Table of Contents
UAV manufacturers operate under strict tolerance, safety, and compliance requirements, where minor CNC machining deviations can cause vibration instability, control failure, or batch rejection, especially when CNC machining parts for uav are required.
As a result, CNC machining UAV components with ISO 9001 certification has become a baseline requirement rather than an optional qualification.
Non-certified suppliers often face issues such as tolerance drift beyond ±0.05 mm, poor process traceability, and rising scrap rates when scaling from prototypes to mass production.
ISO 9001:2015 certified CNC machining services mitigate these risks through standardized quality management systems, documented workflows, mandatory inspection points, and corrective action mechanisms verified by annual third-party audits.
Industry benchmarks indicate that mature ISO 9001 systems can improve machining repeatability by approximately 20–30%.
For UAV projects spanning prototyping, volume scaling, and regulatory audits, ISO-certified CNC suppliers provide predictable quality, traceable documentation, and reduced supply chain risk.
Why UAV Manufacturers Need ISO 9001 Certified CNC Machining Services?
In the realm of UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) component manufacturing, procurement decisions directly impact the final product’s performance and safety.
Manufacturers face stringent tolerance requirements, flight-critical safety risks, and immense compliance pressure.
A minor CNC machining defect—stemming from material issues, process instability, or human error—is enough to trigger vibration instability, control failure, or lead to the rejection of entire assembly batches.
Therefore, selecting a CNC machining supplier with ISO 9001 certification has evolved from a nice-to-have to a critical prerequisite for mitigating UAV CNC manufacturing risks and ensuring supply chain reliability.
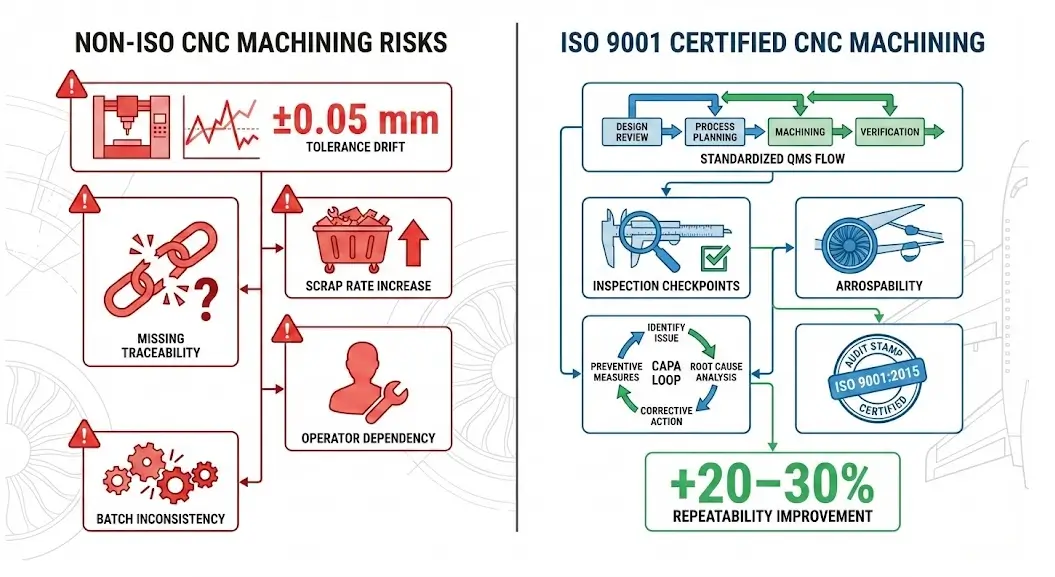
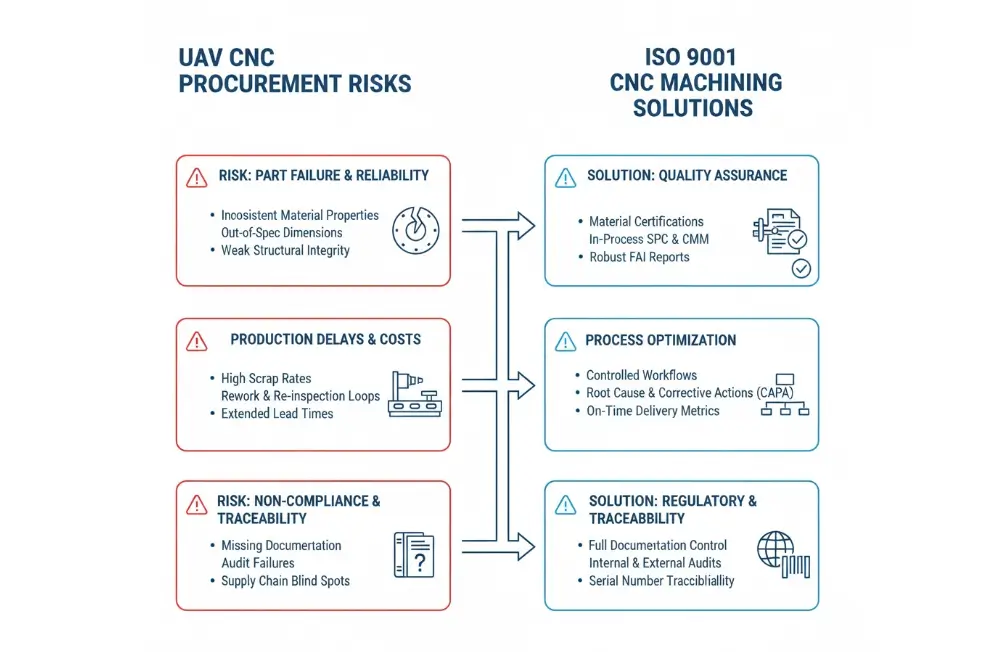
Quality Risks of Non-ISO 9001 Certified CNC Machining in UAV Manufacturing
When a CNC machining supplier lacks the internationally recognized ISO 9001 certification, UAV manufacturers are exposed to systemic quality control vulnerabilities. These risks amplify significantly during the transition from prototyping to mass production:
