Table of Contents
In our previous article, we explored how titanium alloys strike an excellent balance between weight, strength, corrosion resistance, and environmental stability, making them an indispensable high-end material in precision CNC machining.
But titanium alloys are not a single material—their properties vary significantly depending on grade and composition.
In this blog, we systematically review the most common industrial titanium grades, comparing their composition, key properties, advantages, and typical applications, providing clear guidance for material selection and design decisions in titanium CNC machining projects.
Key Takeaways:
Titanium is not one material—grade selection matters.Titanium alloys vary significantly by microstructure (α, α+β, β).
Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5 / TC4) is the safest and most versatile choice for CNC machining.
- Always confirm the grade standard (ASTM vs. GB), material condition (annealed vs. heat-treated), and performance priorities. Early coordination with an experienced titanium CNC machining partner prevents cost overruns and manufacturing risks.
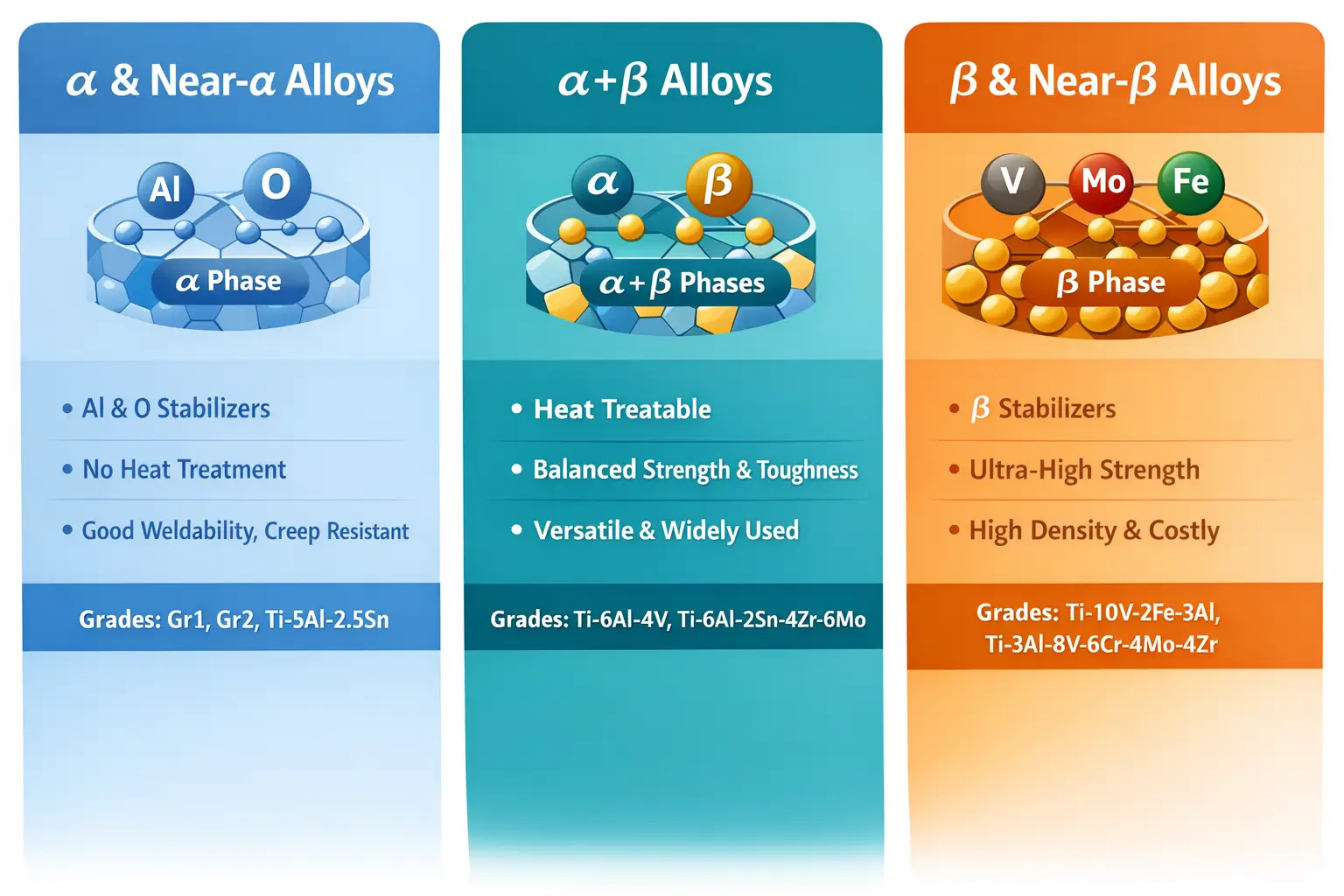
1. Classification by Microstructure
Titanium alloys are categorized by their dominant microstructure at room temperature. This structure directly dictates how the metal behaves during cnc titanium machining.
