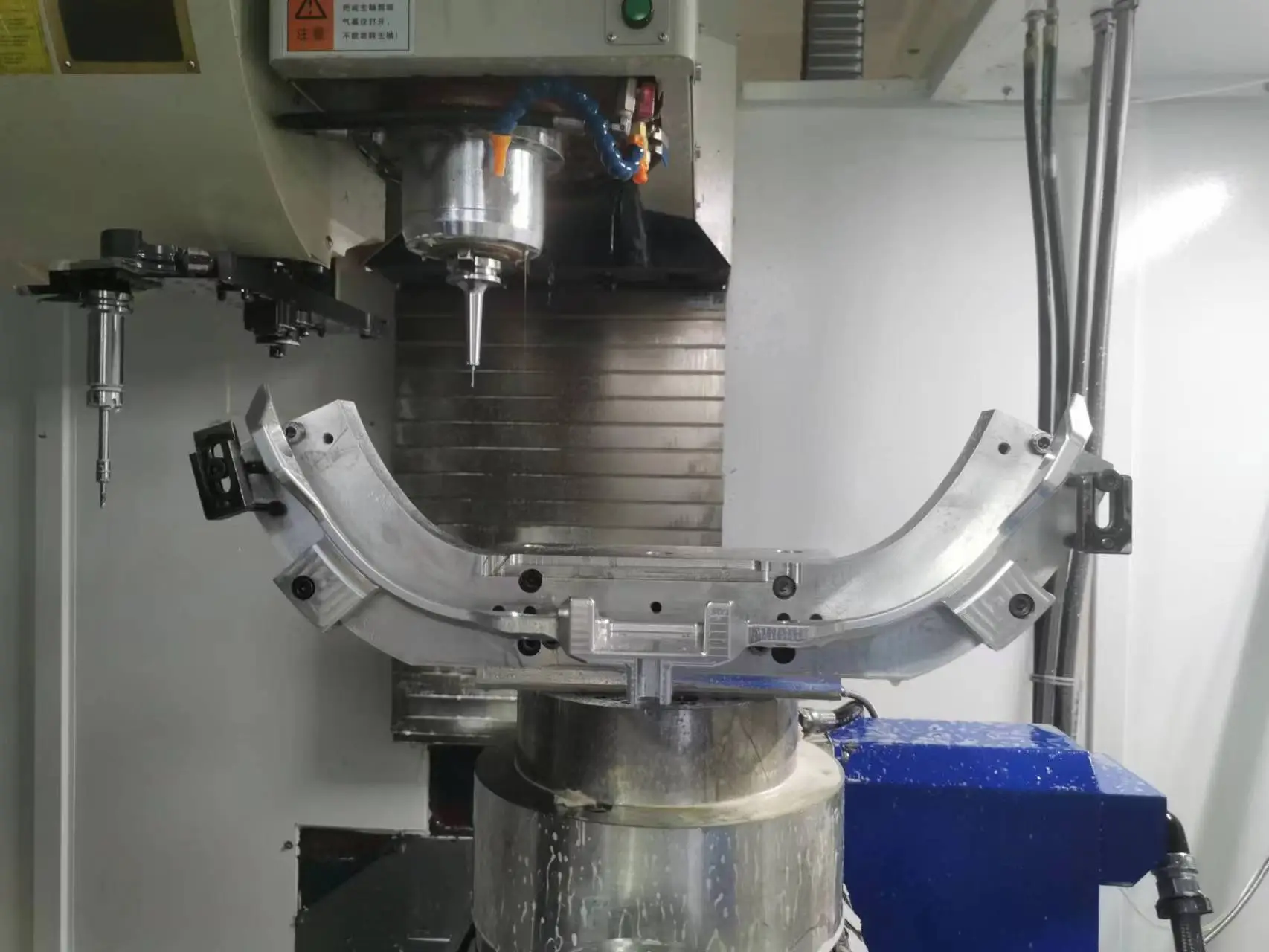
CNC Machining
Tight tolerance and 20+ finishes 3, 4 , 5 axis, as fast as 2 days -
Sheet Metal Fabrication
High-precision, on-demand sheet metal cutting and bending. -

3D Printing
SLA, SLS,MJF,SLM, FDM 3d printing with post treatment. -

Vacuum Casting
Production quality parts without the tooling investment.
-
- Solutions
Rapid Prototyping
Fastest lead time of high-quality prototypes at minimal cost.
Low Volume Production
From one-off prototyping to low-volume production.

Mechanical Assembly
Custom assembly for project-specific needs.

Custom Package
Ready to help you prompt your brand.
- Sources

Materials
Select from 100 more types of metals and plastics.

Finishes
Select from 20 more types of surface fishes.
Industries
Providing precision machining and manufacturing solutions.

Cases
How we assist our clients in bringing their projects to fruition.
- Company

Quality Assurance
Consistent quality, every time.

About Us
Your go-to manufacturer for custom parts.

