Table of Contents
CNC prototyping, which uses computer-controlled machines to turn CAD designs into precise parts, can range anywhere from $50 to $500+ per piece depending on material, complexity, and quantity.
Simple plastic prototypes are generally the most affordable, costing around $50–$150, while aluminum parts can run $150–$400, and stainless steel prototypes may exceed $500.
Factors such as machine time, labor, post-processing, batch size, and lead time all influence the final price.
Understanding these variables helps you plan your budget and choose the most efficient approach for your prototype needs.

What Is the Typical Cost of CNC Prototyping?
CNC prototyping creates one – off or small – batch parts via CNC machining before mass production. Costs vary by material, complexity, and batch size.
For engineers, designers, and procurement managers, knowing typical costs aids budget planning and quote negotiation.
Most prototypes cost $50 – $500 per part, but complex or high – precision metal ones can be over $800 – $1,500. A simple plastic prototype is $50 – $150, aluminum $120 – $400, stainless steel $300 – $800, and multi – axis complex parts $800+.
Setup costs for one – off parts are 30 – 50% of total cost, and regional labor and material prices impact final quotes.
1.Average CNC Prototyping Cost by Material and Complexity
| Material / Part Type | Typical Cost Range (USD) |
|---|---|
| Simple plastic part (ABS, Nylon) | $50–$150 |
| Aluminum CNC prototype | $120–$400 |
| Stainless steel (304, 316) | $300–$800 |
| Complex multi-axis parts | $800+ |
These figures are based on real-world quotes from North American and Asian CNC job shops between 2023–2025.
Keep in mind that the final quote depends not just on material, but on part geometry, tolerances, machining time, and batch size.

