ECOREPRAP Rapid Prototyping Services
ECOREPRAP Rapid prototyping services with state-of-the-art manufacturing processes, including 3D printing, CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication and vacuum casting. Get top-quality prototypes fast and affordably, with the quickest turnaround and cost-effective solutions.
- Various rapid prototyping services
- Abundant materials & finishes
- 24/7 engineering support
Rapid Prototyping Services
- Various rapid prototyping services
- Abundant materials & finishes
- 24/7 engineering support
What Does Rapid Prototyping Mean?
In manufacturing and product development, rapid prototyping means quickly creating a physical model or sample of a product during the early stages of development to test, evaluate, and refine a design. It refers to a set of advanced manufacturing technologies built around one core idea: producing a physical part or prototype directly from a digital model—typically a CAD file—in the shortest time possible.
What Are Different Types of Rapid Prototyping Techniques?
Rapid prototyping includes several major manufacturing techniques used to quickly create prototypes and sample parts, including 3D printing, CNC machining, vacuum casting, rapid sheet metal fabrication, and rapid tooling.
Each rapid prototyping method serves a specific purpose and is selected based on required accuracy, material properties, and the stage of product development.
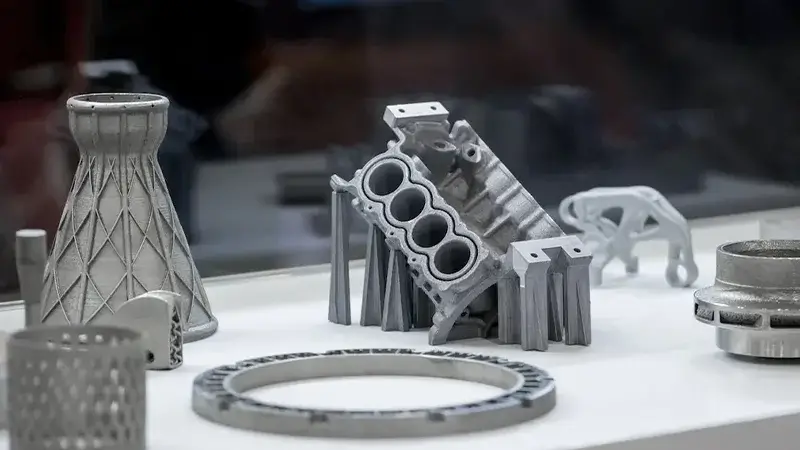

3D Printing for Rapid Prototyping
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a rapid prototyping method that builds parts layer by layer directly from digital CAD models.
Unlike traditional subtractive processes, it creates components without cutting away material, making it ideal for fast design validation and complex geometries.
Because of its short lead time, high design flexibility, and low upfront cost, 3D printing has become one of the most widely used rapid prototyping solutions in modern product development.
Common 3D Printing Technologies Used for Rapid Prototyping
• FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling): FDM works by melting thermoplastic filament and depositing it layer by layer to build a part. It commonly uses materials such as PLA, ABS, PETG, and Nylon.
This method is cost-effective and widely accessible, making it best suited for concept models and basic form checks. However, FDM parts typically have visible layer lines and lower mechanical strength.
• SLA (Stereolithography): SLA uses a laser to cure liquid photopolymer resin, creating parts with high accuracy and excellent surface quality.
It is ideal for detailed prototypes and visual models that require precise features. The main limitation is that most resin parts are relatively brittle and less suitable for load-bearing applications.
• SLS (Selective Laser Sintering): SLS fuses powdered materials using a laser, most commonly nylon such as PA12 or PA11. This technology does not require support structures and produces stronger, more functional prototypes compared to FDM and SLA. The trade-off is a higher cost and a slightly rougher surface finish.
Advantages of 3D Printing for Rapid Prototyping:
- Fast turnaround times
- High design freedom and geometric flexibility
- Low upfront cost with no tooling required
Limitations of 3D Printing for Rapid Prototyping:
- Lower strength and dimensional accuracy compared to CNC machining
- Limited material options that may not match final production materials
- Surface finish and consistency can vary by process
Typical Rapid Prototyping Applications of 3D Printing:
- Early-stage concept validation
- Form, fit, and basic assembly checks
- Complex internal or lightweight structures
- Rapid design iterations
- Low-volume production runs
Generally speaking, 3D printing is often used as the first step in rapid prototyping for concept validation. For certain geometries that are difficult or impossible to achieve with CNC machining, 3D printing can provide an effective solution.
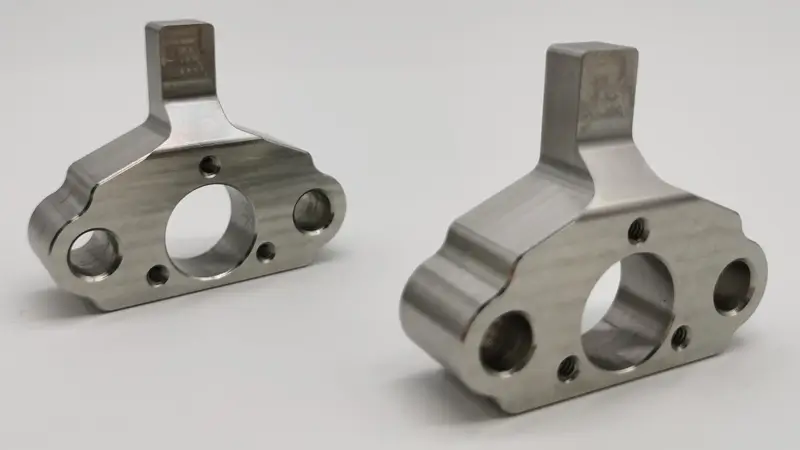

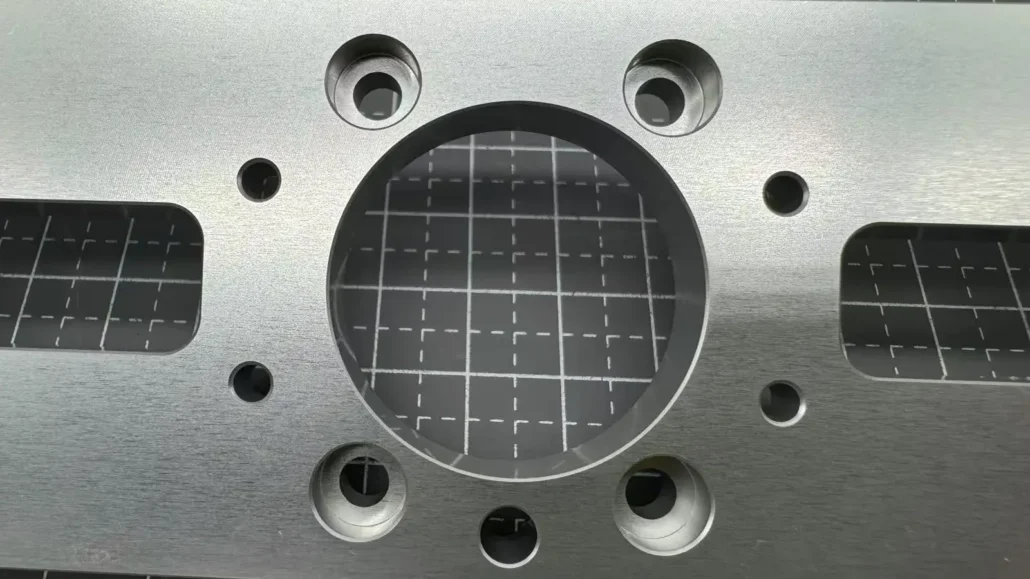
CNC Machining for Rapid Prototyping
CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing method that produces prototypes by cutting away material from a solid block.
Unlike 3D printing, CNC allows the use of real engineering materials such as aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, and high-performance plastics.
Prototypes produced with CNC machining closely replicate the strength, durability, and functionality of final production parts. Different CNC machining methods are used depending on material type, complexity, and required precision.
Common CNC Machining Methods for Rapid Prototypes
• CNC Milling: Milling uses rotating cutting tools to remove material and can produce flat surfaces, slots, steps, and complex contours. It works for most metals and plastics, providing high precision and good surface finish, making it ideal for functional testing and assembly verification.
There are 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC machining in the ECOREPRAP workshop.
• CNC Turning/Lathe: In turning, the workpiece rotates while a cutting tool removes material along its axis. This is best suited for cylindrical or conical parts. Turning is fast, material-efficient, and widely used for shafts and other rotational components.
• CNC Drilling/Boring: Used to create holes, threaded holes, or internal cavities. Drilling and boring are often combined with milling or turning to complete complex prototypes.
• Wire EDM: A thin metal wire cuts through hard materials using electrical discharge. It is ideal for extremely hard materials or high-precision complex internal shapes, commonly used for functional prototypes or mold verification.
Key Advantages of CNC Rapid Prototype:
- CNC can achieve micron-level accuracy, suitable for parts with tight tolerances.
- Using production-grade materials allows functional and mechanical testing.
- CNC machining offers excellent surface finish.
- Suitable for complex functional prototypes, especially mechanical components or assemblies.
Limitations of CNC Rapid Prototype:
- CNC machining generally has a longer lead time than 3D printing for complex parts.
- Higher cost, especially for premium materials like titanium or stainless steel.
- Extremely complex internal structures may require special tooling or multiple setups.
Typical Applications of CNC Rapid Prototype:
- Functional testing: Validate how parts perform under real operating conditions.
- Assembly verification: Ensure that prototype components fit correctly with other parts.
- Low-volume production: Produce small batches of functional parts before full-scale manufacturing.
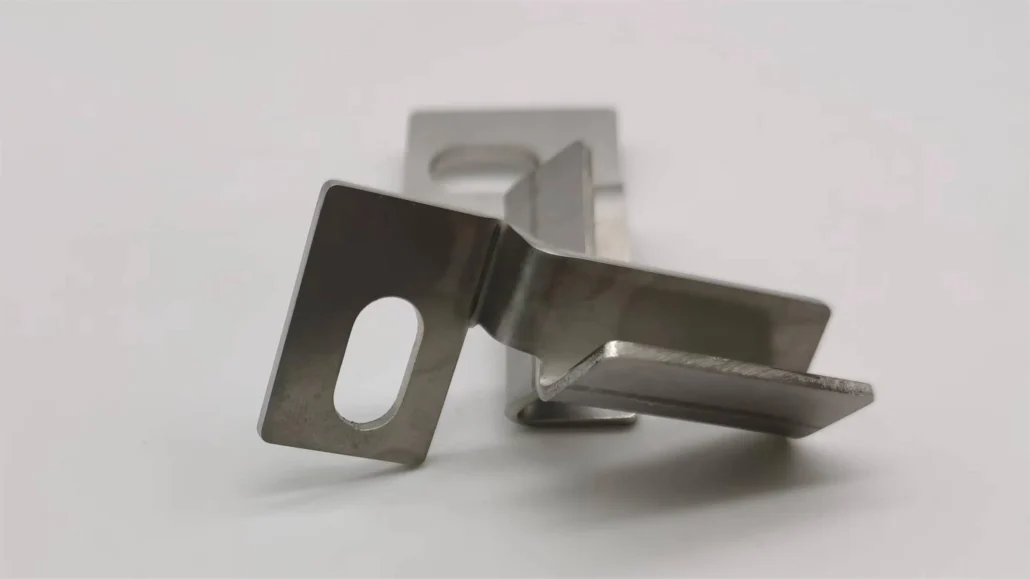

