Table of Contents
Both electroplating and electropolishing are electrochemical surface finishing methods used to enhance the metal surface’s resistance to corrosion. But they differ much in various aspects. It is essential to understand them clearly and then apply the most suitable technique to your CNC projects.
Key Takeaways
- Both electroplating and electropolishing are electrochemical surface finishing techniques. But electroplating adds layer to the base material while electropolishing removes material off.
- Electroplating is mainly used to provide the base material with performances of the plated metal while electropolishing is primarily applied to make the surface bright and smooth.
- The final appearance of the electroplated part depends on the particular type of electroplatingwhile that of the electropolished part would typically not be changed on aspect of color.
1. What is Electroplating?
Electroplating is an electrochemical surface finishing technique during which a thin layer of metal or alloy coating would deposit uniformly on a conductive material (typically metal), to improve the part’s appearance and performance such as corrosion resistance, abrasion resistance and electrical conductivity.
Below is a photo shows gold plating apperances.
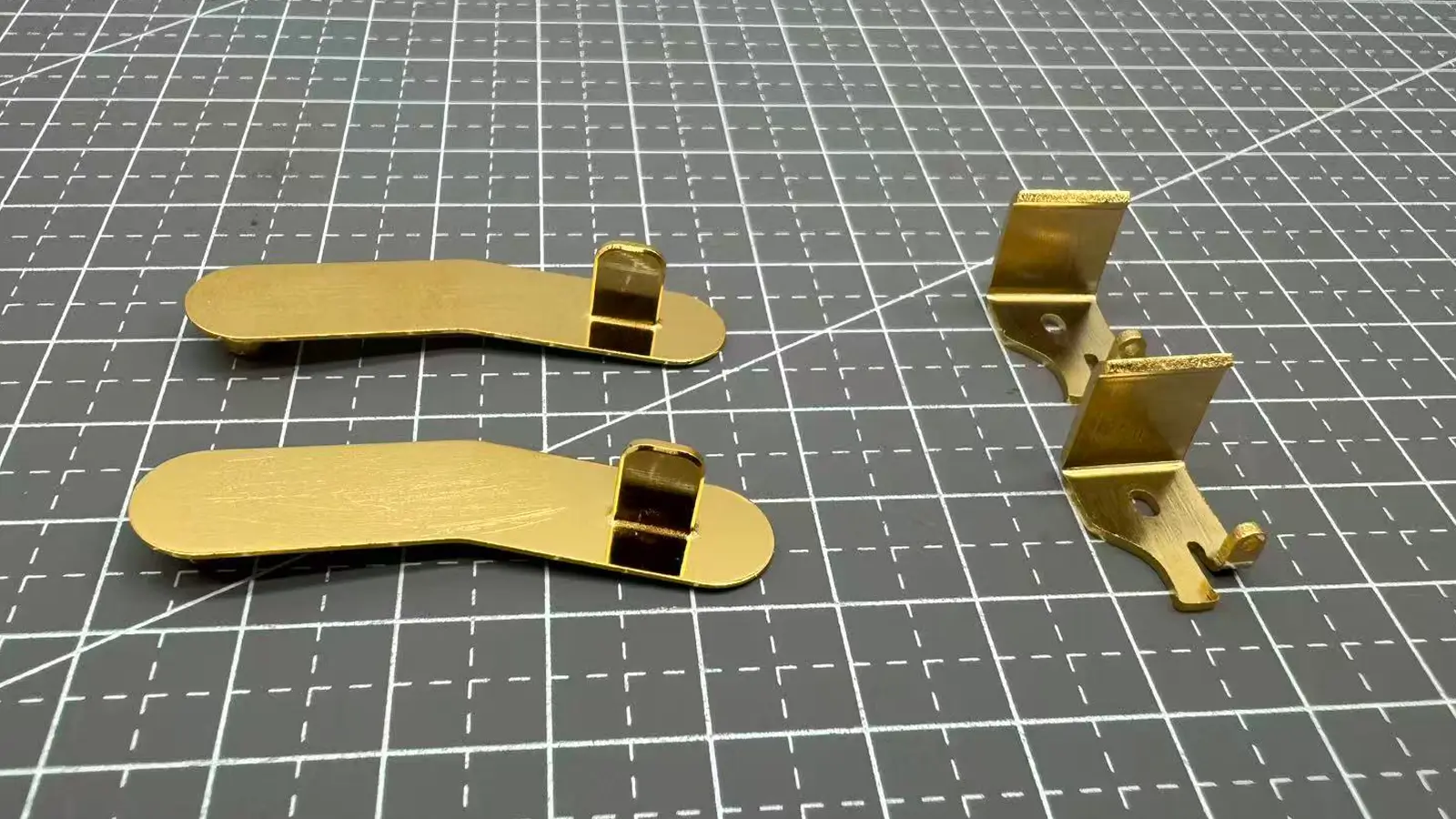
There are four core components of the electroplating process: anode, cathode, electrolyte, and direct current.