2.Why CNC Prototypes Cost More Than Production Parts?
Prototyping inherently carries a higher unit cost because:
- Setup costs are amortized over fewer parts
- Programming and fixture creation time is significant
- Materials are often bought in small quantities
In industry practice, setup costs alone can account for 30–50% of the total prototype price for one-off parts.
Key Factors That Influence CNC Prototyping Pricing
CNC prototyping pricing is affected by multiple factors like material, part geometry, tolerances, machining time, batch size, and finishing/certification needs.
1.Material Selection and Raw Material Cost
Material choice is one of the largest contributors to CNC prototype cost:
- Aluminum (6061, 7075): widely used, machinable, cost-efficient
- Stainless steel (304, 316): more expensive, higher tool wear, longer machining times
- Engineering plastics (ABS, POM, Nylon): lower cost, faster turnaround, ideal for functional testing
In practice, selecting aluminum over stainless steel for a functional prototype can reduce cost by 2–3×, especially for medium-complexity parts.
2.Part Complexity and Geometry
The more complex a part, the higher the cost:
- Deep cavities, thin walls, and undercuts require additional tooling
- Internal features may necessitate multi-axis machining
- 3-axis machining is cheaper than 4-axis or 5-axis operations
More tool changes and longer tool paths = higher CNC prototype cost. Complexity often adds 20–60% to base machining rates.
3.Tolerance Requirements and Precision Standards
Tighter tolerances significantly increase cost:
- Standard tolerance: ±0.1 mm – cost-efficient for most prototypes
- Tight tolerance: ±0.01 mm or tighter – requires advanced equipment, inspection, and often specialized tooling
Parts adhering to ISO 2768-f or equivalent high-precision standards can see a 30–60% cost increase over standard tolerances.
4.Machining Time and CNC Setup Cost
Machining time is directly correlated to cost:
- Programming & CAM setup: 1–3 hours for typical prototypes
- Fixture and setup: may involve custom jigs
- Machine runtime: $40–120/hour depending on CNC type and region
For a single aluminum part, setup can be $100–$150, while machining time may add $200–$250, forming the bulk of the cost.
5.Order Quantity: One-Off vs Small Batch
- 1–2 pcs: highest unit cost due to setup amortization
- 5–20 pcs: setup cost distributed over more units, reducing per-piece cost
- 50+ pcs: approaching low-volume production cost levels
6.Additional Factors
- Finishing requirements: anodizing, plating, or polishing can add $50–$150
- Inspection and certification: ISO 9001 or AS9100 compliance can add 5–10%
- Geographical location: labor and electricity costs vary across regions
Understanding these helps with cost prediction and design optimization.
The main cost drivers are materials, complexity, tolerances, setup, machining time, and order quantity.
Material selection can triple costs. Tighter tolerances (±0.01 mm) may hike costs by 30 – 60%.
Multi – axis machining can raise machining time and cost by 20 – 60%.
Aluminum 6061 and Stainless Steel 304 have a cost difference of $100 – $300.
ISO 2768 – f tolerances add 30 – 60% to cost.
Setup + programming can be 30 – 50% of one – off prototype cost.
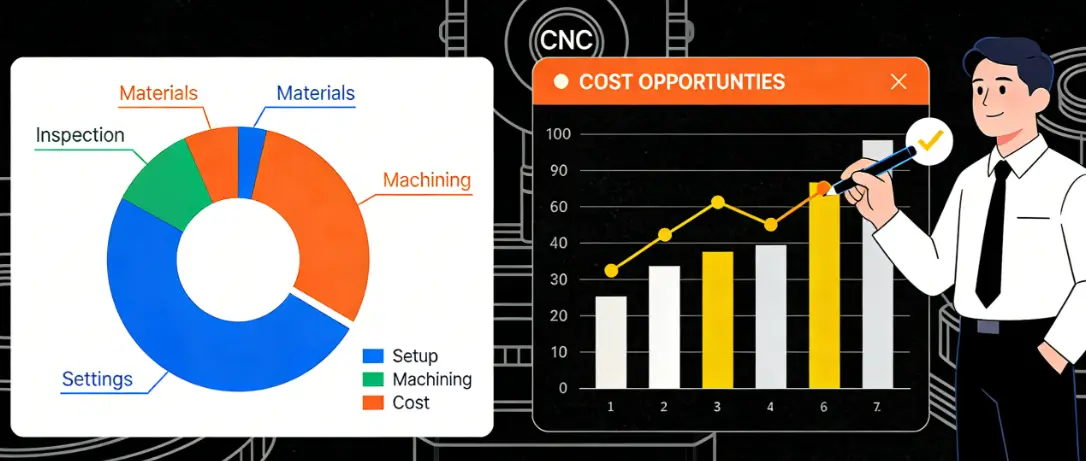
CNC Prototyping Cost Breakdown Example
A cost breakdown illustrates how different components—such as material, setup, machining, and inspection—contribute to the total pricing of CNC prototypes.
Understanding this breakdown provides clarity to procurement managers by showing where money is being spent and highlighting opportunities for cost reduction.
1.Aluminum Prototype Example (Single Part)
| Cost Component | USD |
|---|---|
| Material (Al 6061) | $25 |
| Programming & Setup | $120 |
| Machining Time (2.5 hrs) | $200 |
| Quality Inspection | $40 |
| Total | $385 |
2.Stainless Steel / Multi-Axis Prototype Example
| Cost Component | USD |
|---|---|
| Material (SS 304) | $80 |
| Programming & Setup | $150 |
| Machining Time (5 hrs) | $500 |
| Quality Inspection | $60 |
| Total | $790 |
For example, typical cost distributions can be seen in aluminum and stainless steel prototypes.
An aluminum part may cost $25 for material, $120 for setup, $200 for machining, and $40 for inspection, totaling $385.
In contrast, a stainless steel multi-axis prototype could cost $80 for material, $150 for setup, $500 for machining, and $60 for inspection, totaling $790.
Generally, machining time accounts for roughly 50% of the cost for complex parts, setup costs dominate single or small-batch runs, and inspection usually adds $40–$60 per prototype.
How to Reduce CNC Prototyping Costs Without Sacrificing Quality?
Cost reduction strategies for CNC prototyping focus on design optimization, material substitution, and tolerance adjustment. Implementing these strategies early helps reduce costs without compromising functionality, which in turn accelerates prototyping cycles and minimizes wasted resources.
1.Design for Manufacturing (DFM) Tips
- Avoid unnecessary tight tolerances
- Reduce deep pockets and thin walls
- Use standard hole sizes and radii
Experience insight: Following DFM rules can reduce CNC prototyping cost by 15–30% without affecting part functionality.