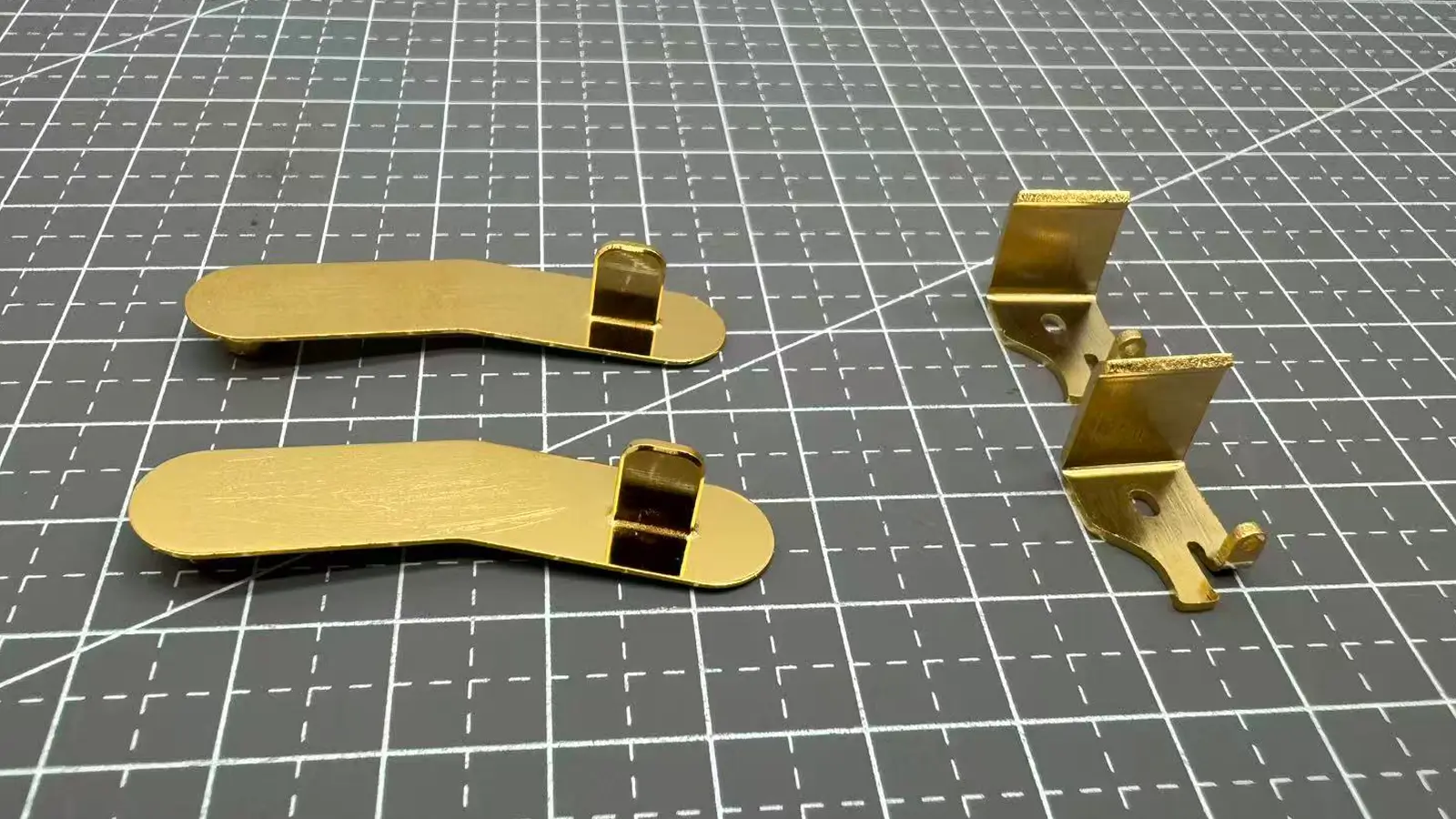
Rapid Sheet Metal Prototyping
Rapid sheet metal prototyping is a method that uses laser cutting, bending, and welding to quickly produce sheet metal parts.
Compared to other prototyping techniques, it can closely match the structure and functionality of final production components, making it ideal for testing assembly, structural strength, and fit.
Common Sheet Metal Technologies Used for Rapid Prototyping
• Laser Cutting: Laser cutting uses a high-powered laser to precisely cut sheet metal into the desired shape. It is highly accurate, capable of creating intricate patterns, slots, and holes, and works with materials like cold-rolled steel, stainless steel, and aluminum.
Laser cutting is ideal for quickly producing flat parts with minimal burrs and clean edges, which reduces post-processing time.
• Bending (Press Brake/Folding): Bending uses a programmable press brake or folding machine to bend sheet metal along specified angles and lines.
This process ensures consistent bends and precise dimensions, making it suitable for brackets, housings, and structural components.
Bending works best with materials like steel, aluminum, and stainless steel, and allows rapid prototyping of complex folded geometries.
• Welding (TIG/MIG/Spot Welding): Welding is used to join multiple sheet metal parts into a single assembly. Techniques such as TIG, MIG, or spot welding are commonly used depending on material and part thickness.
Welding allows the creation of prototypes with functional strength and structural integrity, closely replicating final production assemblies. It is ideal for testing load-bearing capacity and assembly fit.
Advantages of Rapid Sheet Metal Prototyping:
- Produces prototypes that closely match final sheet metal structures.
- Enables functional testing, assembly verification, and small-batch production.
- Flexible for a wide range of materials including steel, aluminum, and stainless steel.
- Reduces lead time compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
Limitations of Rapid Sheet Metal Prototyping:
- Extremely complex internal geometries or highly curved surfaces may require additional tooling or multiple setups.
- Small, highly precise parts may still require CNC machining for better tolerances.
- Welding and bending can introduce local stress points that need design consideration.
Typical Rapid Prototyping Applications of Sheet Metal:
- Brackets
- Housings
- Structural components
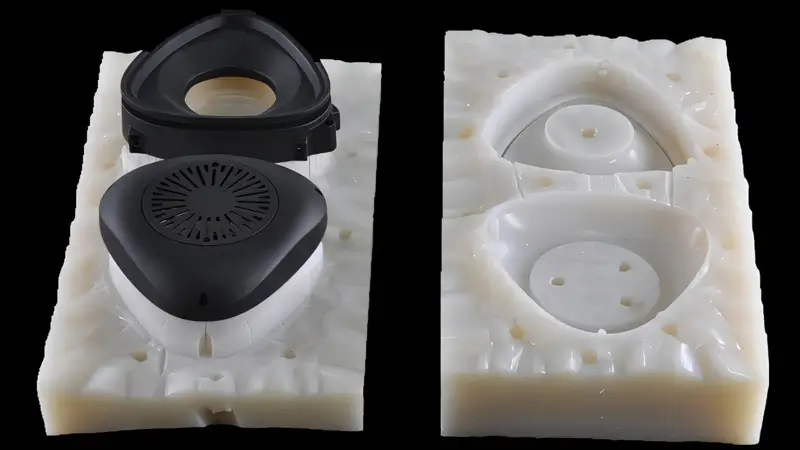

