Heat Treatment Services
Heat treatments can be applied to many metal alloys to drastically improve key physical properties, including hardness, strength, and machinability.
Heat Treatment
Heat treatment is a controlled and systematic process employed to modify the physical and mechanical characteristics of materials, particularly metals and alloys. Through carefully calibrated heating and cooling cycles, this method aims to enhance specific properties such as hardness, toughness, and ductility. By subjecting materials to precise thermal conditions, heat treatment mitigates internal stresses, refines microstructures, and ultimately tailors the material’s performance to meet stringent engineering requirements. It is a vital manufacturing technique widely utilized across industries to optimize the strength, resilience, and overall quality of various components.
| Applicable Materials | Color Options |
| Steel | Black(Usually) |
Heat Treatment Parts


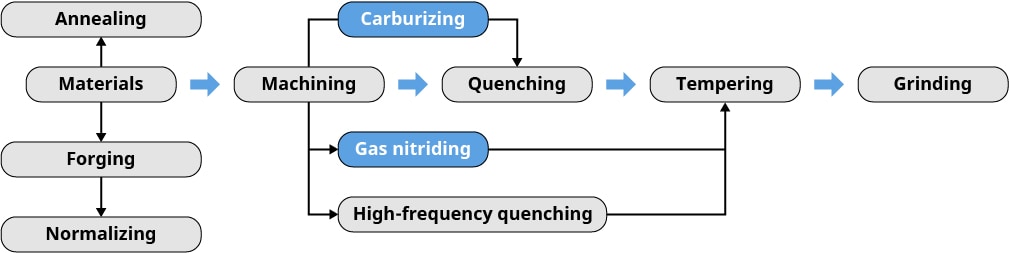
Heat Treatment Process
Heat treatment is the procedure of controlled heating & cooling of a material to preferred material or commercial properties. It alters four of the main product homes of metal parts, which are firmness, strength, toughness, and ductility.
- Heating: The material is heated to a specific temperature range, which varies depending on the desired outcome. This phase can include heating to austenitizing temperatures.
- Holding: The material is held at a certain temperature for some period, allowing for a uniform temperature distribution throughout the material's structure.
- Quenching: The material is rapidly cooled, or quenched, in such as oil, water, or air, to achieve the desired hardness or other mechanical properties.
- Tempering: In some cases, the material is then tempered by reheating it to a lower temperature. Tempering helps reduce brittleness and achieve the desired balance of hardness and toughness.
Heat Treatment Design Consideration
You can apply heat treatments to metal alloys at different phases of the CNC machining process, either before you begin machining your components or after.
Before CNC machining
When a standardized grade of a metal alloy is requested that is readily available, the CNC service provider will machine the parts directly from that stock material. This is often the best option for reducing lead times.
After CNC machining
Some heat treatments significantly increase the hardness of the material or are used as a finishing step after forming. In these cases, the heat treatment is applied after CNC machining, as high hardness reduces the machinability of a material. For example, this is standard practice when CNC machining tool steel parts. The parts after heat treatment need to be CNC machined again