2.Material Alternatives
- Aluminum instead of stainless steel for early prototypes
- Engineering plastics for fit/form testing before metal machining
For functional validation, less expensive materials often suffice, reserving high-cost materials for final verification.
Following Design for Manufacturing (DFM) guidelines, selecting cost-effective materials, and avoiding over-specifying tolerances are key practices.
For instance, adhering to DFM principles can lower costs by 15–30%, substituting aluminum for stainless steel can reduce material costs by 2–3 times, and using plastics for early-stage prototypes can cut costs by 50–70%.
Practical considerations include avoiding deep pockets and thin walls, standardizing hole sizes and radii, and selecting materials suitable for testing rather than final production.
CNC Prototyping vs Production Machining
CNC prototyping and production machining differ significantly in cost structure, quantity, and purpose.
Buyers often misjudge why prototypes cost more per unit than mass-produced parts, but the distinction lies in the allocation of time and resources.
Prototypes are typically more expensive per unit because setup and engineering time dominate the cost, whereas production parts benefit from tooling amortization.
1.Why Prototypes Cost More Per Unit ?
- No tooling amortization
- Higher setup-to-part ratio
- Programming and engineering time included
CNC prototyping is about speed, flexibility, and validation, not unit cost optimization.
For example, a one-off prototype setup can account for 30–50% of the total cost, while production units spread setup costs across multiple parts, reducing per-unit costs by 50–80%.
CNC prototyping prioritizes flexibility and speed over per-unit savings.
Key considerations include the lack of tooling amortization for prototypes, a higher setup-to-part ratio, and the inclusion of engineering and programming time in overall costs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1.Why Do CNC Prototype Quotes Vary So Much Between Suppliers?
- Machine capability differences
- Labor rates and regional costs
- Quality standards (ISO 9001, AS9100)
2.Is CNC Prototyping More Expensive Than 3D Printing?
- CNC provides higher precision and stronger, real-material parts
- 3D printing is cheaper but limited in strength and finish
3.How Can I Quickly Get an Accurate Quote?
- Provide detailed CAD files
- Specify materials, tolerances, and batch size
- Include surface finish and certification requirements
4.Are There Hidden Costs in CNC Prototyping?
- Additional finishing
- Inspection and quality control
- Shipping for international orders
When Does CNC Prototyping Make Financial Sense?
CNC prototyping is ideal for validating designs, testing fit and function, and supporting early-stage iterations.
This process helps engineers avoid costly mistakes during full-scale production by providing tangible, testable parts before committing to large-scale manufacturing.
CNC prototypes are especially useful for functional testing, assembly checks, and producing low-volume end-use parts.
They prevent rework and production failures, allow real-material validation before significant investments, and support iterative design improvements.
1.Best Use Cases
- Functional testing
- Fit and assembly validation
- Low-volume end-use parts
- Rapid iteration before production
Skipping CNC prototyping often leads to higher costs during full-scale production due to rework or failed parts.
Primary use cases include functional testing and fit validation, while rapid iteration cycles help shorten product development timelines.
Additionally, producing low-volume end-use parts via prototyping offers a cost-effective solution compared with full-scale production.
Conclusion: Understanding Costs to Make Smart Decisions
CNC prototyping is a strategic investment.
By understanding:
- Material choice and machining complexity
- Tolerances and precision standards
- Batch size and setup cost
Engineers and procurement managers can estimate fair prices, reduce waste, and make faster design decisions.

Lucas is a technical writer at ECOREPRAP. He has eight years of CNC programming and operating experience, including five-axis programming. He’s a lifelong learner who loves sharing his expertise.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy

What is 5-axis Machining? A Complete Guide.
5-Axis CNC machining is a manufacturing process that uses computer numerical control systems to operate 5-axis CNC machines capable of moving a cutting tool or a workpiece along five distinct axes simultaneously.

Which Country is Best for CNC Machining?
China is the best country for CNC machining service considering cost, precision, logistic and other factors. Statistical data suggests that China emerges as the premier destination for CNC machining.

Top 5 Prototype Manufacturing China
Selecting the right prototype manufacturing supplier in China is a critical decision that can significantly impact the success of your product development project.

CNC Machining Tolerances Guide
Machining tolerances stand for the precision of manufacturing processes and products. The lower the values of machining tolerances are, the higher the accuracy level would be.