Vacuum Casting for Rapid Prototyping
Vacuum casting is a rapid prototyping method that uses silicone molds made from a master pattern—often 3D printed—to replicate multiple plastic parts.
Liquid polymer is poured into the mold under vacuum to reduce air bubbles and ensure high-quality surface finish, then cured to produce functional or visual prototypes.
Common Materials for Vacuum Casting Prototyping
• Polyurethane (PU) resin – PU resins are versatile polymers that can simulate a wide range of hardness and flexibility, from soft, rubber-like parts to rigid components.
They are ideal for functional prototypes, ergonomic testing, and parts that require slight mechanical stress. PU resins also allow for post-processing such as painting, coating, or polishing.
• Nylon-like resins – These resins are stronger and more durable than standard PU, making them suitable for functional prototypes that need to withstand moderate loads or repeated assembly.
They are often used for mechanical components, brackets, and structural prototypes where toughness is required.
• Transparent resins – Transparent or clear resins are perfect for optical parts, housings, or display prototypes. They allow designers to test light transmission, visual appearance, and product aesthetics.
Some transparent resins also offer scratch resistance or can be polished to achieve a glossy finish.
• Heat-resistant or UV-resistant resins – Heat-resistant resins can endure elevated temperatures, while UV-resistant resins are suitable for outdoor exposure, preventing yellowing or degradation. These materials are used when prototypes need to mimic environmental durability or simulate real-world operating conditions.
Key Advantages:
- Parts have smooth surfaces and can undergo painting, printing, or coating for realistic look.
- Each silicone mold can produce dozens to over a hundred parts, enabling quick design validation.
- Various polyurethane (PU) resins, nylon-like materials, or transparent polymers can be used to simulate final product properties.
- Certain resins allow light mechanical testing and assembly checks.
Limitations:
- Limited mechanical performance; not suitable for high-load applications
- Mold lifespan is limited, generally producing only dozens to hundreds of parts
- Complex internal geometries or thin-walled parts can be challenging to replicate
Typical Applications:
- Enclosures
- Consumer products
- Visual or display prototypes
What Are Advantages of Rapid Prototyping?

Faster Design Validation and Iteration
Physical prototypes allow engineers to test dimensions, structure, and functionality early, identifying design flaws and making improvements quickly.

Reduced Development Costs and Risks
Validating a design before mass production prevents costly errors, minimizes rework, and reduces material waste.

Complex Geometries and Innovative Designs
Techniques like 3D printing enable shapes and lightweight structures that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing.
Improve Decision-Making
Physical prototypes clearly convey design intent, facilitating better collaboration among designers, engineers, and clients.

Be Faster Time-to-Market
By shortening the development cycle, rapid prototyping allows companies to launch products more quickly and gain a competitive edge.
What Are Rapid Prototyping Processes?
Rapid prototyping is an efficient loop that quickly turns digital designs into physical parts for testing and refinement. The core workflow has five key stages:3d model design, 3d model conversion, prototype fabrication, evaluation and Iteration.

3D Design & Model
Create a digital model using CAD software. Optimize the design early for your chosen process.

File Prep & Conversion
Export the model to a standard format like STL. For 3D printing: “Slice” it into layers. For CNC machining: Generate toolpaths (G-code).

Prototype Fabrication
3D printing for complex, fast designs; CNC machining for high precision; vacuum casting, sheet metal, or rapid tooling for low-volume or functional prototypes.

Evaluation
Assess the prototype for fit, function, assembly, and aesthetics. Identify issues early to refine the design quickly.
Testing & Iteration
Test fit, function, and gather user feedback. Use the insights to update the CAD model and repeat the cycle until the design is perfect.
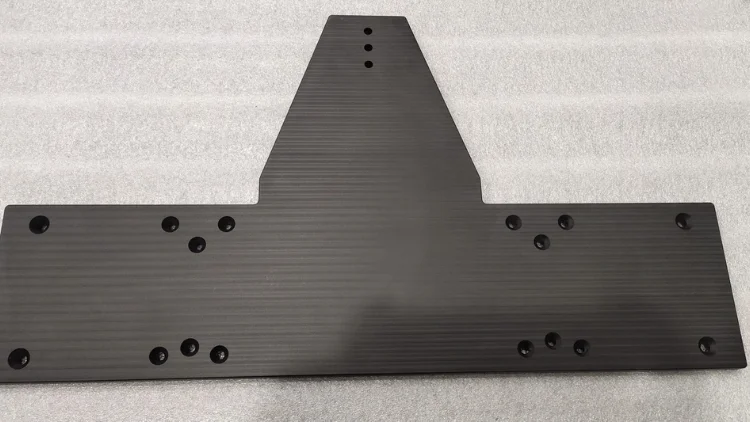
Rapid Prototyping Metal Materials
In rapid prototyping, metal materials are selected based on performance, machinability, and application requirements, supporting structural validation, functional testing, and low-volume production. Common rapid prototyping metal materials include aluminum, stainless steel, titanium and copper.
Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum Alloys are among the most frequently used materials for rapid prototyping due to their lightweight, high strength, good thermal conductivity, and ease of machining. Common grades include 6061, 7075, 5052.
Aluminum can be fabricated using CNC machining, 3D printing (SLM/DMLS), or rapid sheet metal, making it ideal for structural prototypes, functional testing, and low-volume parts.

Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel is known for corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and stable mechanical properties, with common grades such as 304, 316, 316L and 17-4PH.
It can be produced using CNC machining, 3D printing (SLM/DMLS), or rapid sheet metal, suitable for industrial components, mechanical prototypes, and durable functional testing parts.

Titanium Alloys
Titanium Alloys offer high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. Common grades include Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5) and Ti-6Al-4V ELI.
Titanium rapid prototypes are typically fabricated through CNC machining or 3D printing, supporting aerospace components, medical device prototypes, and durable functional testing.
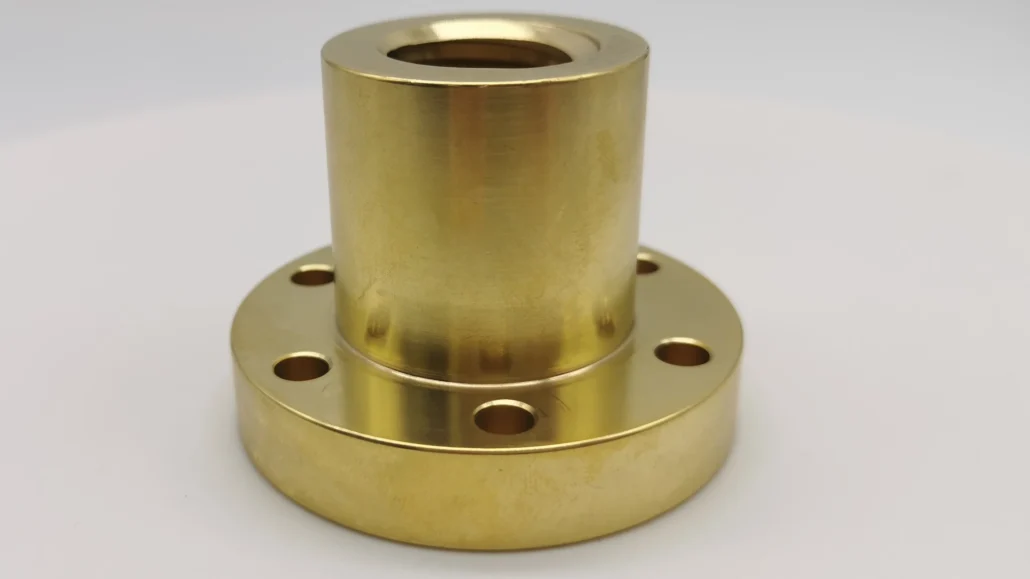