Inconsistent Machining Tolerances: Precision for critical components (such as rotor hubs and airframe structural parts) may drift beyond the allowable ±0.05 mm range, directly compromising the UAV’s aerodynamic performance and structural integrity.
Lack of Process Control and Traceability: Without documented machining workflows and inspection milestones, it is impossible to quickly isolate the root cause if a failure occurs. Consequently, the quality of precision CNC machining cannot be consistently guaranteed.
High Rework and Scrap Rates: Due to unstable processes during the scaling phase, high frequencies of batch non-conformities significantly drive up costs and delay delivery cycles.
Supplier Dependency and Batch Fluctuations: Quality often relies on the individual experience of specific technicians rather than a standardized system. This leads to inconsistent part quality between different batches, introducing massive uncertainty into UAV assembly.
How ISO 9001 Certification Mitigates Risks in UAV Component CNC Machining?
CNC machining service providers certified under the ISO 9001:2015 standard maintain a comprehensive Quality Management System (QMS) that systematically addresses and controls the aforementioned risks:
Standardized and Auditable QMS: Systematic management ensures every step—from order review and process design to production and final inspection—follows established protocols. These are verified by annual third-party audits to guarantee ongoing effectiveness.
Documented Workflows and Inspection Points: All CNC machining workflows are clearly documented, with mandatory inspection points at key stages. This ensures machining precision is controlled throughout the process, achieving full product traceability.
Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) System: This mechanism ensures that any deviation or defect is systematically analyzed. Root-cause corrective actions are then implemented to prevent recurrence, continuously driving down defect rates.
Supplier Accountability Aligned with Aerospace Expectations: Certification aligns the supplier’s responsibilities with high-stakes industry standards. Through formal contracts and audit mechanisms, it reinforces their commitment to consistent delivery quality.
Authoritative Quantitative Signal: Industry data suggests that implementing a mature ISO 9001 QMS can result in approximately a 20–30% improvement in repeatability (industry benchmark) for CNC machining processes.
