Table of Contents
There are usually tooling marks for as machined CNC parts. To achieve smooth and clean surfaces, it is required to polish the parts. Compared with mechanical polishing, magnetic polishing can polish precision parts well without dimensional and geometric changes as well as surface hardening.
The article will provide a detailed guide for magnetic polishing.
Key Takeaways:
- Magnetic polishing excels at finishing parts with intricate geometries (like internal holes, threads, and blind spots) that are difficult for traditional methods to reach.
- The choice of magnetic abrasive media (pins)—based on their shape, material, size, and length—directly determines the finish quality and suitability for a part.
- A magnetic polishing machine is an integrated system with precise controls. Its core is a magnetic field system (permanent or electromagnetic) that drives the media, combined with specialized fixtures and often CNC-driven part movement, allowing for automated, consistent, and efficient polishing.
1. What is Magnetic Polishing?
Magnetic polishing, also known as magnetic fluid polishing or magnetic abrasive finishing, is a precision finishing process that utilizes magnetic field energy to drive abrasive media, typically magnetic steel pins or similar abrasive particles, to deburr and clean the surfaces.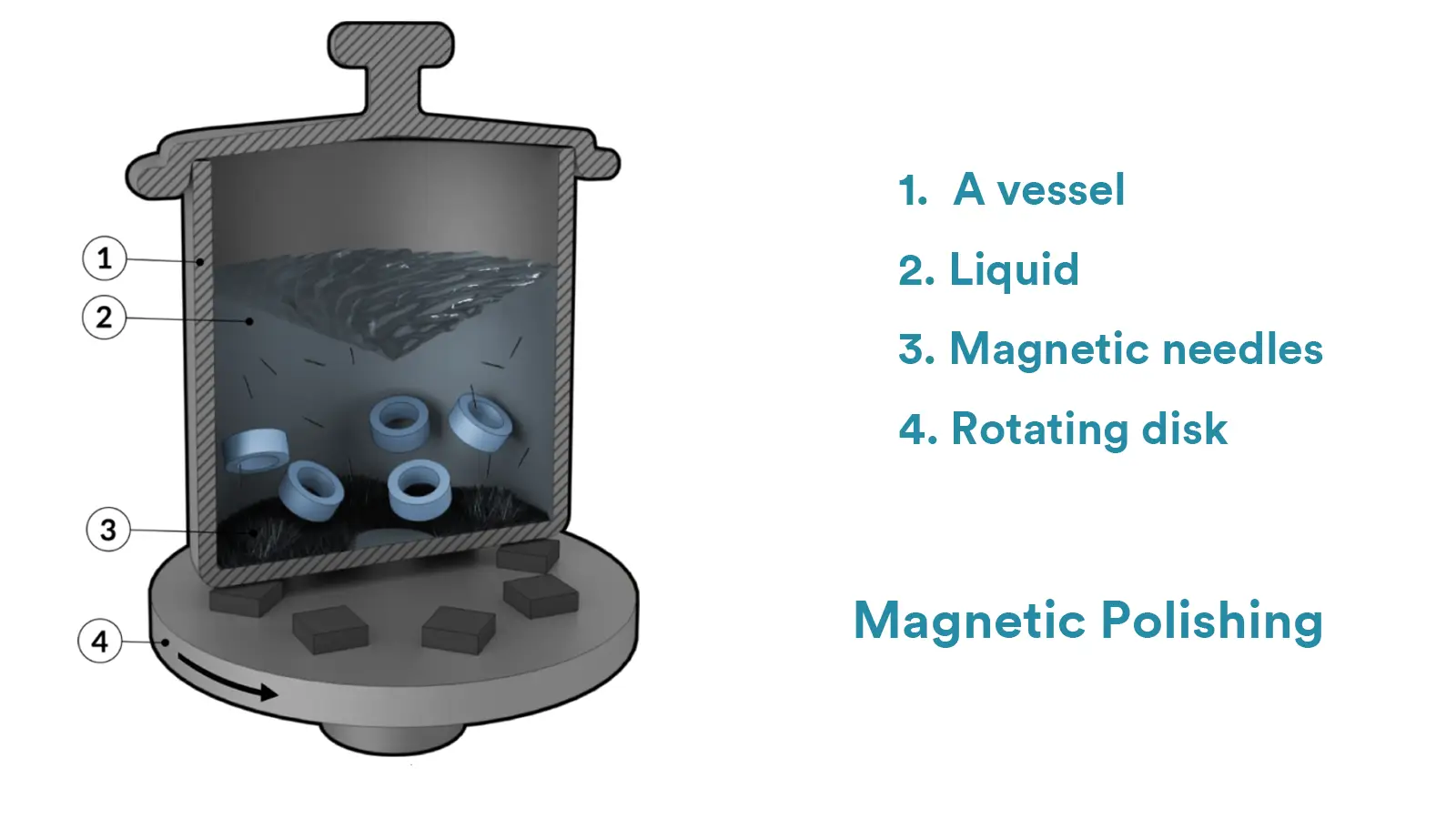
Through magnetic induction, the media can flexibly brush parts with complex geometries, blind spots, and certain areas that are hard to reach.