Copper Alloys
Copper Alloys provide excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, with common grades such as C11000 (Electrolytic Copper) and C93200 (Tin Bronze).
Copper parts can be made using CNC machining or 3D printing, often for electronics components, heat-dissipating structures, and functional prototypes.
Rapid Prototyping Plastic Materials
In rapid prototyping, plastic materials are among the most widely used options, especially for concept validation, visual evaluation, functional testing, and low-volume production. Compared to metals, plastics offer faster lead times, lower costs, and a wide range of mechanical and aesthetic properties. Common rapid prototyping plastic materials include ABS, PC, PA, PMMA, POM.
ABS
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is one of the most commonly used engineering plastics, offering good strength, toughness, and heat resistance.
It can be manufactured using 3D printing (FDM) or CNC machining, with common grades such as ABS-M30 and ABS-P430, and is widely used for enclosures, industrial parts, and functional prototypes.
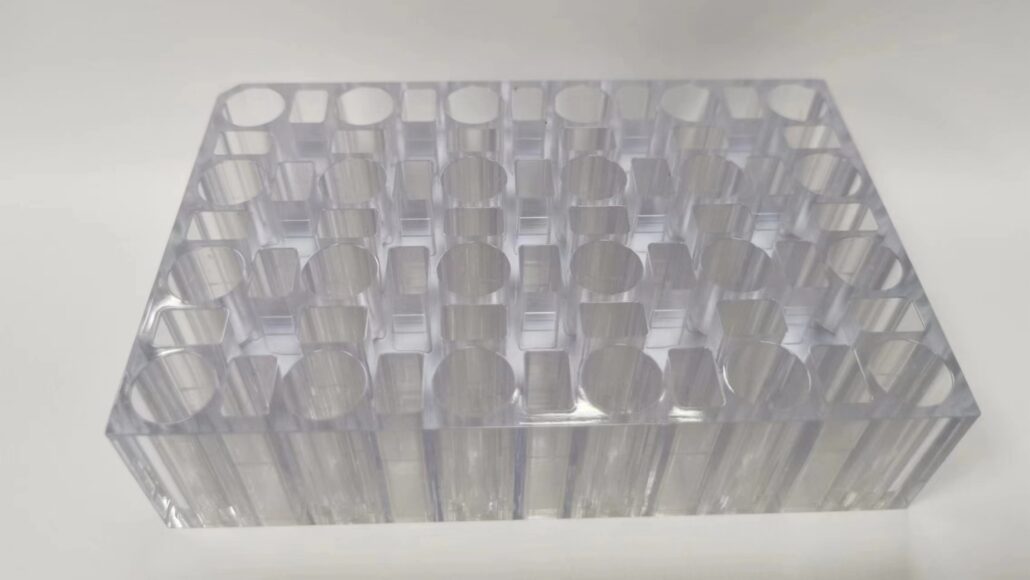

PC
PC(Polycarbonate) is known for its high strength, excellent impact resistance, and transparency, making it ideal for durable rapid prototypes.
It can be produced through CNC machining, 3D printing, or thermoforming, with common grades like PC-ISO and Lexan, often used for housings, protective components, and functional testing.
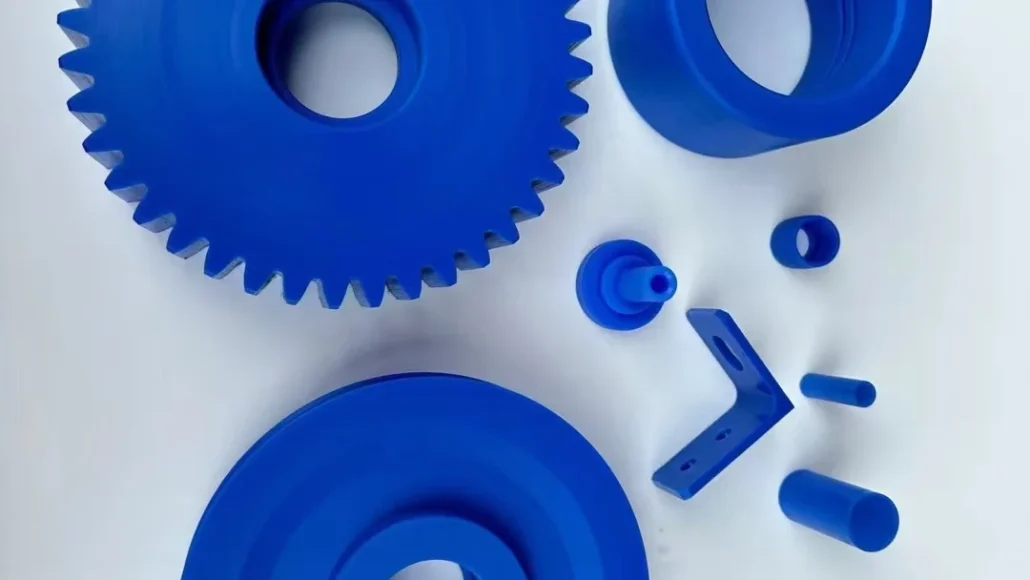

Nylon
Nylon (PA) offers excellent wear resistance, low friction, and high toughness, making it suitable for mechanical functional prototypes.
PA is commonly fabricated using SLS 3D printing or CNC machining, with popular grades such as PA6 and PA12, and is widely used for gears, clips, and moving components.
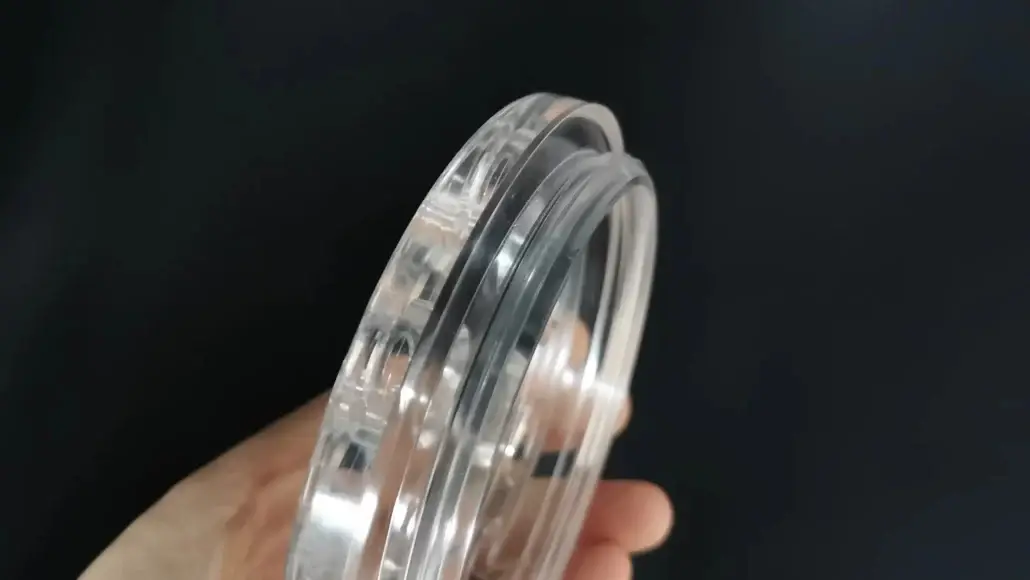

PMMA
PMMA (Acrylic) is valued for its high transparency and smooth surface finish, making it suitable for visual and optical prototypes.
It is typically produced using CNC machining or laser cutting, available in cast and extruded PMMA, and commonly used for display parts and transparent structures.

POM
POM (Acetal, Delrin) provides high stiffness, dimensional stability, and excellent wear resistance, making it ideal for high-precision functional prototypes.
It is usually manufactured through CNC machining, with common grades such as Delrin 100 and 500, and is often used for precision components and mechanical structures.
Surface Treatment for Rapid Prototype Parts
Surface treatment plays a critical role in rapid prototyping, as it improves not only the appearance of prototype parts but also their functionality, durability, and realism. Common surface treatments for rapid prototype parts include polishing, sandblasting, anodizing, painting, plating, and coating.

Anodizing
Anodizing is a widely used surface treatment for rapid prototype metal parts. Its main benefits include improved corrosion resistance, higher surface hardness, and better wear resistance, while also enhancing the overall appearance.
Color options also make anodizing ideal for visual and near-production prototypes.
Common materials suitable for anodizing include:
• Aluminum Alloys: the most common choice for CNC rapid prototypes
Typical grades: 6061, 6063, 5052, 7075
Among these, 6061 and 6063 are preferred due to their stable anodizing performance and consistent color results.
• Titanium Alloys: excellent corrosion resistance and biocompatibility
Typical grades: Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5), Grade 2
Titanium anodizing is often used in medical, aerospace, and high-end product prototypes, with colors controlled by voltage rather than dyes.
• Magnesium Alloys: extremely lightweight, requires specialized anodizing or MAO
Typical grades: AZ31, AZ91
These are mainly used in weight-sensitive prototype applications, though process control is more demanding.