This is vital for meeting the UAV industry’s demand for high-quality, high-consistency components.
Common CNC Machining Scenarios in UAV Projects: From Prototyping to Mass Production
For UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) buyers, the requirement extends far beyond finding a simple machine shop.
They are looking for a long-term manufacturing partner capable of full-lifecycle involvement and effective risk control.
This partnership must flexibly navigate the challenges of different stages—from design verification to high-volume delivery—centered on a stable, predictable quality output system.
Below is a deep dive into three critical scenarios.
CNC Machining for UAV Prototypes (Small Batch, Ultra-High Precision)
The core objective of the UAV prototype CNC machining stage is to rapidly achieve design verification and functional testing.
While the part count is low, the requirements for precision and iteration speed are exceptionally high for critical components such as airframes, motor mounts, and sensor housings.
Demand for Rapid Iteration: Designs may undergo multiple revisions. Suppliers must respond quickly to Engineering Change Orders (ECOs) while ensuring machining consistency for each revised version.
Stringent Typical Tolerances: To verify assembly fit and flight performance, prototype parts often require precision CNC machining tolerances of ±0.01–0.03 mm.
The Critical Role of ISO 9001: At this stage, the certification system ensures that the machining process is documented and standardized. This means that even for a “one-off” or a revised part, machining parameters and inspection records are traceable. This guarantees consistency and comparability of results across different iteration batches, providing a reliable data foundation for design decisions.
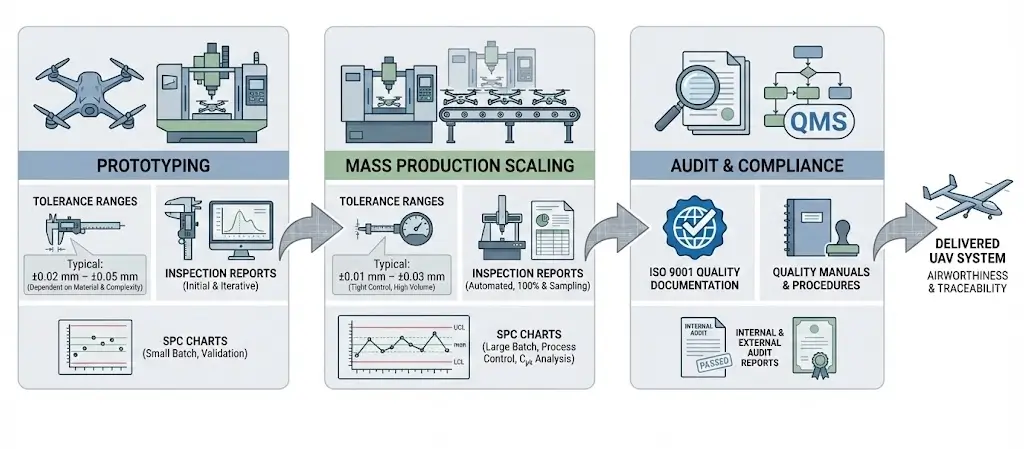
Controlling Quality Drift in Scaled Mass Production
The leap from 50 prototypes to over 5,000 mass-produced units is the stage where UAV CNC manufacturing risks are most concentrated.
A common industry proverb is: “Most UAV quality issues emerge during the scaling phase, not the prototyping phase.
This is because variables such as production tempo, tool wear, multi-batch material differences, and operator consistency are exponentially amplified.
The Scaling Challenge: The balance between cost control, lead times, and quality stability becomes extremely sensitive.
ISO-Controlled Work Instructions and Inspection Plans: Under ISO 9001, standardized Work Instructions (WIs) and Inspection Plans become the “law” of the production line. They ensure every operator and every machine adheres to the exact same quality standard—the cornerstone of process consistency.
Statistical Process Control (SPC) under ISO 9001: The certification system promotes and regulates the continuous monitoring of critical process capabilities. By analyzing machining data in real-time via SPC charts, process anomalies can be detected before a tolerance shift leads to scrap. This shifts the quality paradigm from “after-the-fact inspection” to “proactive prevention,” fundamentally eliminating quality drift.