The core working principle of magnetic polishing lies in the interaction between the magnetic field and the abrasive media.
There would be powerful magnets installed beneath the rotating base of a magnetic polishing machine, typically neodymium iron boron permanent magnets.
Driven by a motor, the base rotates at high speed and then an alternating rotating magnetic field would be generated.
And the finishing chamber is filled with water, polishing compound, and specially designed stainless steel magnetic pins.
Under the influence of the magnetic field, these pins would rapidly rotate, tumble, and oscillate within the liquid like countless tiny brushes.
They would continuously impact and rub against the parts during high-speed motion to remove burrs, oxides, and bright the surfaces.
More importantly, they can reach internal holes, blind spots, narrow gaps, and contoured surfaces from all directions.
Therefore, magnetic polishing can effectively clean precision parts with complex geometries and meanwhile maintain their shapes and dimensions.
And it would not harden the parts or introduce residual stresses that mechanical polishing would.
Magnetic polishing is suitable for small precision parts and can provide high efficiency and excellent polishing performance.
2. What are the Types of Magnetic Abrasive Media?
Unlike conventional vibratory finishing or barrel tumbling processes, magnetic polishing primarily relies on magnetic stainless-steel pins. Depending on its material, shape, and size, the abrasive media has a direct impact on the surface finish quality.
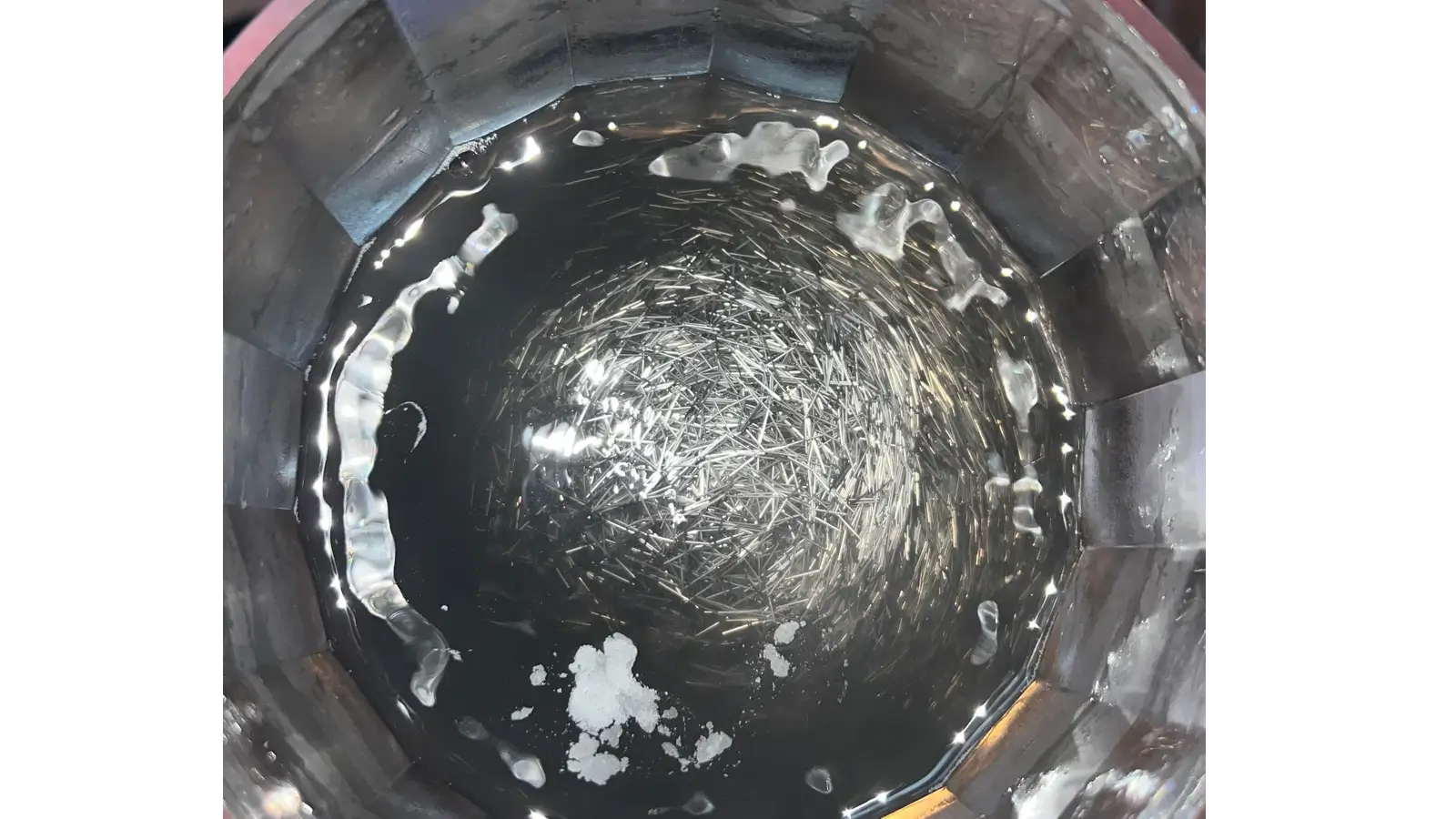

2.1 Classification by Shape
- Flat End Pins: They are the most common type for general deburring, oxide removal, and initial polishing, with strong cutting capability.
- Ball End Pins: Their ends are chamfered roundly, which can reduce the impact marks by pins on the surfaces. They are more suited for high-precision components and jewelry since they can achieve finer and more uniformluster without pitting or dimples.
2.2 Classification by Material
- SUS420 Stainless-Steel Pins:
With excellent magnetism and hardness, their impact and cutting force are strong and lasting. Their polishing efficiency is high.
