Sheet Metal Fabrication Design Tips: Crafting Excellence
Discover essential tips for designing sheet metal fabrication projects. Dive into the world of precision manufacturing with our expert insights on sheet metal fabrication design.

Introduction
In the world of manufacturing, sheet metal fabrication is a versatile and essential process. Whether you’re a seasoned engineer or a newcomer to the field, mastering the art of sheet metal design is crucial. This article will take you on a journey through valuable tips and strategies for sheet metal fabrication design, ensuring your projects are a cut above the rest.
Understanding the Basics of Sheet Metal
Before we dive into the intricacies of sheet metal design, it’s essential to understand the basics. Sheet metal is a metal formed into thin and flat pieces. These pieces can be easily cut, bent, and manipulated, making them ideal for various applications. Let’s explore 12 design tips below together.
1. Material Selection
The choice of material is the foundation of any successful sheet metal project. Consider factors like strength, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness when selecting materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, or carbon steel.

2. Design for Manufacturability
Designing for manufacturability is key. Create designs that are easy to produce, reducing lead times and costs. Consider the capabilities of the fabrication shop you’re working with and optimize your design accordingly.
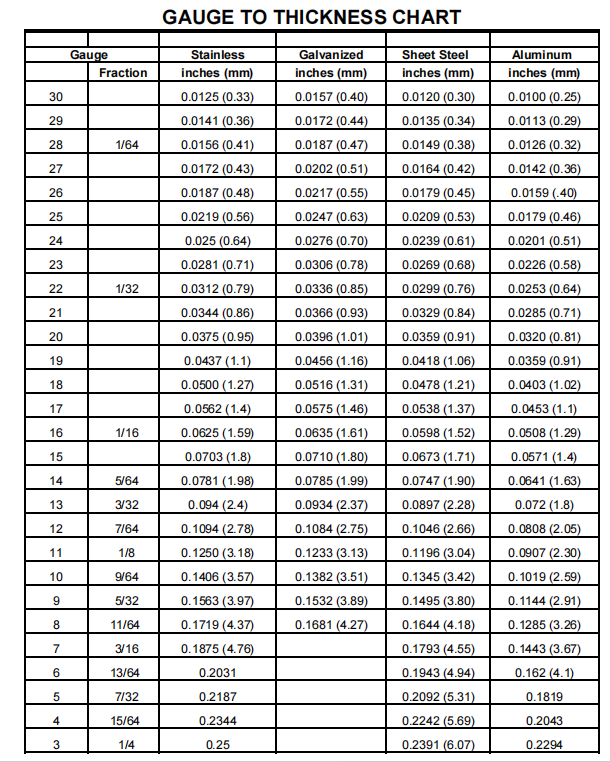
3. Thickness Matters
Sheet metal thickness is measured in gauges, with a lower gauge number indicating thicker material. The thickness of the sheet metal impacts its performance. Thinner sheets are more flexible, while thicker sheets offer greater strength. Understand the needs of your project and choose the appropriate thickness accordingly.
4. Minimize Wastage
Efficiency is critical in sheet metal fabrication. Minimize wastage by designing parts that maximize the use of the material. Nest components to reduce scrap and cut costs.
5. Bend Radii
Consider the bend radii when designing bends and folds. A smaller bend radius requires less force to achieve, but too small can lead to cracks. Strike a balance that suits your application.
6. Tolerance and Fit
Sheet metal parts often fit with others in an assembly. Pay close attention to tolerances to ensure proper fit and alignment. This reduces rework and enhances the overall quality.
7. Welding Considerations
When welding sheet metal, take into account the type of weld and the location. Proper welding techniques can prevent warping and distortion.

8. Cutouts and Perforations
Design cutouts and perforations with care. They not only serve a functional purpose but also impact the sheet’s structural integrity. Reinforce edges where necessary.
9. Surface Finish
The finish of your sheet metal parts can impact their appearance and functionality. Consider coatings, anodizing, or polishing to enhance the final product.

10. Prototyping
Before committing to a full production run, create prototypes. This allows you to identify and resolve issues, saving time and resources.
Safety and Sustainability
11. Safety Features
Incorporate safety features into your design, especially if your sheet metal parts will be used in applications where safety is paramount.
12. Sustainability
Consider sustainable design practices, such as designing for recycling and minimizing waste. It’s not only environmentally friendly but can also reduce costs.
Conclusion
Sheet metal fabrication design is a delicate dance of creativity and precision. By selecting the right materials, optimizing for manufacturability, and paying attention to detail, you can create sheet metal components that stand out in terms of functionality and aesthetics.