1.1 Commercially Pure Titanium (Unalloyed,α alloys)
Grade 1 Titanium
Type: Unalloyed, α Phase.
The softest and most ductile grade. Offers maximum formability and excellent corrosion resistance, but the lowest strength.
Common CNC Applications: Chemical processing linings, heat exchanger plates, and architectural components.
Grade 2 Titanium
Type: Unalloyed, α Phase.
The most widely used pure titanium. Provides the best balance of strength, ductility, weldability, and corrosion resistance. It is the standard “workhorse” grade.
Common CNC Applications: Marine components, chemical piping, medical device housings, automotive exhaust systems, and fluid handling systems.
Grade 3 Titanium
Type: Unalloyed, α Phase.
A medium-strength pure titanium. Offers higher strength than Grade 2 while maintaining good formability.
Common CNC Applications: Aerospace hydraulic tubing, chemical processing equipment, and pressure vessels.
Grade 4 Titanium
Type: Unalloyed, α Phase.
The strongest of the pure titanium grades. Used when higher strength is required alongside excellent corrosion resistance, though formability is reduced.
Common CNC Applications: Aerospace fasteners, surgical bone screws, orthopedic cables, and high-strength corrosion-resistant structures.
1.2 α and near-α alloys
Titanium α and near-α alloys is excellent for high-temperature stability and weldability.
Grade 6 Titanium (Ti-5Al-2.5Sn)
Type: α Alloy.
A classic alloy known for good weldability, stability at elevated temperatures (up to ~900°F / 480°C), and excellent corrosion resistance. It cannot be heat-treated for increased strength.
Common CNC Applications: Aircraft engine casings, airframe components, and cryogenic vessels.
1.3 α+β alloys
The most common category for high-strength structural applications. Can be heat-treated.
Grade 5 Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V)
Type: α-β Alloy.
The “workhorse” of titanium alloys, accounting for over 50% of all titanium usage. Renowned for its outstanding strength-to-weight ratio, good fatigue resistance, and excellent corrosion resistance. It can be solution treated and aged to increase strength.
Common CNC Applications: Aerospace structural components, jet engine parts, high-performance automotive and racing parts, medical implants (non-ELI), and marine fittings.
Grade 23 Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V ELI)
Type: α-β Alloy (ELI: Extra Low Interstitial).
A purer, medical-grade version of Grade 5. Lower oxygen and iron content provides enhanced fracture toughness, better fatigue crack resistance, and superior biocompatibility.
Common CNC Applications: The premium choice for critical medical implants like orthopedic joint replacements, spinal fusion cages, and dental implants.
1.4 β and near-β alloys
Offer the highest strength, excellent hardenability, and good cold formability.
Beta C Titanium (Ti-3Al-8V-6Cr-4Mo-4Zr)
Type: β Alloy.
Known for exceptional resistance to stress corrosion and superb corrosion resistance in saline environments. Can achieve very high strength after aging.
Common CNC Applications: Marine components, chemical processing equipment, high-performance springs, and fasteners.
Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al
Type: Near-β Alloy.
Known for deep hardenability, allowing large cross-sections to be heat-treated to very high strength with good toughness.
Common CNC Applications: Aircraft landing gear components, critical airframe forgings, and other high-strength structural aerospace parts.
Ti-15V-3Cr-3Sn-3Al
Type: β Alloy.
Offers exceptional cold roll formability in the solution-treated condition, similar to stainless steel. Can be aged to high strength levels.
Common CNC Applications: Aerospace sheet metal components, honeycomb panels, springs, and brackets.
Ti-13Nb-13Zr
Type: Near-β Alloy.
A biomedical-specific alloy. Its low elastic modulus is closest to human bone, minimizing stress shielding. It offers excellent biocompatibility and corrosion fatigue strength.
Common CNC Applications: Advanced orthopedic and dental implants.