Polishing
Polishing is a common surface treatment used in rapid prototyping to improve surface smoothness and visual quality.
It removes machining marks, layer lines, and minor surface defects, resulting in a glossy or semi-gloss finish.
Polishing is especially suitable for appearance models, demo parts, and prototypes where aesthetics are critical.
Polishing for rapid prototype parts can be broadly categorized into mechanical polishing (manual or machine-based, suitable for metals and plastics), mirror polishing (high-precision, optical-grade surfaces), vapor polishing (chemical smoothing for plastics like ABS, PC, PMMA), electropolishing (electrochemical smoothing for metals, improves brightness and corrosion resistance), and tumbling/vibratory polishing (batch smoothing using abrasive media, ideal for small parts and edge rounding).
• Metals:Aluminum, stainless steel, brass, copper
Widely used for CNC-machined prototypes requiring a clean, refined appearance.
• Plastics:ABS, PC, PMMA, Nylon
Often used for visual models and consumer product prototypes.
Polishing in rapid prototyping is primarily an appearance-enhancing process.

Black Oxide
Black oxide is a widely used and cost-effective surface treatment for rapid prototype metal parts, especially for steel components. Black oxide forms a thin conversion layer on the metal surface, which improves durability while maintaining tight tolerances, making it suitable for functional prototypes and engineering validation.
Its key benefits include enhanced corrosion resistance, improved wear resistance, reduced light reflection, and a uniform black appearance.
Black oxide-treated parts are often more resistant to fingerprints and minor scratches, helping prototypes maintain a clean and high-quality appearance during handling or demonstration.
Common materials suitable for black oxide include:
• Carbon and Alloy Steels:
Steel is the most common material for black oxide treatment in prototyping.
The process enhances corrosion and wear resistance while maintaining dimensional accuracy.
Typical grades: AISI 1018, 1045, 4140, 4340
Black oxide is particularly suitable for functional prototypes, mechanical components, tooling, and demo parts that require both durability and a professional appearance.

Passivation
Passivation is a chemical treatment that enhances the corrosion resistance of stainless steel by removing free iron from the surface and forming a protective oxide layer.
It does not significantly alter appearance but increases durability, reduces staining, and prolongs part life, making it ideal for functional prototypes and engineering validation.
Common materials suitable for passivation include:
• Stainless Steel Typical grades: 304, 304L, 316, 316L, 420, 440C, 17-4PH
Note: Free-machining grades like 303 are not suitable for nitric acid passivation.
• Aluminum Alloys Typical grades: 6061, 6063, 2024, 7075
Note: Thorough cleaning is essential; choose chromium-free solutions when possible.
• Titanium Alloys
Typical grades: Ti Grade 1, Grade 2, Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5)
• Copper and Copper Alloys
Typical grades: C1100 (copper), C36000 (brass), bronze
Note: Surface color may change slightly; adjust process for alloys with tin or zinc.
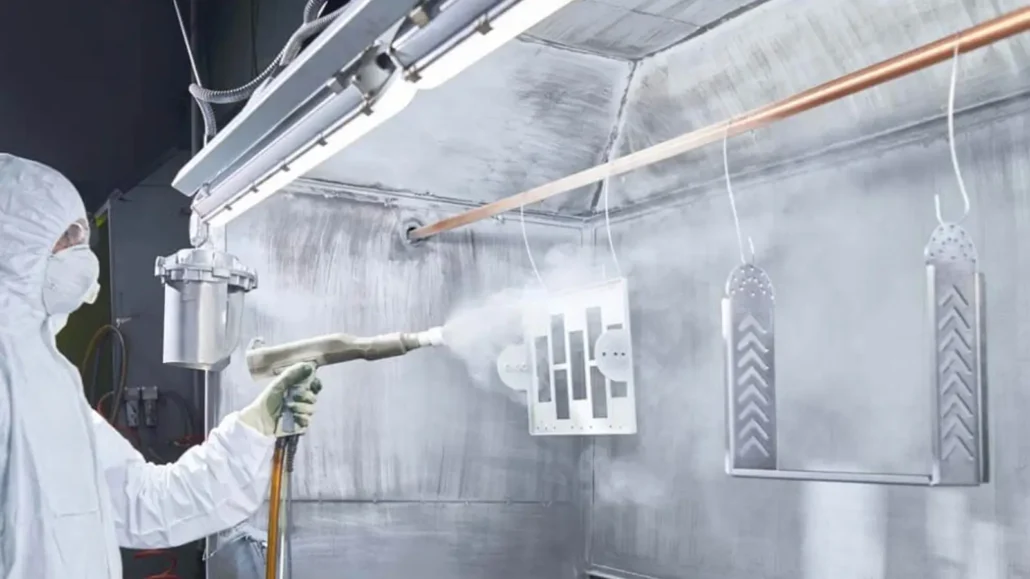

Powder Coating
Powder coating is a durable surface finishing method where powdered paint is electrostatically applied and then cured under heat, forming a hard, protective layer.
It offers excellent corrosion and wear resistance, as well as vibrant, uniform colors.
Powder coating is particularly suitable for prototypes that require long-term handling, functional testing, or demonstration of production-like finishes.
Common materials suitable for powder coating include:
• Metals
Aluminum alloys, steel, stainless steel – ideal for CNC prototypes or functional parts exposed to wear or environmental conditions.
Overall, powder coating is ideal for rapid prototype metal parts requiring durable, production-like surface protection, aesthetic appeal, and resistance to scratching, chipping, or fading.
Note: When planning CNC machining, it is important to leave extra material allowance on the surface to account for the thickness of the paint layer. This ensures that after spray painting, critical dimensions and tolerances still meet the design specifications. Typically, this extra allowance ranges from 0.05 mm to 0.2 mm, depending on the paint type and surface finish requirements.
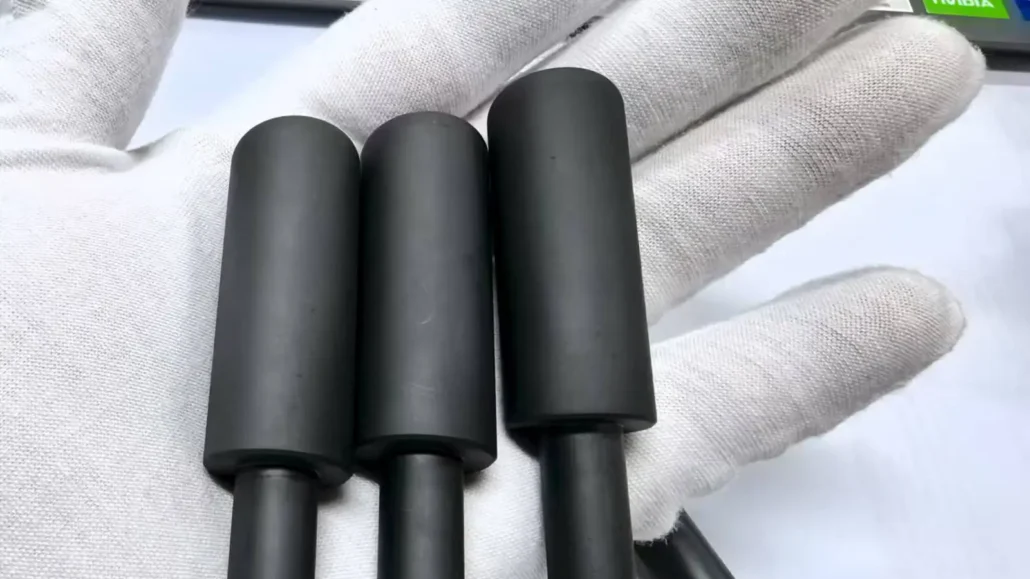

Phosphating
Phosphating is a chemical surface treatment that converts the metal surface into a layer of insoluble phosphate crystals. This layer enhances corrosion resistance, provides a better base for coatings or painting, and improves wear resistance for steel parts.
Phosphating is an effective surface treatment for steel rapid prototype parts, functional prototypes, mechanical assemblies, and tooling components, particularly for parts requiring lubrication or coating adhesion.
Common types of phosphating include:
Iron Phosphate: forms a thin gray or blue-gray film, mainly for pre-coating surface preparation and mild corrosion protection.
Zinc Phosphate: produces a white or gray crystalline layer with better corrosion resistance, suitable for functional prototypes and mechanical components.
Manganese Phosphate: creates a thick, wear-resistant layer, ideal for high-load mechanical parts, gears, and tooling prototypes.
Suitable materials: Steel and low-alloy steel
Typical grades: AISI 1018, 1045, 4140, 4340
Commonly used for functional mechanical parts and rapid prototypes requiring coating adhesion or lubrication.
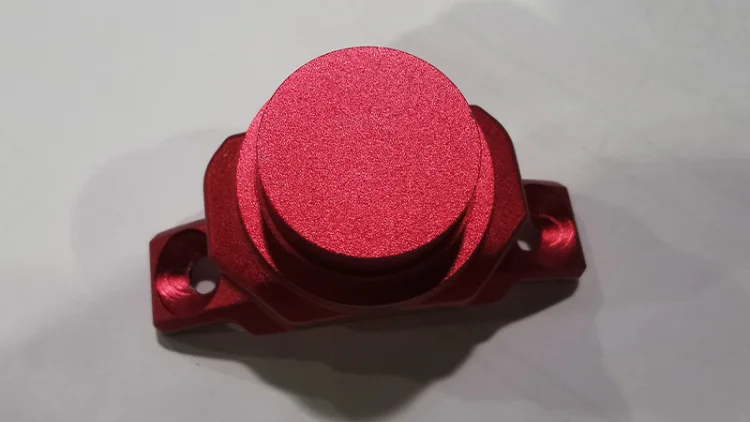