But they are generally more expensive than SUS430 stainless steel. Due to their higher hardness, improper control of polishing time may result in tiny pitting marks on the surface
. They are suitable for deburring and polishing hard materials.
- SUS430 Stainless-Steel Pins:
They offer a similar magnetic property to that of SUS420 stainless steel. However, their hardness is slightly less than that of SUS420 stainless steel.
With milder impacting action, they are more suited for softer materials and precision parts. And their corrosion resistance is a few better than that of SUS420 stainless steel.
However, their polishing efficiency is lower for large burrs. In addition, they are easier to wear.
- Composite Abrasive Media:
Some specialized stainless-steel pins would be coated with ceramic or diamond powders for stronger cutting action to extremely hard materials.
2.3 Classification by Size
- 2-0.3mm Diameter Pins: With strong penetration capability, they are able to reach extremely small blind holes. But their polishing force is relatively light. They are suitable for fine gaps, jewelry, and precision electronic connectors.
- 5mm Diameter Pins: 0.5mm is the most common diameter size for magnetic stainless-steel pins. Balancing the cutting force and the ability to access narrow gaps, they are commonly used for aluminum or copper die-cast parts andmedical devices.
- 8-1.2mm Diameter Pins: With strong force and high efficiency, they are used for heavy burrs and large parts. But they are unable to enter very fine hole or narrow crevices.
Note: The common lengths are typically 3mm, 5mm, and 10mm. The shorter pins are more flexible while the longer pins have greater mass and deliver stronger force.
Polishing compounds are mainly used for lubrication, cleaning, and brightening. They can reduce dry friction between pins, as well as between the pins and the parts.
Additionally, they can also quickly encapsulate and carry away removed metal fines to prevent secondary contamination. And they usually contain chemical brightening agents for mirror-like finish.
2.4 Practical Tips
- The diameter of the pins must never be equal to that of the holes.
For example, if the hole diameter is 0.5 mm, it is recommended to use 0.3 mm or 0.8 mm pins. Otherwise, the pins may become firmly lodged in the hole and be difficult to remove.