Supplier Audits and Document Management in UAV Projects
UAV Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) face their own audit pressures from customers and regulatory bodies. Consequently, a CNC supplier’s audit readiness and compliance documentation management directly impact the compliance of the entire project.
Verification of ISO 9001 Scope: It is essential to verify that the supplier’s certification scope explicitly covers precision CNC machining or “aerospace component manufacturing,” rather than just general machining.
Full Material Traceability Records: Suppliers must provide a complete record from the batch number and Material Test Report (MTR) of the raw material (e.g., a specific grade of aluminum ingot) to the finished part. This is the baseline for meeting aerospace-grade quality requirements.
Standardized Inspection Reports: Suppliers should proactively provide critical quality documents, such as First Article Inspection (FAI) reports and Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) reports. These documents serve as objective evidence that parts meet design specifications and are indispensable for the OEM’s incoming inspection and final product certification.
Choosing a CNC machining partner with a mature ISO 9001 system means gaining reliable design verification during prototyping, systemic quality assurance during mass production, and a transparent, auditable document chain throughout the project lifecycle—effectively minimizing supply chain risk.
How to Evaluate ISO 9001 Certified CNC Machining Suppliers for UAV Components?
The core challenge is this: not all ISO 9001 certificates are equal when it comes to superior CNC machining capabilities.
While a certificate proves the existence of a quality system, it is the supplier’s actual machining precision, technical expertise, and production consistency that guarantee the success of a UAV project.
Evaluation must go beyond the document itself, diving deep into the technical prowess and production evidence behind it.
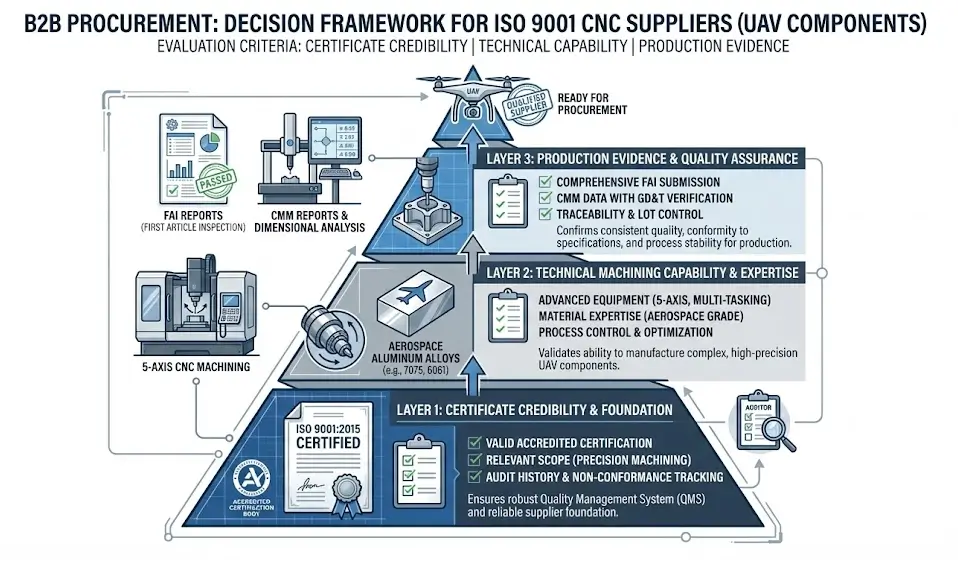
Verifying Authentic CNC Machining Capabilities for UAV Structural Components
When evaluating a supplier, the primary task is to look past the paperwork and scrutinize their technical reserves and process experience.
Equipment and Process Relevance: Explicitly verify the equipment used for UAV aluminum alloy CNC machining. For complex thin-walled parts, integrated frames, and contoured surfaces, 5-axis CNC machining capabilities offer a distinct advantage over standard 3-axis machines by reducing setups and improving overall precision and efficiency.