2. Performance Comparison of Common Industrial Titanium Alloys
| Grade | Composition | Typical State | Key Features | Advantages | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gr2 / TA1 (Pure Ti) | >99% Ti | Annealed | Excellent corrosion resistance, cold formability, and weldability; lower strength (~345 MPa Y.S.) | Low cost, best manufacturability | Chemical heat exchangers, marine platforms, non-load-bearing medical implants |
| Gr5 / TC4 (α+β) | Ti-6Al-4V | Annealed or solution treated | Exceptional overall performance: high strength (>830 MPa Y.S.), toughness, weldable, corrosion resistant | “All-rounder” with the best value, most data and experience | Aerospace structures, engine parts, high-performance racing components, load-bearing medical implants |
| Gr5 / TC11 (α+β, high-temp) | Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-6Mo | Annealed | Excellent high-temperature performance (~500°C), high strength | Outstanding creep and fatigue resistance | Aerospace engine compressor disks, blades, high-temp fasteners |
| Beta-C / TB3 (β) | Ti-3Al-8V-6Cr-4Mo-4Zr | Solution + aged | Ultra-high strength (>1300 MPa), excellent cold formability, corrosion-resistant | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio, suitable for complex cold-formed parts | Aerospace fasteners, springs, high-strength supports, medical devices |
Tip for CNC machining: Gr5 (Ti-6Al-4V) is the most mature titanium CNC machining material. β alloys, while stronger, have lower thermal conductivity and are stickier, demanding more from tooling and cooling.
3. Common Titanium Grades in China
In China, titanium grades typically follow GB/T (China), HB (aerospace), and ASTM (US) standards. Names may vary, but the material is essentially the same.
3.1 Naming Rules
TA: α-type titanium alloys (including industrial pure titanium)
TB: β-type titanium alloys
TC: α+β-type titanium alloys (most widely used in CNC titanium parts)
3.2 TA Series: Industrial Pure Titanium
| Chinese Grade | ASTM | Features | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| TA1 | Gr1 | Lowest strength, excellent ductility | Chemical, corrosion-resistant parts |
| TA2 | Gr2 | Most commonly used, well-balanced | Industrial structures, marine equipment |
| TA3 | Gr3 | Slightly higher strength, lower plasticity | Specific structural parts |
| TA4 | Gr4 | Highest strength among CP titanium | High-strength, corrosion-resistant parts |
TA2 is the most popular for custom CNC titanium parts due to stable supply, reasonable cost, and superior machinability.
3.3 TC Series: α+β Alloys (Core CNC Materials)
TC4: Corresponds to ASTM Gr5 (Ti-6Al-4V), high strength, excellent fatigue resistance, widely used in robotics, UAVs, aerospace, and precision CNC titanium machining.
TC4 ELI: Extra Low Interstitials, ASTM Gr23, higher toughness, medical-grade. Used for implants and high-reliability components.
TC11: High-temperature α+β alloy, used for aerospace engine hot-section components.
3.4 TB Series: β Alloys
Mainly used in aerospace, military, or research. Rarely used in commercial CNC machining due to high cost, complex heat treatment, and unstable supply.
3.5 Common China & USA Titanium Grades Table
Common Titanium Grades & Applications (China & USA)
| Chinese Grade (GB/T) | Equivalent US Grade (ASTM) | Alloy Type | Key Features | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA1, TA2, TA3 | Gr1, Gr2, Gr3 | Industrial Pure Titanium | Excellent corrosion resistance, good ductility, low strength | Chemical equipment (heat exchangers, reactors), marine engineering, seawater desalination, non-load-bearing medical implants |
| TA7 | Ti-5Al-2.5Sn | α-type Alloy | Moderate strength at mid-temperatures, excellent weldability, good creep resistance | Aerospace engine casings, skins, components operating below 500°C |
| TC4 | Ti-6Al-4V (Gr5) | α+β Alloy | Best overall performance, most widely used, heat-treatable | Aerospace structural components (airframes, landing gear), medical implants (joints, bone plates), high-end sports equipment |
| TC4 ELI | Ti-6Al-4V ELI (Gr23) | α+β Alloy | Extra-low interstitial elements, improved toughness and fatigue resistance | High-end medical implants (load-bearing implants requiring high reliability) |
| TC11 | Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-6Mo | α+β (High-Temperature) | Outstanding high-temperature performance, excellent thermal strength | Aerospace engine compressor disks, blades, high-temperature fasteners |
4. How to Choose the Right Titanium Alloy for Your CNC Project?
Selecting the optimal titanium grade is a crucial first step that balances performance, manufacturability, and budget.
Here’s a simple decision guide to point you in the right direction:
For Maximum Corrosion Resistance & Formability
Choose: Commercially Pure Titanium (Grades 1 & 2 / TA1 & TA2)
Best For: Electrochemical components, marine hardware, non-load-bearing medical devices, and enclosures requiring complex cold forming.