- There might be residualoil or fine metal debris on the surfaces of the pins. It is recommended to run the machine with only polishing compounds for 10 to 15 minutes to clean the pins. Once the liquid becomes clear, the pins are ready for actual processing.
- For parts with complex geometries, it is recommended to mix differentpins for balance of cleaning effectiveness and efficiency.
3. What are the Components of a Magnetic Polishing Machine?
A magnetic abrasive polishing machine is an integrated system for magnetic polishing processes. It utilizes a controlled magnetic field to drive magnetic abrasive media, allowing for flexible and non-contact interaction with the surfaces.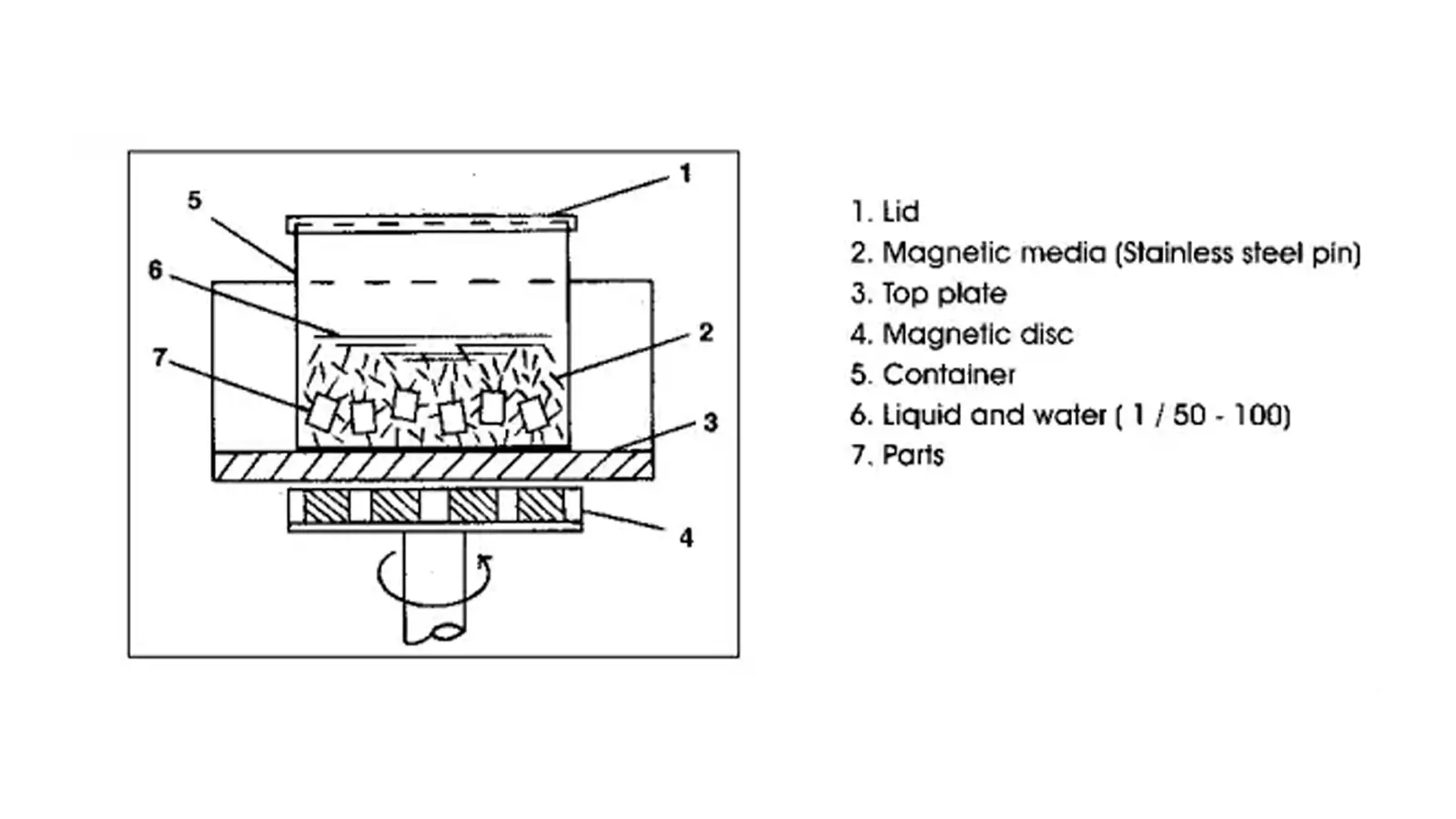
It is well-suited for deburring, surface finishing, and mirror polishing of precision components.