Spray Painting
Spray painting is a versatile and widely used surface treatment for rapid prototype parts, offering both aesthetic enhancement and basic surface protection.
It allows prototypes to achieve a uniform color, smooth finish, and improved visual appeal, making it ideal for appearance models, demo parts, and consumer product prototypes.
Spray painting does not significantly increase wear or corrosion resistance but is effective for simulating the look of production parts.
Common materials suitable for spray painting include:
• Metals:
Aluminum, steel, stainless steel, brass – commonly used for CNC-machined prototypes requiring a specific color or finish.
• Plastics:
ABS, PC, PMMA, Nylon – widely used for 3D-printed parts and consumer product prototypes.
Overall, spray painting is an excellent choice for rapid prototypes where color, finish, and visual realism are priorities, helping parts better represent final production aesthetics.
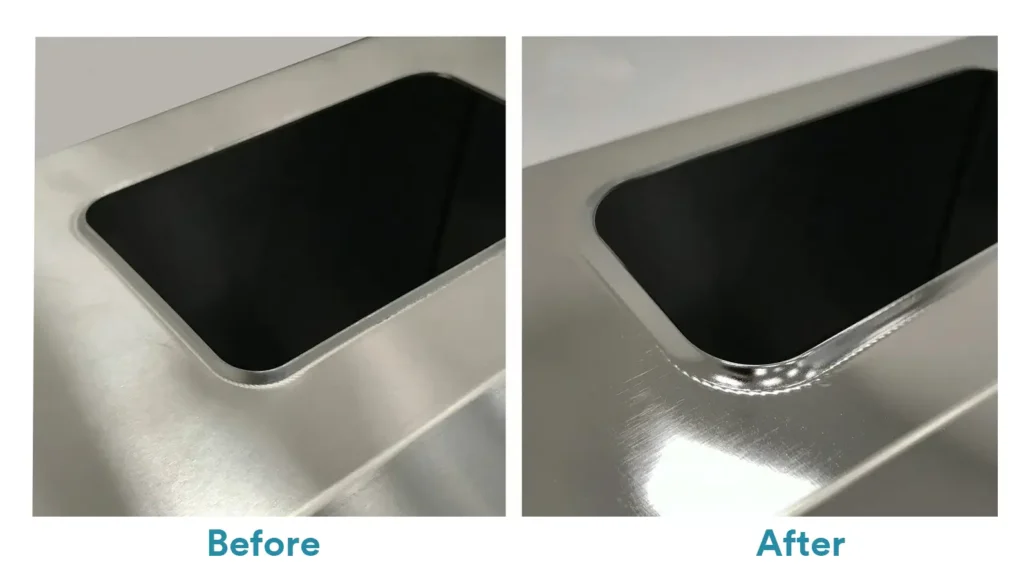

Electroplating
Electroplating is an electrochemical process that deposits a thin metal layer onto a substrate, improving corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and surface appearance.
It is also widely used for decorative finishes, giving prototypes a production-like look. Common types of electroplating:
• Nickel Plating: Provides corrosion resistance, smooth finish, and good wear properties; commonly used on steel and brass.
• Chrome Plating: Hard, shiny surface with high corrosion resistance; often used for decorative parts and automotive prototypes.
• Gold Plating: Offers premium aesthetics, electrical conductivity, and oxidation resistance; used in electronics or high-end demos.
• Silver Plating: Improves conductivity and provides a reflective finish; suitable for electrical contacts or display pieces.
• Copper Plating: Often used as an underlayer for subsequent plating or for conductive prototypes.
Common materials suitable for electroplating:
• Steel (carbon steel, stainless steel)
• Aluminum alloys
• Copper and copper alloys, brass
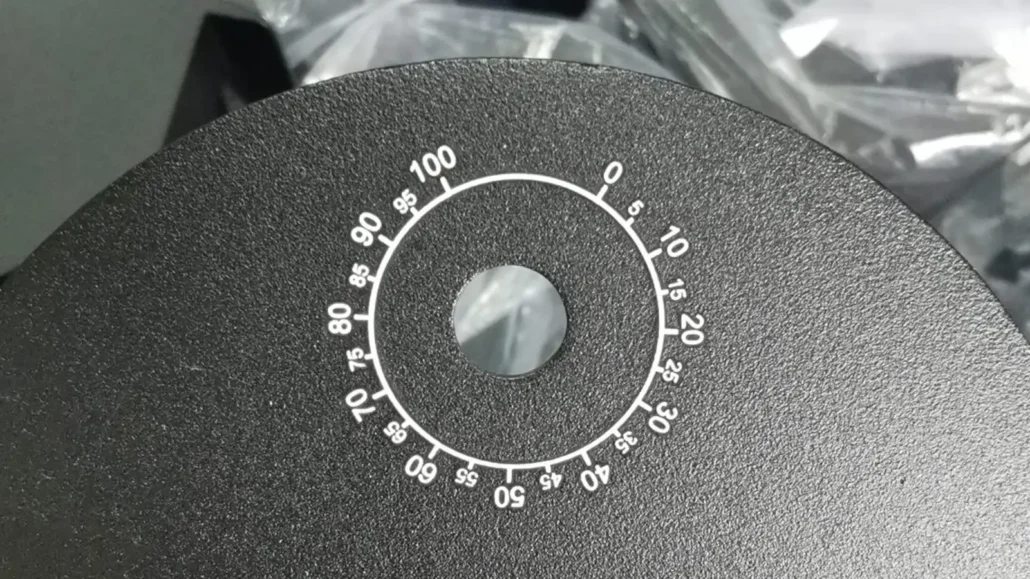