- For the Best All-Around Performance & Value
Choose: Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5 / TC4)
Best For: The vast majority of structural components, load-bearing frames, landing gear parts, and standard medical implants. This is the universal first choice when you’re unsure. Most precision CNC machined titanium parts and custom CNC titanium parts successfully use this versatile alloy.
- For High-Temperature Applications (>300°C / 570°F)
Choose: High-Temperature Alpha-Beta Alloys (e.g., TC11)
Pro-Tip from Our Shop: Our extensive CNC machining titanium experience with TC11 shows it has a stronger tendency to work-harden than TC4. We recommend more conservative cutting parameters to ensure quality.
Best For: Jet engine components (non-blades), high-speed airframe skins, and high-temperature hydraulic tubing.
- For Ultra-High Strength & Maximum Weight Savings
Choose: Beta Alloys (e.g., Beta-C, Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al)
Best For: Weight-critical, high-stress components like aerospace fasteners and racing suspension links, as well as parts requiring complex cold heading.
- For Superior Biocompatibility & Fatigue Performance
Choose: Medical-Grade Ti-6Al-4V ELI (Grade 23)
Best For: Long-term implants like hip joints, knee replacements, and bone plates/screws. Its extra-low interstitial (ELI) content provides exceptional fracture toughness.
- Practical Advice for a Smooth Project:
- Clarify the standard. Chinese drawings often use GB codes (e.g., TC4), while international supply chains use ASTM (e.g., Gr5). Always confirm the equivalence to prevent misunderstandings with your titanium CNC machining supplier.
- TC4 (Gr5) has the most robust supply chain, offers the best relative cost, and has the deepest reservoir of CNC titanium machining experience. Prioritize it when performance requirements allow.
- Properties vary drastically between conditions like “Annealed” and “Solution Treated & Aged.” For example, heat-treated TC4 can be ~20% stronger. Always define this clearly in your technical requirements.
- The β series offers exceptional performance but at a higher cost, with greater challenges in CNC milling titanium and welding. Use them only when the design critically requires it, ideally with expert guidance.
5. Summary
Choosing the correct titanium grade is the foundational step in balancing performance, manufacturability, and cost. Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5/TC4) remains the universal first choicedue to its unparalleled all-around capabilities.
For applications with extreme demands in corrosion resistance, high temperature, or ultra-high strength, the specialized families of Commercially Pure, high-temperature, or Beta alloys come into play.
Understanding these differences and having a detailed conversation with your titanium CNC machining services provider is the key to your project’s success.
6. FAQ
Q1: What are α-stabilizing elements?
α-stabilizers (like aluminum) increase the temperature at which titanium transforms from α (hexagonal close-packed) to β (body-centered cubic). They enhance strength and heat resistance but may reduce room-temperature ductility.
Q2: What are β-stabilizing elements?
β-stabilizers (like vanadium, molybdenum, chromium, iron) lower the β-phase transformation temperature, enabling heat treatment to adjust strength, toughness, and formability.
Q3: Are TC4 and Grade 5 the same?
Yes, TC4 (China GB/T) corresponds exactly to ASTM Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V). Chemically and mechanically identical.
Q4: Is α titanium the same as pure titanium?
Not exactly. Pure titanium (Gr1/Gr2) is α-type, but α alloys can also contain α-stabilizing elements like aluminum.
Q5: Why is Ti-6Al-4V most used in CNC machining?
It offers the best balance of performance, machinability, and cost, with mature cutting strategies, predictable results, and stable supply.
Source: SAE International. (n.d.). AMS4928: Titanium Alloy 6Al – 4V Annealed.

Lucas is a technical writer at ECOREPRAP. He has eight years of CNC programming and operating experience, including five-axis programming. He’s a lifelong learner who loves sharing his expertise.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy

What is 5-axis Machining? A Complete Guide.
5-Axis CNC machining is a manufacturing process that uses computer numerical control systems to operate 5-axis CNC machines capable of moving a cutting tool or a workpiece along five distinct axes simultaneously.

Which Country is Best for CNC Machining?
China is the best country for CNC machining service considering cost, precision, logistic and other factors. Statistical data suggests that China emerges as the premier destination for CNC machining.

Top 5 Prototype Manufacturing China
Selecting the right prototype manufacturing supplier in China is a critical decision that can significantly impact the success of your product development project.

CNC Machining Tolerances Guide
Machining tolerances stand for the precision of manufacturing processes and products. The lower the values of machining tolerances are, the higher the accuracy level would be.