The machine overly consists of core functional modules as well as supporting and auxiliary systems.
3.1 The Main Housing
Typically constructed from cast iron, steel frames, or aluminum alloys to ensure sufficient rigidity and effective vibration damping, the main housing provides the structural support, alignment, and overall protection for the machine.
It has both open-frame type and fully enclosed type. The former is designed for easy loading and unloading of parts while the latter is for dust containment, noise reduction, and operation safety.
Some models are equipped with transparent viewing windows for real-time monitoring of the polishing process.
3.2 The Magnetic Field System
As the power source of a magnetic polishing machine, it directly determines the motion behavior of the abrasive media and the overall polishing capability.
The magnetic field primarily consists of two types of magnetic sources. One is a permanent-magnet type, and the other is an electromagnetic type.
The permanent-magnet type utilizes high-quality NdFeB magnet blocks as the magnetic source. It does not require external power supply, so its cost is relatively low. And its structure is simple.
But its magnetic field strength is fixed and difficult to adjust.
The electromagnetic type takes an iron mandrel around with copper coils as the magnetic source. It would produce a magnetic field once when energized.
Since its magnetic field strength can be precisely controlled by adjusting the current and its magnetic field type covers alternating, rotating, and pulsed one, it is suitable for high-precision and multi-process CNC polishing machines.
But it requires a cooling system to prevent coil overheating.
In addition, the configuration of magnetic pores is various for different requirements.
Parallel pole pairs are used for flat surface or external cylindrical surface.
Rotating pole pairs make the magnets rotate around the part to provide a dynamic magnetic brush. They are commonly applied in polishing tubes and internal bores.
Multi-pole arrays can increase the magnetic field gradient and enhance abrasive retention and cutting efficiency.
Adjustable-gap poles are used for parts of different sizes and geometries.
3.3 The Abrasive Media Handling System
It consists of three parts, including media hopper, distribution system, as well as recovery and screening
The media hopper is used for storage of magnetic abrasive media, typically positioned above or beside the processing zone. It supports manual loading or automatic feeding, depending on machine configuration.
The media distribution system ensures uniform coverage of abrasive media over the surfaces through vibration, airflow, or mechanical conveying. For internal bores, the abrasive media are directly filled into the holes.
The recovery and screening system uses magnetic attraction or screening meshes to separate abrasive media and debris after polishing. The residual media can be reused for lower cost. And some machines integrate automatic recovery pipelines and dust collection units.
3.4 The Holding and Driving System
Consisting of fixtures and driving mechanism, it determineshow the parts relatively reacted with the magnetic abrasive media.
The fixtures must be comprised with non-magnetic materials such as aluminum, copper 304/316 stainless steel, or engineering plastics. They ensure the parts remain within the effective magnetic field. And specific fixtures can be designed for complex or irregular components.
The driving mechanism includes spindle motor, vibratory platform, linear driving mechanism, and multi-axis CNC mechanism.
The spindle motor can drive the parts rotating with adjustable speed ranging from 50 to 300 rpm. The vibratory platform is used for flat surfaces, operating at 10 to 100 Hz.
And the linear driving mechanism controls axial movement of the parts, suitable for long tubes and bar stocks. The multi-axis CNC mechanism coordinates three dimensional rotary axes, enabling polishing of complex freeform surfaces.
3.5 The Control System
It enables process parameter setup, operational monitoring, and automated operation of the magnetic abrasive polishing machine.
The PLC serves as the core control unit. And the touchscreen control panel is for setting rotation speed, processing time, magnetic field strength, and other parameters. The power supply provides stable and adjustable current for electromagnetic system.
3.6 The Auxiliary and Safety System
It includes cooling or lubrication system as well as dust collection and ventilation system.
The cooling or lubrication system provides spray cooling, oil mist lubrication, or compressed-air blowing to prevent abrasive agglomeration and reduce heat.
The dust collection and ventilation system would capture metal dust and fine abrasive particles generated during polishing.
4. What are the Processes of Magnetic Polishing?
Step 1: Clean any dust, oil, and grease away from the surface.
Step 2: Choose the right abrasive media and polishing compounds based on the material and polishing requirements.
Step 3: Load the magnetic pins, CNC machined parts, water, and polishing compound into the polishing barrel according to the specified ratio.