Anode is usually made of the metal to be plated. During electrolysis, the anode dissolves and releases metal ions into the solution.
For instant, when nickel electroplating is applied to a metal surface, a nickel material would serve as the anode to provide the surface with nickel ions.
Cathode is typically the conductive part to be plated. It would be connected to the negative terminal of the power supply and provide electrons for metal ions.
They would gain electrons on the cathode’s surface and be reduced to metal atoms.
Finally, a metal coating will deposit on the surface to provide desired protection.
Electrolyte is a solution containing the metal ions to be deposited.
The solution plays key role in providing primary source of metal ions to deposit and ensuring efficient current flow between the anode and the cathode.
It may also include conductive salts, complexing agents, buffers, brighteners, and other additives to regulate deposition rate, coating structure, and appearance.
Direct power supply provides a constant current to drive ion migration and reduction reactions.
2. What is Electropolishing?
Electropolishing, also known as electrochemical polishing, is a surface-finishing process that uses an electrochemical method to smooth, brighten, and deburr metal surfaces.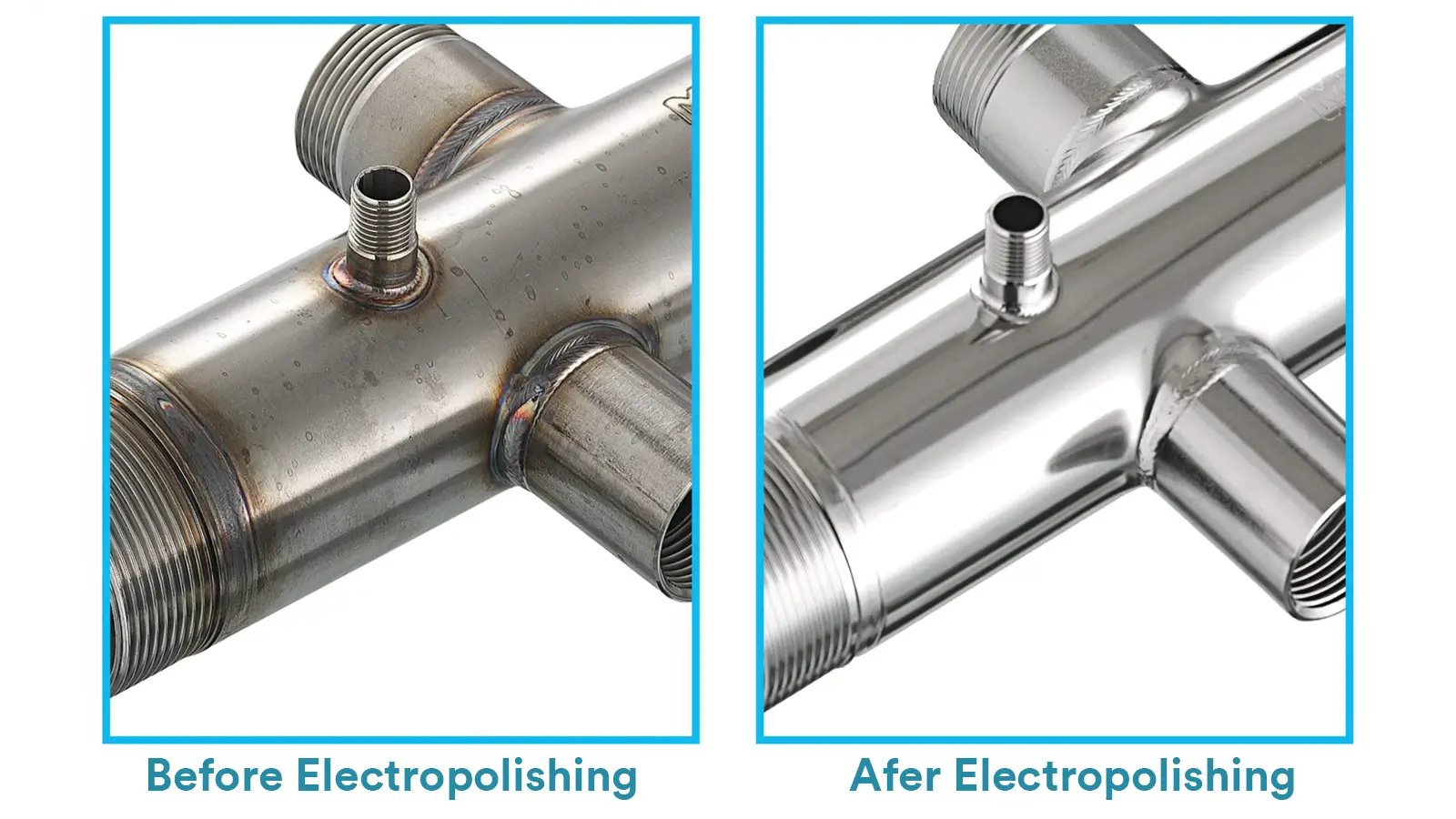
By applying direct current in a specially formulated electrolyte, the metal workpiece would undergo selective dissolution as the anode, where microscopic high areas are preferentially removed.
This produces a smooth, clean surface with high reflectivity.
The process of electropolishing also covers four important elements, including anode, cathode, electrolyte, and direct current.
Unlike the electroplating process, the anode within the electropolishing process is often the part to be polished.
The part would be connected to the positive terminal of the power supply, and when the current is applied in the electrolyte, an oxidation reaction would occur.
The metal atoms would lose electrons and become ions dissolved into the solution.
