Table of Contents
Are you looking for a reliable vacuum casting rapid prototyping service? Vacuum casting is an ideal solution for creating high-quality prototypes that closely mimic final production parts.
In a recent automotive project, vacuum casting enabled the delivery of 15 functional prototypes within two weeks, closely matching production specifications.[ARRK, Rapid Prototyping Guide, 2023]
To ensure quality and timely delivery, it is recommended to work with verified suppliers.
Examples include ISO-certified rapid prototyping companies or those recognized in industry reports.
These suppliers can provide professional support throughout the process, from design to finished prototype.
Key Takeaways:
- Vacuum casting is a cost-effective, rapid prototyping method ideal for small to medium batches (5-100 parts), producing high-quality, production-like prototypes with tight tolerances and smooth finishes.
- Typical lead times range from 7 to 15 days, making it suitable for quick iteration and functional testing.
- It offers versatile material options such as polyurethane, epoxy, and ABS-like resins that closely simulate production plastics, supporting diverse design requirements.
- Vacuum casting excels over 3D printing in part durability, surface quality, and material properties, especially for small batch runs, though it requires mold making which adds time.
- Selecting trusted suppliers with certifications (ISO 9001, ISO 13485) ensures quality, timely delivery, and expert support.
- The step-by-step vacuum casting process includes master model creation, silicone mold making, resin mixing, vacuum pouring, curing, and finishing.
- The method handles complex geometries with some limitations and accommodates very low minimum order quantities, even single prototypes.
What is Vacuum casting for rapid prototyping?
Vacuum casting for rapid prototyping is a flexible molding process that reproduces high-quality plastic or rubber parts from a master model, typically created through 3D printing or CNC machining.
Using silicone molds and vacuum pressure, it eliminates air bubbles and ensures excellent surface finish and accuracy.
This technique is widely used for functional testing, design verification, and small-batch production.
It allows engineers to evaluate form, fit, and performance before investing in expensive injection molds, making it an efficient bridge between prototyping and mass production.
Vacuum Casting Core Benefits
Vacuum casting delivers high-quality prototype parts quickly and affordably, making it ideal for low-volume production.
It ensures smooth surfaces, excellent dimensional accuracy up to ±0.05 mm, and reliable repeatability.
With flexible material choices and short lead times of about 7–15 days, it bridges the gap between prototype testing and full-scale manufacturing, helping designers validate both function and appearance efficiently.
- Cost-effective for small to medium batches – Ideal for low-volume production without the need for expensive tooling, with typical cost savings of 30–50% compared to injection molding for small runs.
- Rapid prototyping – Typical lead times range from 7–15 business days depending on complexity and supplier capacity.
- High-quality surface finish capturing fine details accurately – Achieves surface roughness as low as Ra 0.8 μm, suitable for functional prototypes and visual models [ISO 2768-1:2021]. For example, a consumer electronics prototype retained micro-scale design features after casting.
- Versatile material options simulating production plastics – Materials include polyurethane, epoxy, and ABS-like resins with mechanical properties closely matching injection-molded plastics (tensile strength, elongation, heat deflection).
- Precision and tight tolerances for complex geometries – Typically ±0.3 mm or better for small features, suitable for engineering validation.
- Quick mold production using silicone molds – Molds can be produced within 1–2 days depending on part size, enabling fast iteration.
- Parts suitable for functional testing depending on material and process conditions – Functional prototypes can undergo mechanical and thermal testing within specified limits.
- Minimal material waste, environmentally efficient – Silicone molds and reusable resin reduce scrap, supporting greener prototyping.
- Ability to simulate multi-material overmolding – Enables testing of soft-touch coatings or dual-material components in a single prototype.
- Consistent quality across batches – Reproducibility can be maintained within ±10% of key mechanical properties across 10–20 units per mold, depending on process control.
These benefits make vacuum casting ideal for prototypes and low-volume production runs requiring production-like quality at an affordable cost, while allowing flexibility in materials, design iteration, and functional testing.
1.How does vacuum casting compare to 3D printing?
vacuum casting provides high-quality, durable parts with excellent surface finish, making it suitable for producing small to medium batches with consistent results; meanwhile, 3D printing excels in rapid prototyping and complex geometries but may face limitations in material strength and surface smoothness.