Newsroom
Learn updated news about ECOREPRAP.
How Does Heat Affect CNC Machining Part?
Updated: December 02, 2023
Introduction
We all know that plastic & metal material is sensitive to heat, and their dimension will enlarge in high-temperature circumstances. The CNC machining process involves the material cutting. Hence heat is inevitably generated. If you want to get quality CNC machining parts, the vital step is to eliminate excess heat in this process.
This article will explain the potential causes that can generate heat in CNC machining shops. Meanwhile, you will learn some tips that can be employed to reduce the heat in the machining environment.

1. Factors that affect CNC machining part temperature
1. Natural Climate
According to the laws of thermodynamics, objects adapt to ambient temperature. That is to say, the hotter a room is, the hotter the objects in that room will be. Because of this, machines used in extreme heat environments run at temperatures above recommended or “normal” temperatures.
If your operation is in a naturally hot environment, you need to take extra measures to ensure that your CNC machine runs at the recommended temperature.
2. Ongoing Environment
Best practice suggests positioning your CNC machine frame as far as possible from other heat sources such as a heat-treating oven. For example, when planning the layout of a new factory, place the machine shop as far from the boiler or steam room as possible.
As your machine runs, it already has two sources of heat: natural climate heat and machining process heat. Process heat is the heat generated by the machine itself while in operation. These two sources are unavoidable although they can be mitigated and controlled. Positioning your CNC machine far from other heat sources eliminates a third heat source from adding to the heat gain of the CNC machining environment.
3. The Machining Tool
The temperature of the machining tool plays an integral part in the machining process. If the tool overheats, it leads to problems such as thermal deformation and thermal expansion which lead to diminished machining accuracy. Overheating of the tool also leads to a shorter tool life thereby increasing the cost of running the machining operation. In other words, tool hardness decreases with increasing temperature.
Common materials for machine tools include Tungsten Carbide and High-Speed Steel. Tungsten carbide maintains a sharp cutting edge longer than High-Speed -Steel, it produces a better finish, and can cut harder materials. Tungsten also withstands higher temperatures and therefore can achieve faster cutting speeds than steel. Faster cutting speeds reduce production time.
4. Material Properties
The type of material or material properties of the workpiece has an effect on the temperature generated in the machining environment. The harder a material is, the more energy is required to machine it or remove material from it.
The more energy required, the higher the temperature generated at that point if other parameters such as feed rate are kept constant. Following this observation, it is important to consider material properties when selecting materials.
The heat generated at the tool-workpiece is able to produce in the workpiece effects similar to heat treating. Stainless steel is a material that is prone to work hardening during the machining process.
There are different types of heat-treating processes such as annealing and hardening that can be done to a material to give it specific characteristics. Heat treatment processes are done to change metal alloy/ alloy steel physical properties such as hardness, toughness, tensile strength, and ductility.
However, hard materials are more difficult to machine thus some heat treatment processes are best done after machining.
An advantage of machining before heat treatment is that sourcing material is easier. Heat-treated profiles are more common than non-heat-treated profiles. Pre-treated materials also hold tighter tolerances better than non-treated materials.
An advantage of heat treating after machining is that you can choose which method of treatment you want to use in order to obtain your desired characteristics.

2. Tips to keep your CNC machine and tool cooling
1. Facility Cooling
Facility cooling, also known as assisted cooling, helps to control the ambient temperature. Assisted cooling helps to keep the temperature at an optimal level that is conducive to machinery operation. The cooler the ambient temperature, the cooler the machines run.
There is a wide variety of options available to keep the facility cool such as central air conditioning, pumped refrigeration, and custom-designed ventilation. Factors to consider when choosing a cooling system include allowable humidity, size of premises, and installation cost. Assisted cooling helps to keep all electronic CNC machine sub-components in good working condition.
2. Conduct Maintenance Regularly
Machines are not designed to run indefinitely without care and maintenance. Moving parts are subject to wear and tear. The machine manufacturer specifies when and how to replace specific components. This schedule must be adhered to ensure optimum performance.
Worn-out parts cause undue stress on the system causing the machine to overheat and malfunction. Conducting maintenance regularly also helps to notice loose parts that may be rubbing on neighboring components leading to undesired overheating.
3. Use a Cooling Medium During Machining
The heat generated due to friction during machining is transferred to the machining tool through thermal conductivity. Machining with a hot tool result in undesired characteristics on the machined part.
Using a coolant helps to lower the tool temperature thus keeping the tool working in its optimum range. The cooling medium, also known as cutting fluid improves tool life by lowering the friction and temperature at the tool-material interface. A longer tool life translates to lower machining costs.
4. Clear Craps from the Machine
It is important to clear the process shavings from the machine so that they do not interfere with the current processes. Swarf can get caught in the current cutting process and this results in the tool needing to exert more energy to machine the workpiece. This generates excess heat.

3. Summary
It is critical to know the properties of the workpiece material before beginning the machining process. Knowing the material properties helps you to choose the most suitable tool. It also helps to select other machining process parameters such as feed rate, cutting speed, and depth of cut.
A rise in ambient temperature must always result in checking that the CNC process is still operating under ideal conditions.Maintaining a cool temperature is key to obtaining the best results from CNC machining. Failing to correct the temperature can result in increased costs due to frequent breakdowns and shorter tool life.
Excessive heat also leads to part deformation and reduces the quality of products obtained from your CNC machining processes.
To get your prototypes machined in high quality, just contact ECOREPRAP.