And the cathode is usually inert materials such as stainless steel, lead, or aluminum. It only functions as a conductor but will not participate in the reaction.
Electrolyte is very crucial for the electropolishing process. The solution is not only the medium for conducting current, but also the essential carrier that enables surface leveling, brightening, and selective dissolution of the metal.
To promote a controllable and preferred dissolution of the metal part, the electrolyte solution must contain acids or salts that can form soluble complexes or salts with metal ions to prevent the formation of passivation films, while maintaining sufficiently high conductivity to ensure uniform current flow across the workpiece surface.
Once when the current is applied, the metal ions generated by the dissolution of the metal surface would react with the electrolyte and form an anodic film near the anode, with high viscosity and low conductivity.
At the peak of surface, the current density is higher, leading to faster dissolution and therefore thinner viscous film. As the film is thin, the resistance to ion diffusion would be lower, thus promoting continuous dissolution.
While the dissolution at the valley of surface would be restricted. During such a process, the part’s surface would be smoother and brighter.
Direct current provides the electrochemical power for the whole process. Under the effect of electric filed, the atoms of the metal surface would lose electrons and be converted into metal ions by oxidation.
3. What is the Process of Electroplating?
Pre-process
- Mechanical Grinding:
Using grinding wheels, abrasive belts, or polishing wheels to remove burrs, rough surface layers, or larger defectsfor smoother surface.
For small parts, deburring and polishing are preferred to be performed by abrasives in a tumbling barrel or vibratory machine.
- Degreasing:
Thoroughly remove oils, dust, wax, or fingerprints from the surface of the part by chemical degreasing or electrolytic degreasing.