Step 4: Set the proper magnetic field strength and polishing time.
Step 5: Check the protective measures of the machine for operation
Step 6: Turn on the machine. The parts would be uniformly polished by the abrasivemedia within the magnetic field.
Step 7: Turn off the machine after polishing and separate the magnetic pins from the parts by a sieve or a magnet. And then clean the parts completely.
5. What are the Pros and Cons of Magnetic Polishing?
5.1 Advantages of Magnetic Polishing
- No Dead Zones:
Magnetic polishing can effectively process parts with various complex geometries such as internal holes, threads, and gaps.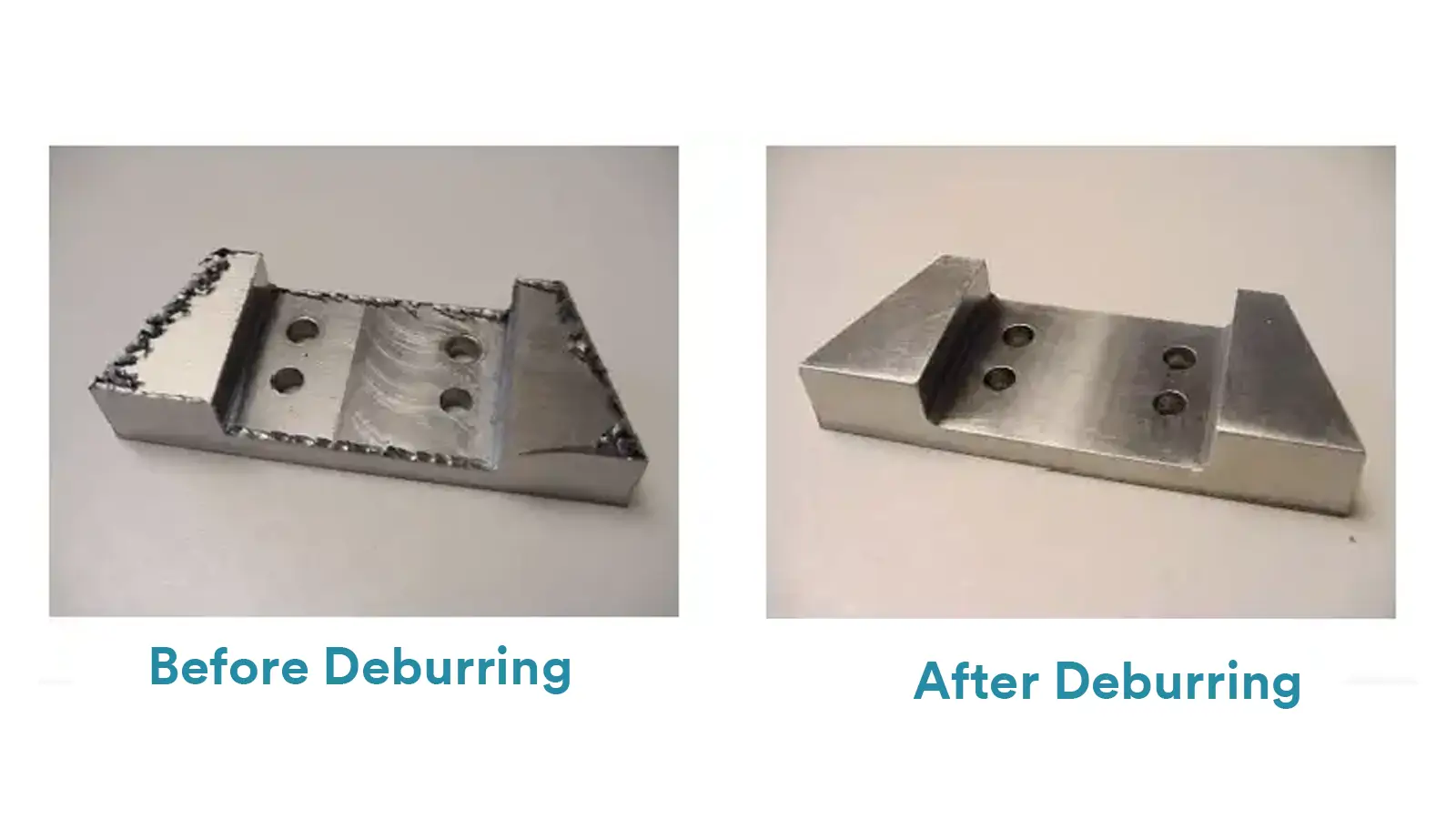
- No Mechanical Damages:
There are no rigid tools that directly contact the part’s surface, so magnetic polishing does not lead to deformation, scratches, or residual stresses that can occur with conventional mechanical polishing.