Aerospace-Grade Material Experience: Confirm they have a mature database of machining parameters (such as cutting speeds, tool selection, and heat treatment deformation control) for common UAV aerospace alloys like 6061-T6 and 7075-T6. Inexperienced suppliers may cause excessive internal stress or micro-cracks in the parts.
Verification of Key Quality Indicators: Directly inquire about their ability to control surface finish (e.g., requiring Ra ≤ 1.6 μm to minimize fatigue points) and ask for an explanation of their process measures for maintaining tolerances (such as temperature compensation and tool wear monitoring). This is a direct reflection of precision CNC machining competence.
Digging Deeper into the ISO 9001 Certificate (Beyond the Logo)
An authoritative certificate is the starting point of trust, but the details determine its true “weight.”
Credibility of the Certification Body: Preference should be given to certificates issued by top-tier international bodies such as TÜV (Germany), SGS (Switzerland), or BSI (UK), as their audits are typically more rigorous.
Precision of the Certification Scope: Ensure the Scope of Certification in the annex explicitly includes terms like CNC Machining or Aerospace Component Manufacturing, rather than vague descriptions like General Metal Processing.This directly correlates to the auditor’s depth of understanding of the specialized field.
Ongoing Validity of the Certificate: Verify the expiration date and confirm the supplier can provide recent surveillance audit reports. Continuous ISO 9001:2015 certification and regular annual audits indicate that their quality management system is dynamically operating and continuously improving, rather than just a “set it and forget it” document.
Production Evidence Required by Procurement Teams
Ultimately, trust is built on objective evidence. Before making a final decision, request and evaluate the following:
Real-World UAV Case Studies: Request anonymous case studies of previously manufactured components such as UAV airframes, landing gears, or payload bays to understand their end-to-end solutions from blueprint to delivery.
Verifiable Dimensional Inspection Reports: Ask for First Article Inspection (FAI) reports and CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) reports for typical parts. Directly reviewing the measurement data against drawing tolerances is the most objective proof of machining capability.
Long-Term Customer References in UAV or Aerospace: The existence of long-term partners is the strongest signal that a supplier’s quality, delivery, and service reliability have stood the test of time.
In the highly specialized world of aerospace CNC machining, The certificate opens the door, but the production data wins the trust.
A robust ISO 9001 system is the essential foundation, but it must be combined with cutting-edge equipment, professional material knowledge, and a traceable record of excellence to be a truly reliable UAV manufacturing partner.
Common CNC Machining Materials, Tolerances, and Standards for UAV Components
The flight performance, endurance, and reliability of a UAV are fundamentally rooted in two physical pillars: Material Selection and Machining Precision. The correct material determines the part’s strength-to-weight ratio and environmental adaptability, while stringent tolerance control directly impacts assembly consistency, aerodynamic efficiency, and flight stability. Below is a guide to the key specifications for UAV manufacturing.
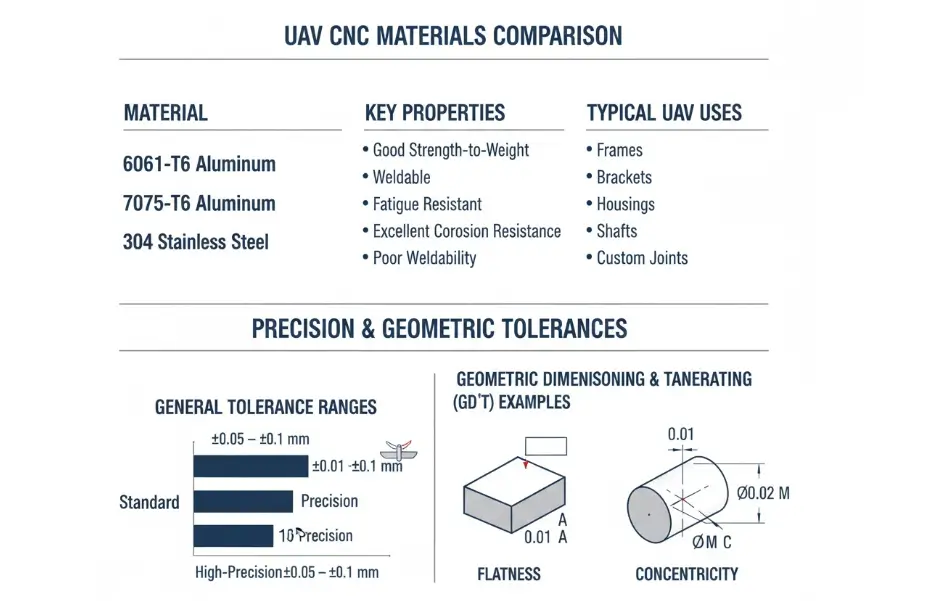
Common CNC Machining Materials for UAV Components
Material selection is the starting point of design and manufacturing, directly balancing weight, strength, cost, and machinability.