Part Marking
Part marking refers to the process of adding identification, logos, serial numbers, or other marks on rapid prototype parts.
It is essential for traceability, assembly guidance, quality control, and branding, especially for functional prototypes, demos, and small production runs.
Common part marking methods:
• Laser Engraving: Creates permanent, high-precision marks with minimal surface distortion; suitable for metal and some plastics.
• Inkjet or Pad Printing: Allows multicolor markings on plastic or coated surfaces; ideal for logos or product information.
• Stamping / Embossing: Adds raised or recessed characters; commonly used on metal prototypes.
• Etching / Chemical Marking: Uses acids or chemicals to mark metals; often used for fine, durable markings on stainless steel or aluminum.
• CNC Part Marking: CNC marking can be combined with other surface treatments but should be performed before coatings like anodizing or powder coating if the mark must remain visible.
Part marking is a practical surface treatment for rapid prototypes, enhancing traceability, functionality, and professional appearance while maintaining part integrity.
How to Make the Right Rapid Prototypes
Making the right rapid prototyping is not just about speed or cost. The best solution depends on the purpose of the prototype, expected performance, material requirements, and future production plans. Making the wrong choice can lead to misleading test results, unnecessary costs, or delays in product development.
Step1: Clarify the Purpose of the Prototype
Before selecting a rapid prototype, define what the prototype is for:
Concept / Appearance validation – focus on shape, size, and visual quality
Functional testing – require mechanical strength and dimensional accuracy
Assembly or fit check – need tight tolerances and realistic geometry
Customer demo or investor presentation – appearance and surface finish matter most
Step 2: Select Right Prototyping Method
Avoid choosing a process only because it is “fast” or “cheap.”
3D Printing – fast, cost-effective, ideal for early-stage design and complex geometries
CNC Machining – high precision, real engineering materials, suitable for functional prototypes
Vacuum Casting – good for small batches with production-like appearance
Sheet Metal Prototyping – best for enclosures, brackets, and structural parts
Step 3: Choose The Right Material
Material choice directly affects test results:
Use engineering plastics or real metals if mechanical behavior matters
Avoid overly soft or brittle materials for functional validation
Consider whether surface treatments (anodizing, passivation, electroplating) are required
A prototype that does not reflect real material behavior can lead to wrong engineering decisions.
Step 4. Consider Tolerance and Accuracy
Tolerance planning is critical for reliable testing.
CNC prototypes are preferred for tight tolerances and mating parts
3D printed parts may require post-processing to meet precision needs
If coatings or powder coating are needed, leave sufficient machining allowance
Step 5: Consider Surface Finish
Surface treatments such as polishing, anodizing, passivation, electroplating, or part marking should be considered early:
Appearance models require consistent surface quality
Functional parts may need corrosion or wear resistance
Marking methods (laser or CNC engraving) may affect later coatings
Step 6: Balance Cost, Lead Time, and Risk
Rapid prototypes should reduce development risk, not increase it:
Early-stage: prioritize speed and flexibility
Later-stage: prioritize accuracy, material realism, and repeatability
The “best” prototype is the one that delivers the right information at the right stage.
Why Choosing Prototyping Services in China
For many overseas companies, especially startups and engineering-driven teams, choosing rapid prototyping services in China is no longer just a cost decision. It has become a strategic choice driven by speed, capability, and manufacturing ecosystem advantages.
1. Faster Iteration and Shorter Lead Times
China’s prototyping suppliers are highly experienced in fast-turn manufacturing.
With in-house CNC machining, 3D printing, sheet metal, and surface treatments, many Chinese providers can deliver prototypes in days rather than weeks. This allows overseas customers to:
Iterate designs faster
Identify issues earlier
Reduce overall product development cycles
Speed is often more valuable than marginal cost savings.
2. Rich Engineering and Manufacturing Experience
Chinese prototyping companies handle a wide range of industries, including:
Consumer electronics
Automotive and EV components
Medical and industrial equipment
This exposure means suppliers are familiar with DFM feedback, tolerance control, material selection, and surface treatments, helping customers avoid design risks before mass production.
3. Broad Material and Process Availability
From common aluminum alloys to titanium, stainless steel, engineering plastics, and specialty surface treatments, China offers:
Easy access to diverse materials
One-stop solutions from machining to finishing
Fewer process limitations compared to smaller local shops
This is especially valuable for complex or multi-process prototypes.
4. Cost Efficiency Without Sacrificing Capability
While cost is not the only factor, China still provides excellent value for money:
Competitive pricing for CNC machining and rapid tooling
Lower cost for complex geometries or small-batch prototypes
Flexible order quantities with professional quality
For many overseas customers, this enables more prototype iterations within the same budget.
5. Seamless Transition From Prototype to Production
Many Chinese prototyping suppliers are closely connected to or operate their own production facilities. This allows:
Smooth scaling from prototype to low-volume or mass production
Better consistency between prototype and final parts
Reduced risk during production ramp-up
This continuity is highly attractive for global customers planning long-term manufacturing.
6. Mature Export and Communication Capabilities
Experienced Chinese rapid prototyping suppliers are familiar with:
International standards and drawings
English technical communication
Export packaging and logistics
This reduces communication friction and makes collaboration reliable, even across time zones.
Why Choose ECOREPRAP for Rapid Prototyping Services
When global customers search for rapid prototyping services in China, they are not only comparing prices — they are evaluating engineering capability, manufacturing stability, communication efficiency, and long-term reliability. ECOREPRAP is trusted by overseas customers because we consistently deliver engineering-grade prototypes with consistent quality every time.
Engineering-Driven Rapid Prototyping
Unlike many prototype shops that focus mainly on visual samples, ECOREPRAP approaches rapid prototyping from a manufacturing and engineering perspective.
We review designs with real production logic in mind, offering DFM suggestions on tolerances, material selection, wall thickness, and surface treatments.
This helps customers identify potential risks early and avoid costly redesigns later.
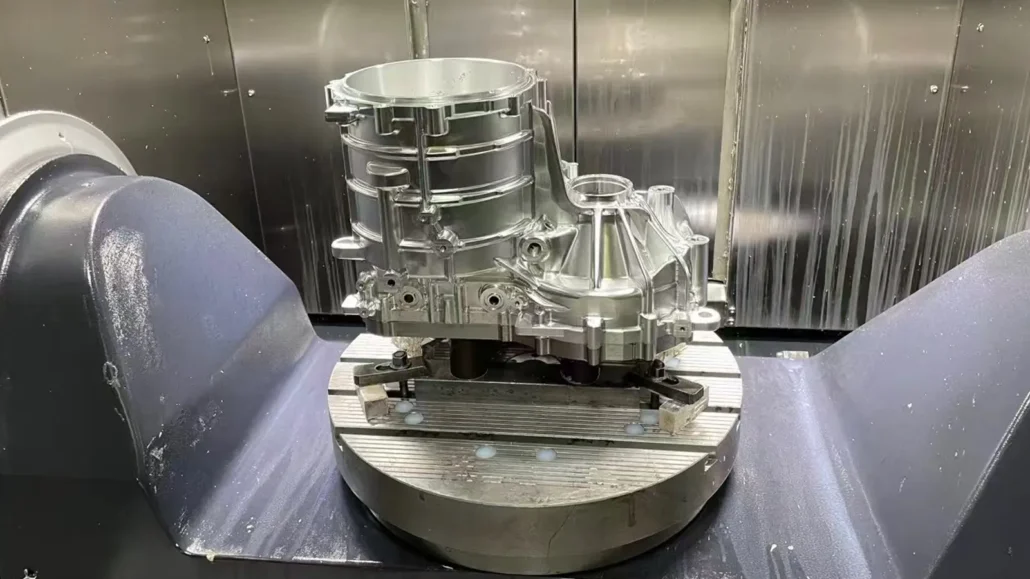

One-Stop Rapid Prototyping Capabilities
As a full-service rapid prototyping manufacturer, ECOREPRAP supports a wide range of processes, including CNC machining, 3D printing, vacuum casting, rapid sheet metal fabrication, and post-processing.
This allows us to recommend the most suitable rapid prototyping method based on design complexity, functional requirements, material properties, and budget, rather than forcing a single process.
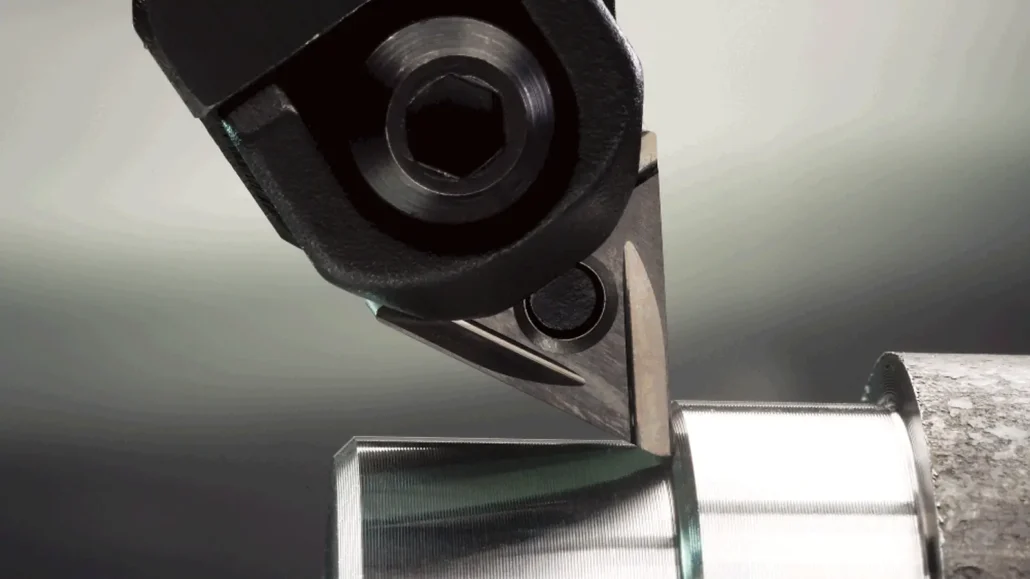
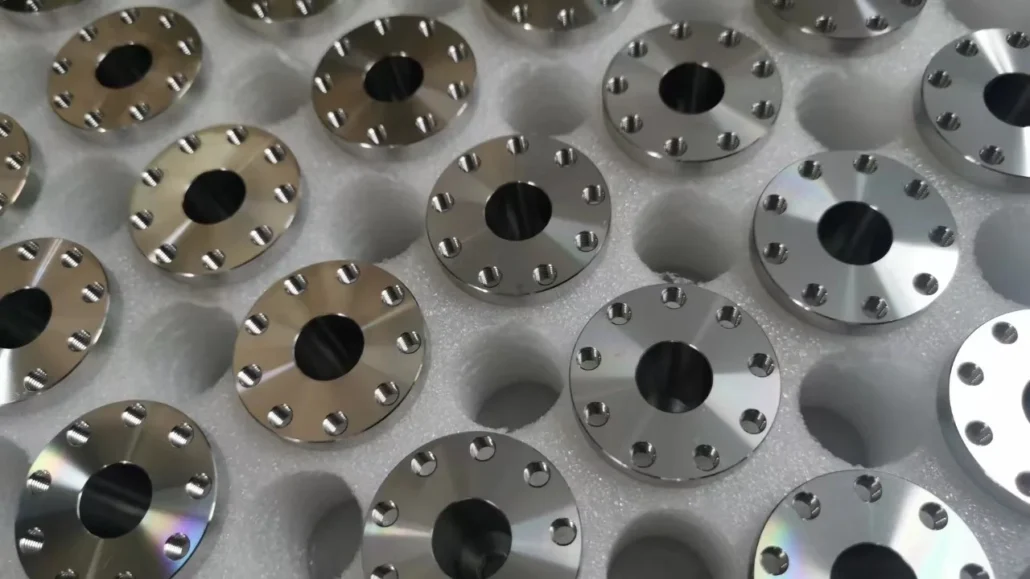
Precision With Consistent Quality Every Time
Our rapid prototypes are built to reflect real production standards, not just prototype-level acceptance. We focus on tight tolerance control, stable material sourcing, and standardized manufacturing workflows.
Whether it is the first prototype or the fifth iteration, customers receive repeatable results and consistent quality every time, which is critical for engineering validation and decision-making.