- High Efficiency:
A single polishing cycle can be completed in just 5 to 20 minutes, and the process supports batch processing.
- Easy Operation:
The whole process is highly automated and relatively simple to operate.
5.2 Disadvantages of Magnetic Polishing
- Limited Deburring:
Magnetic polishing is well-suited for removing fine machining burrs left by CNC cutting; however, for larger and harder burrs, its effectiveness is generally inferior to that of mechanical polishing or vibratory polishing.
- Limitation on Dimension:
Magnetic polishing is typically suitable for small or medium-sized precision parts due to the magnetic field range and polishing chamber size. Extremely large parts cannot be polished using magnetic polishing.
- High Cost:
The initial investment in magnetic polishing equipment is high.
6. What are the Common Applications of Magnetic Polishing?
- Aerospace and Defense:
Magnetic polishing is commonly used for turbine blades, precision aerospace bolts, complex hydraulic valve blocks, engine micro-tubes.
These components often have thin-walled and high-precision structures. Magnetic polishing can reach extremely narrow gaps between blades and uniformly remove surface burrs and unevennesswithin dimensional tolerances.
- Medical Devices:
Magnetic polishing is often applied to orthopedic implants, surgical forceps, dental frameworks, syringe components andother medical devices that require extremely clean and smooth surfaces. Magnetic polishing ensures no chemical contamination and can polish even the tiniest grooves and cavities.
- Electronic Components:
Magnetic abrasive polishing can well polish various electronic components that are very small, geometrically complex, and prone to deformation, such as connector pins, waveguides, shielding enclosures, micro-sized springs.
- Automative Components:
For components with deep holes, irregular internal geometries, or internal threads, magnetic polishing is one of the most effective automated surface finishing methods. Therefore, it is commonly used to polish automative components such as automotive fuel injectors, spark plug electrodes, and precision gears.
- Jewelry:
Magnetic polishingis popularly applied to jewelry. It can clean and brighten intricate patterns and fine details of even soft metals such as gold and
7. Summary
Magnetic polishing is an automated surface finishing process that can provide fine polishing and excellent brightening service for various precision CNC machining parts with complex geometries.
Compared with conventional mechanical polishing, it can offer better polishing effect for precision parts. More importantly, it would not cause issues of deformation and residual stresses.
All in all, magnetic polishing is a good choice for fine precision parts.
8. FAQs
8.1 How does Magnetic Polishing Differ from Vibration Polishing?
They mainly differ in polishing speed and performance. Magnetic polishing usually takes only 5 to 20 minutes for once while vibratory polishing needs several hours.
And magnetic polishing is more suitable for fine polishing of small precision parts while vibration polishing is more suitable for general deburring of large surfaces.
8.2 How much Material does Magnetic Polishing Remove?
Very little. Magnetic polishing does not change the part’s dimension and geometry.
8.3 How to Deal with Darkened Magnetic Polishing Pins?
The problem is usually caused by the buildup of metal residues on the pin, or by the improper use of chemicals. You should run the machine without parts to clean the pins by water and dedicated cleaner for about 15 minutes.

Lucas is a technical writer at ECOREPRAP. He has eight years of CNC programming and operating experience, including five-axis programming. He’s a lifelong learner who loves sharing his expertise.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy

What is 5-axis Machining? A Complete Guide.
5-Axis CNC machining is a manufacturing process that uses computer numerical control systems to operate 5-axis CNC machines capable of moving a cutting tool or a workpiece along five distinct axes simultaneously.

Which Country is Best for CNC Machining?
China is the best country for CNC machining service considering cost, precision, logistic and other factors. Statistical data suggests that China emerges as the premier destination for CNC machining.

Top 5 Prototype Manufacturing China
Selecting the right prototype manufacturing supplier in China is a critical decision that can significantly impact the success of your product development project.

CNC Machining Tolerances Guide
Machining tolerances stand for the precision of manufacturing processes and products. The lower the values of machining tolerances are, the higher the accuracy level would be.