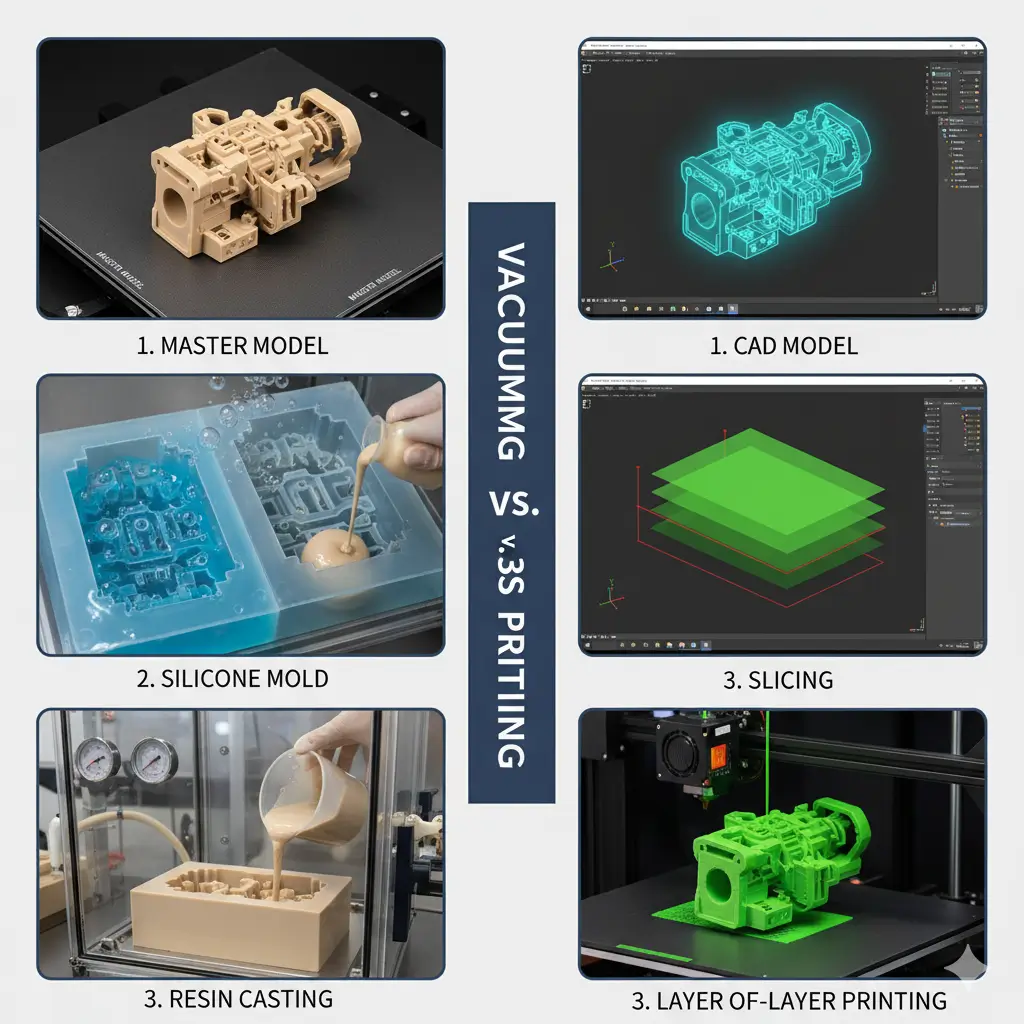
Vacuum casting typically involves molds made from silicone or similar materials, offering a cost-effective approach for limited runs, whereas 3D printing uses additive layer-by-layer fabrication, allowing for quick design modifications but potentially higher per-unit costs for larger quantities.
Overall, vacuum casting is favored for precision and finish in production, while 3D printing is more suited for fast iteration and complex design exploration.
2.Can I get production-like prototypes in a few weeks?
Yes, you can get production-like prototypes in a few weeks using vacuum casting. The process typically takes about 10 to 15 days from master model creation to final cast parts. Vacuum casting produces high-quality replicas with tight tolerances, smooth finishes, and material properties close to production plastics, making it ideal for rapid prototyping and small-batch production before mass manufacturing.
3.Which materials are suitable for my design?
Materials commonly used in vacuum casting include:
- ABS-like polyurethane resins – Good impact resistance and dimensional stability, suitable for consumer electronics housings.
- PC-like polyurethane resins – High strength and heat resistance, ideal for functional prototypes requiring toughness.
- PP-like polyurethane resins – Excellent fatigue resistance, often used in snap-fit automotive prototypes【Source: ISO 527, ISO 178 testing standards】.
- Epoxy systems – High stiffness and chemical resistance, suitable for structural or decorative parts.
- Specialty silicones – Flexible or rubber-like parts for soft-touch applications.