For the former method, the part should be immersed in an alkaline solution, where saponification and emulsification reactions help remove oils and grease.
While for the latter method, the part should be placed in an electrolytic bath as the anode (or cathode), and electricity is applied to generate gas bubbles. The mechanical action of the bubbles helps strip oil and contaminants from the surface.
- Pickling:
Dissolve scale, rust, and oxide films caused after heat treatment on the surface by immersing the part in specific acid solution within strictly controlled time.
- Activation:
Immerse the part in a dilute acid such as 5–10% sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acidfor a short time to remove the thin oxide film and activate the metal surface.
This can ensure that the coating can be deposited directly and securely onto a clean and uncontaminated metal surface. Proper activation is particularly important for easily passivated metals such as aluminum and stainless steel.
- Rising:
Note to thoroughly rinse the part after every step to prevent chemical residues left by the previous step from being carried into the next one and causing cross-contamination.
Electroplating Process
- Racking:
Connect the part to the cathode power supply through designedconductive racks. Note to ensure proper contact points and shield areas not to be plated.
- Plating:
Immerse the part in the electroplating tank and apply direct current. During the process, metal ions would be reduced and deposited on the surface. Note to properly control key parameters such as current density, temperature, pH value, plating time, and stirring frequency.
Post-process
- Rising:
Rinse the part completely to clean any residual electrolyte off and thus to prevent corrosion or contamination to subsequent processes.
- Passivation(Optional):
Form a passive oxidation film on the plated metal surface for additionally protection from corrosion.
- Embrittlement-Off(Optional):
Hydrogen gas can be generated during the electroplating process and absorbed into high-strength steel, causing hydrogen embrittlementand worse toughness. Therefore, a baking heat-treatment is required to allow the absorbed hydrogen to diffuse out.
- Drying:
Dry the part completely by hot air, centrifugal drying, or an oven to prevent water stains or oxidation.
4. What is the Process of Electropolishing?
Pre-process
- Degreasing: Use degreasers or solvents, combined with brushing or ultrasonic agitation, to thoroughly remove oils, waxes, and other contaminants from the workpiece surface.
- Rinsing: Rinse the part completely to remove any residualdegreasing agents.
- Pickling: For parts with oxide scale or rust, perform acid pickling to eliminate these surface impurities.
- Rinsing: Rinse the part again with clean water to remove any remaining pickling solution residues.
Electropolishing
- Mounting: Secure the pretreated part on the anode rack, ensuring good electrical contact.
- Immersing: Submerge the part in the electrolyte as the anode.
- Power Applying: Apply a DC power supply, conducting the electrolytic reaction under specified voltage, current density, temperature, and time. Current density is typically controlled within the polishing region to form a stable anodic film and achieve optimal polishing results. And the processing time generally ranges from tens of seconds to a few minutes, depending on the desired level of smoothness.
Post-process
- Rising: Rinse the part immediately to completely clean off any residual solution.
- Neutralizing: Use a mild alkaline solution to neutralize any residual acidic electrolyte on the surface.
- Rising: Rinse the part again with purified or deionized water.
- Drying: Wipe or dry the part to preventwater spots or residue.
5. What are the Top 7 Differences between Electroplating and Electropolishing?
On Process
Electropolishing can be seen as a reverse electroplating process. Electroplating adds an additional layer of the base material while electropolishing removes certain material off.
What’s more, although they are both electrochemical process, electroplating takes the part act as the cathode while electropolishing serves the part as the anode.
And both the cathode and anode within the electroplating function in the chemical reaction while the cathode of the electropolishing process just used to transport current.
On Function
The main functions of electroplating and electropolishing are also different.
Electroplating can typically change the surface performance such as corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, abrasion resistance, and appearance. It can also restore the worn dimension of the part.
Compared with electroplating, electropolishing primarily plays role in improving surface cleanliness.
It can remove burring and micro roughness of the surface and polish the surface to achieve mirror-like appearance.
On Dimension
Electroplating would certainly increase the part’s dimension since it adds an additional layer on the surface. And the dimension change depends on the coating type and desired protection level.