Aluminum 6061-T6: This is the most widely used structural material in the UAV industry. It offers a good strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, superb machinability, and high cost-effectiveness. It is ideal for CNC precision machining of lightweight structural components such as airframe frames, housings, and brackets.
Aluminum 7075-T6: An aerospace-grade high-strength aluminum alloy with strength comparable to many steels but at a fraction of the weight. It is primarily used for critical load-bearing components subject to high stress, such as motor mounts, landing gear, and rotor head connectors. While its machining difficulty and cost are higher than 6061, it is essential for enhancing overall aircraft performance.
Optional Material: Stainless Steel: Used primarily for specialized components requiring extreme hardness, wear resistance, and vibration fatigue resistance, such as engine test fixtures, high-load hinges, or specific sensor mounts. However, its high density limits its widespread use in the primary airframe structure.
Typical CNC Machining Tolerances for UAV Applications
In the UAV sector, the core value of precision CNC machining is demonstrated through the pursuit of extreme tolerances. Tolerance requirements are typically strictly graded based on the component’s function.
General Structural Tolerances: For non-critical support structures or external covers, typical machining tolerances are maintained within ±0.05 mm. This ensures smooth assembly and basic structural integrity.
Critical Functional Part Tolerances: For high-precision UAV components that directly affect flight performance—such as motor mounts, servo linkages, and optical payload platforms—tolerances for mating surfaces and locating holes are extremely strict, usually requiring ±0.01–0.02 mm. This is vital for ensuring powertrain alignment and precise control response.
The Criticality of GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing): Compared to linear dimensions, geometric tolerances such as flatness, concentricity, and perpendicularity have a more direct and significant impact on flight stability. For example, poor flatness on a motor mounting surface causes off-axis vibration, while concentricity errors in a rotor hub can trigger resonance. Therefore, technical drawings and machining for high-precision UAV parts must specify these geometric features, often requiring control within a few hundredths of a millimeter.
Successful UAV CNC machining begins with a deep understanding and correct selection of aerospace-grade aluminum alloys, eventually manifesting in a rigorous tolerance system that spans design, programming, and manufacturing.
Choosing an ISO 9001 certified supplier who can not only process these materials but also consistently achieve these micron-level accuracies and critical geometric tolerances is the decisive step in transforming a design blueprint into a reliable aircraft.
Why Scenario-Based CNC Content Wins UAV Procurement Trust?
Procurement decisions for UAVs—especially industrial and military-grade models—are essentially risk-driven, not price-driven.
A buyer’s top priority is not the lowest quote, but rather how to minimize the risk of project failure, such as delivery delays, batch rejections, or flight accidents.
In this context, ISO 9001 certification serves as a critical risk filter rather than just a marketing label.
Scenario-based content is persuasive because it speaks directly to the buyer’s deep-seated anxieties regarding potential risks and provides clear, systemic solutions.
Reducing Supplier Risk in UAV CNC Projects
A CNC machining partner strictly vetted through the ISO 9001 framework translates their predictable and traceable management processes directly into project management certainty and cost control.