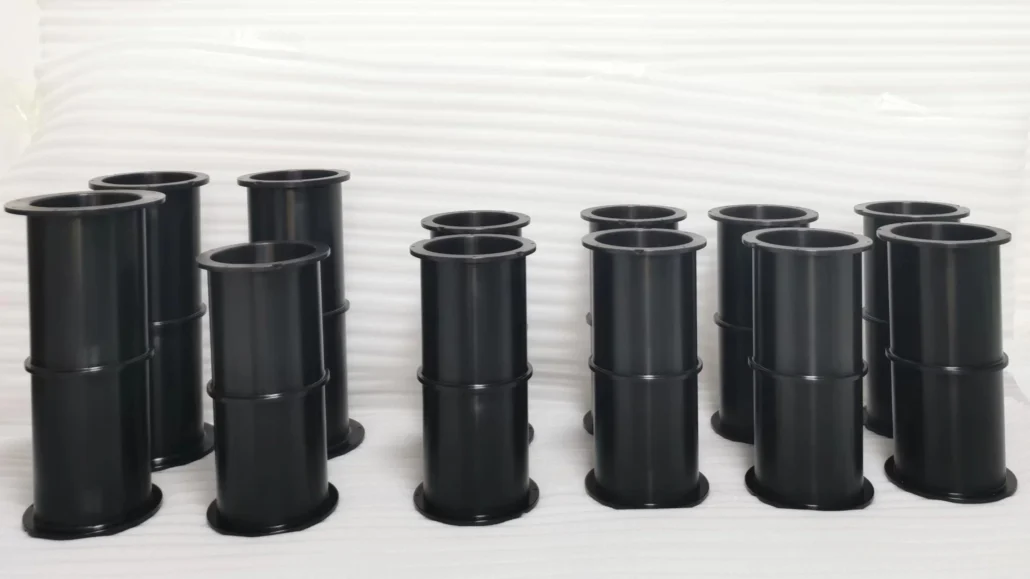
Fast Turnaround With Predictable Delivery Schedules
Speed is essential in product development. ECOREPRAP provides fast turnaround rapid prototyping services while maintaining quality.
Our internal coordination and experienced supply chain allow us to respond quickly to design changes, provide realistic lead times, and deliver prototypes on schedule — helping customers shorten development cycles and accelerate time to market.

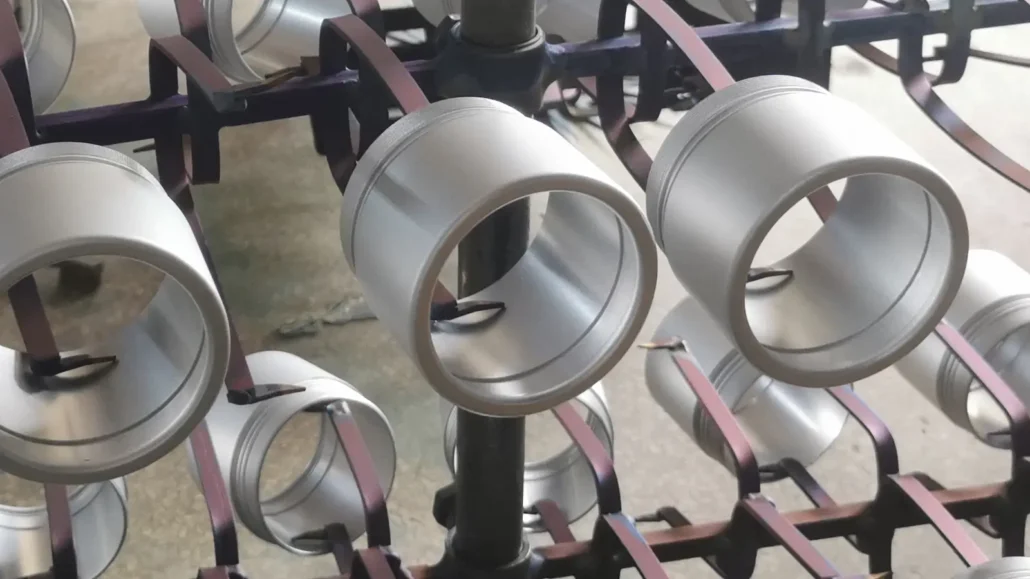
Cost-Effective Rapid Prototyping
By leveraging China’s mature manufacturing ecosystem, ECOREPRAP offers cost-effective rapid prototyping solutions for overseas customers.
We help clients achieve better value per iteration, enabling more design testing and refinement within budget — without sacrificing material authenticity, machining accuracy, or surface quality.

Smooth Transition From Rapid Prototype to Production
ECOREPRAP supports customers beyond prototyping. We assist with low-volume production, process optimization, and quality consistency planning, ensuring a smooth transition from prototype to mass production.
This continuity reduces supplier switching risks and ensures that what works at the prototype stage can scale reliably.
What Customers Say




Rapid Prototyping FAQs
ECOREPRAP provides rapid prototyping services with state-of-the-art manufacturing processes, including 3D printing, CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication and vacuum casting.
SLA, SLS, SLM, MJF and FDM.
Yes, for 3d printing parts, spray painting is available. For CNC and sheet metal fabrication parts, more than 20 surface finishes are provided.
A rapid prototype is a physical sample or model of a part or product that is quickly produced to evaluate design, function, fit, or appearance before mass production. It is typically made directly from a digital CAD model using fast manufacturing methods such as CNC machining, 3D printing, or vacuum casting.
There are several common types of rapid prototyping, including:
3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing): FDM, SLA, SLS for fast iteration and complex geometries
CNC Machining: High-precision prototypes using real production materials
Vacuum Casting: Small-batch plastic prototypes with production-like appearance
Rapid Sheet Metal Fabrication: Metal enclosures and structural parts
Rapid Tooling: Short-run molds for functional testing
Each method serves different stages of product development.
Rapid prototyping originated in the late 1980s, with the invention of stereolithography (SLA) by Chuck Hull in 1986. This marked the beginning of modern rapid prototyping technologies based on digital-to-physical manufacturing.
In 3D printing, rapid prototyping refers to the process of quickly producing prototypes by building parts layer by layer directly from a CAD file. It enables fast design validation, especially for complex shapes, internal structures, and early-stage concept models.
No. Rapid prototyping is not the same as 3D printing.
3D printing is one method of rapid prototyping, while rapid prototyping is a broader concept that also includes CNC machining, vacuum casting, and other fast manufacturing techniques.
Rapid prototyping is important because it:
Reduces development time
Identifies design issues early
Lowers overall development cost
Improves communication between design and engineering teams
Accelerates time to market
It allows companies to test and refine ideas quickly before committing to mass production.
Rapid prototyping is used for:
Concept validation and design visualization
Functional and mechanical testing
Fit and assembly verification
User experience evaluation
Pre-production and engineering validation
It is widely used in industries such as electronics, automotive, medical devices, and consumer products.
When selecting a rapid prototyping consultancy for electronics, consider:
Experience with electronic enclosures and PCB-related tolerances
Ability to handle tight tolerances and EMI/thermal considerations
Access to CNC machining, 3D printing, and sheet metal processes
Engineering support and DFM feedback
Proven quality consistency and fast turnaround
A consultancy that understands both mechanical and electronic integration is essential.
The cost of rapid prototyping depends on:
Manufacturing method (3D printing vs CNC machining)
Material type
Part size and complexity
Tolerance and surface finish requirements
Quantity
Simple 3D-printed prototypes may cost tens of dollars, while high-precision CNC prototypes can range from hundreds to thousands of dollars per part.
Enterprises use rapid prototyping technology to:
Reduce product development risk
Speed up innovation cycles
Validate designs before large investment
Improve product quality
Gain competitive advantage
By enabling faster iteration and better decision-making, rapid prototyping helps companies bring better products to market more efficiently.