It is supposed to leave properly enough dimensional tolerance for such an increase.
But electropolishing makes the converse impact on the part’s dimension.
After electropolishing process, the part’s dimension would be slightly reduced but such a change can usually be ignored.
On Corrosion Resistance
Both electroplating and electropolishing can improve the part’s corrosion resistance. But their methods are different.
Electroplating can directly enhance the part’s corrosion resistance by coating a protective layer on the surface. The electroplating coating can provide a physical barrier from corrosive elements and the layer usually much more chemically stable.
While electropolishing cannot directly enhance the part’s corrosion resistance. Instead, it makes the surface more resistant to corrosion by removing contaminants away and assembling passive elements together.
On Smoothness
Electropolishing can significantly improve the surface’s smoothness and even make it reflective. It can remove burrs and tiny scratches off and level the micro peaks of the surface.
Compared with electropolishing, electroplating cannot obviously change the surface’s roughness. The roughness of electroplated surface depends on the condition of base material coating type. It is supposed to polish the surface first before electroplating.
On Appearance
Since electroplating would additionally add a metal layer on the base material, the part’s final surficial appearance would be directly determined by the coating’s appearance. However, electropolishing would not change the part’s appearance on aspect of color or luster, etc.
On Purpose
Electroplating is primarily used to provide the surface with performance of those metal coatings while electropolishing is applied to achieve bright appearance and clean surface.
Electroplating vs. Electropolishing – Quick Comparison
| Item | Electroplating | Electropolishing |
|---|---|---|
| Material Change | Adds a metal layer | Removes a thin surface layer |
| Part Role | Part acts as Cathode | Part acts as Anode |
| Dimensional Impact | Dimension increases | Dimension slightly decreases |
| Main Purpose | Protection & functional performance | Surface cleanliness & smoothness |
| Surface Roughness | Little to no improvement | Significantly improved (lower Ra) |
| Appearance | Determined by coating material | Same material, brighter finish |
| Corrosion Method | Protective coating barrier | Cleaner, more uniform passive layer |
| Typical Use | Functional & protective finishes | High-smoothness, clean surfaces |
6. FAQs
6.1 Which process can brighten and smooth the surface, electroplating or electropolishing?
It is electropolishing. Electroplating does not have impact on surface roughness and brightness. If smooth coating is needed, the base material must be mechanically or electrochemically polished first.
6.2 Is electropolishing a type of coating method?
No, it is not. Electropolishing is a surface finishing technique but will not coat a layer on the surface. Instead, it will remove certain material off.
6.3 Which process improves corrosion resistance more: electroplating or electropolishing?
It depends on the material and environment. Electroplating can provide excellent corrosion resistance if using sacrificial or inert coatings.
Electropolishing can enhance the inherent corrosion resistance of metals by removing surface impurities. For stainless steel in clean environments, electropolishing often offers superior long-term performance.
6.4 Can you apply both electroplating and electropolishing on the same part?
Yes. Electropolishing is usually done before plating to ensure a clean and smooth base for better adhesion. But if electropolishing is applied after plating process, the plated layer would dissolve.

Lucas is a technical writer at ECOREPRAP. He has eight years of CNC programming and operating experience, including five-axis programming. He’s a lifelong learner who loves sharing his expertise.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy

What is 5-axis Machining? A Complete Guide.
5-Axis CNC machining is a manufacturing process that uses computer numerical control systems to operate 5-axis CNC machines capable of moving a cutting tool or a workpiece along five distinct axes simultaneously.

Which Country is Best for CNC Machining?
China is the best country for CNC machining service considering cost, precision, logistic and other factors. Statistical data suggests that China emerges as the premier destination for CNC machining.

Top 5 Prototype Manufacturing China
Selecting the right prototype manufacturing supplier in China is a critical decision that can significantly impact the success of your product development project.

CNC Machining Tolerances Guide
Machining tolerances stand for the precision of manufacturing processes and products. The lower the values of machining tolerances are, the higher the accuracy level would be.