Minimizing Production Delays: Standardized operating procedures (SOPs) and preventive maintenance schedules ensure stable execution of production plans. Clear change control and supply chain management effectively prevent unexpected shutdowns caused by material shortages or process confusion.
Lowering Rejection Rates and Rework Costs: End-to-end quality monitoring—from First Article Inspection (FAI) to Statistical Process Control (SPC)—ensures consistency in part quality. For the UAV OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer), this means a higher pass rate during incoming inspections, significantly reducing emergency handling, sorting, or rework costs on the assembly line.
Predictable Long-Term Quality Performance: The management review and continuous improvement mechanisms required by the certification mean a supplier’s quality level is not static; it is constantly evolving within a controlled framework. This gives procurement teams confidence in long-term stability, protecting them from the uncertainty of fluctuating performance over time or increasing order volumes.
Aligning CNC Partners with UAV Industry Compliance Expectations
For UAV manufacturers targeting regulated markets (such as North America and Europe), they must satisfy rigorous aviation or industry-specific certification requirements.
Their suppliers—especially those providing critical structural components—must possess a matching foundation of compliance.
Streamlining Supplier Onboarding for Regulated UAV Projects: A functional, well-maintained ISO 9001 system means the supplier already has a complete management framework in place. This drastically reduces the time required for second-party audits or for including them in a “Qualified Supplier List” (QSL).
Ensuring Smoother Internal Approvals and External Audits: When a procurement team recommends a supplier with a mature quality system, internal engineering, quality, and compliance departments can proceed with higher confidence. During audits from end-customers or regulatory bodies, the supplier can readily provide standardized, traceable quality record sets, significantly mitigating audit risks.
Instilling Confidence for International Supply Chain Entry: For UAV OEMs looking to export to the U.S., EU, or other global markets, supply chain compliance is a prerequisite for market entry. A CNC machining partner with internationally recognized certification is a solid piece of the compliance puzzle, providing a vital foundation for global market expansion.
Scenario-based content is effective because it transforms the abstract concept of ISO 9001 certification into concrete solutions for the daily challenges buyers face.
It sends a clear message: choosing a certified partner is choosing manageable risk, predictable project outcomes, and a compliant path toward more demanding markets and more reliable products.
This is not just about part quality; it is about the very foundation of the UAV project’s success.
Conclusion
In UAV manufacturing, supplier selection is fundamentally risk-driven rather than price-driven.
ISO 9001 certified CNC machining enables consistent control over materials, tolerances, and process stability across the full product lifecycle.
From prototype stages requiring ±0.01–0.03 mm precision to mass production runs exceeding thousands of units, ISO-controlled work instructions, inspection plans, and SPC monitoring help prevent quality drift.
Certification also ensures audit readiness through material traceability records, FAI and CMM reports, and documented corrective actions.
While an ISO 9001 certificate alone does not guarantee machining capability, suppliers combining certified systems with aerospace-grade materials such as 6061-T6 and 7075-T6 and verified production data are better positioned to meet UAV performance and compliance expectations.
In practice, ISO 9001 transforms CNC machining from reactive inspection into proactive risk prevention.

Lucas is a technical writer at ECOREPRAP. He has eight years of CNC programming and operating experience, including five-axis programming. He’s a lifelong learner who loves sharing his expertise.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy

What is 5-axis Machining? A Complete Guide.
5-Axis CNC machining is a manufacturing process that uses computer numerical control systems to operate 5-axis CNC machines capable of moving a cutting tool or a workpiece along five distinct axes simultaneously.

Which Country is Best for CNC Machining?
China is the best country for CNC machining service considering cost, precision, logistic and other factors. Statistical data suggests that China emerges as the premier destination for CNC machining.

Top 5 Prototype Manufacturing China
Selecting the right prototype manufacturing supplier in China is a critical decision that can significantly impact the success of your product development project.

CNC Machining Tolerances Guide
Machining tolerances stand for the precision of manufacturing processes and products. The lower the values of machining tolerances are, the higher the accuracy level would be.