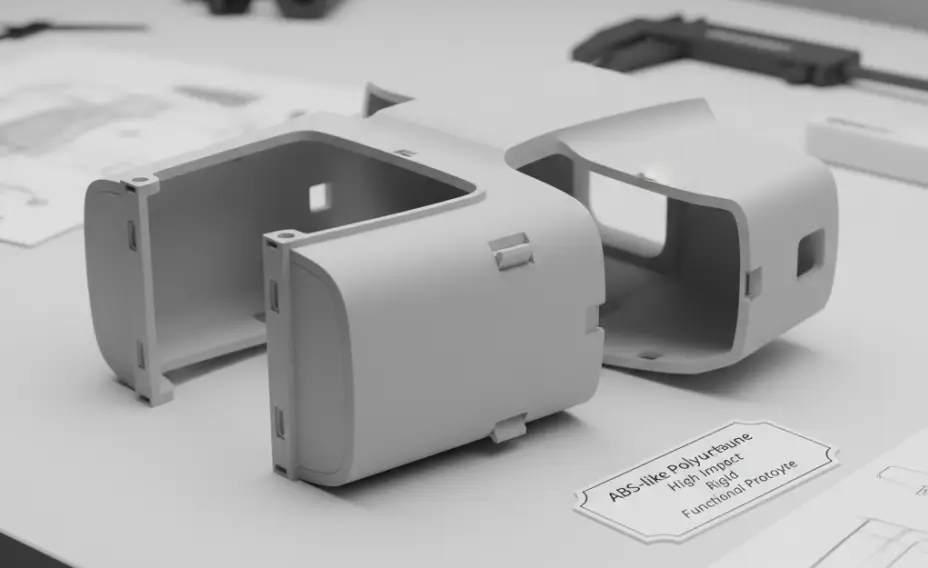

These materials replicate the mechanical properties, surface finishes, and durability of production plastics. Soft-touch elastomers and rubber-like materials expand the versatility for flexible components.
Material Selection Guidelines:
- Strength & rigidity: Choose PC-like or epoxy systems for load-bearing prototypes.
- Flexibility & elasticity: Use PP-like or silicone materials for snap-fit or soft-touch applications.
- Heat resistance: PC-like resins withstand higher temperatures for functional testing.
- Transparency or optical requirements: Certain epoxy or clear polyurethane formulations are suitable for visual or display prototypes.
Vacuum casting supports a broad range of materials to match diverse design requirements, making it ideal for functional prototypes, aesthetic models, and small-batch production.
Selecting the right material based on part function, environmental conditions, and mechanical requirements ensures prototypes are reliable and representative of final production parts.
Step-by-Step Vacuum Casting Process
| Step | Key Actions | Typical Duration | Tools / Materials | Tips / Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Create Master Model | 3D print or CNC machine master; smooth surfaces | 1–2 days | 3D printer or CNC machine, sandpaper, release agent | Apply thin release agent on complex areas for easy demolding |
| 2. Make Silicone Mold | Pour silicone over master in mold box; degas in vacuum chamber | 1–2 days (curing 8–24h) | Silicone, mold box, vacuum chamber | Pour slowly from one corner to reduce air entrapment |
| 3. Prepare for Casting | Remove master, mix & degas resin, add color if needed | 0.5 day | Casting resin (polyurethane), pigments, vacuum chamber | Degas under vacuum 3–5 min to minimize micro-bubbles |
| 4. Pour Resin in Vacuum | Pour resin into silicone mold inside vacuum chamber | 0.5 day | Vacuum chamber, silicone mold | Pour continuously along one edge to avoid air pockets |
| 5. Cure and Demold | Cure resin at elevated temperature; remove, trim, finish | 1–2 days | Oven (optional), cutting tools, sandpaper, paint | Flex silicone mold slightly when demolding; follow resin curing temperature |
1.Create Master Model
- Produce a precise master model using 3D printing or CNC machining. Ensure surface is smooth and free of defects to minimize post-processing.
- Tip: Apply a thin release agent to complex features to facilitate mold removal.
2.Make Silicone Mold
- Place the master model in a mold box and pour liquid silicone over it. Use a vacuum chamber to remove trapped air bubbles.
- Tip: Pour slowly from one corner to reduce air entrapment and achieve uniform coverage.
- Cure the silicone for 8–24 hours, depending on material type and thickness.
3.Prepare for Casting
- Carefully remove the master model by cutting the silicone mold along planned parting lines.
- Mix and degas the casting resin (typically polyurethane), adding color pigments if needed.
- Tip: Degassing under vacuum for 3–5 minutes reduces micro-bubbles in the final part.
4.Pour Resin in Vacuum
- Pour the resin into the silicone mold placed in a vacuum chamber to eliminate trapped air and ensure full cavity fill.
- Tip: Pour continuously along one edge to prevent air pockets.
5.Cure and Demold
- Allow the resin to cure, usually at an elevated temperature (e.g., 40–60°C for polyurethane) for the recommended time.
- Open the mold, remove the cast part, trim excess flash, and apply finishing such as sanding, polishing, or painting.
- Tip: For easier demolding, slightly flex the silicone mold rather than pulling aggressively.
6.Practical Example / Timeline
- For a medium batch of 20–30 parts, the complete process from 3D printing the master model to finished parts can typically be completed within 10 days, including mold curing and resin casting.
- This workflow allows repeated casting from a single mold, producing high-quality, production-like prototypes and small batches efficiently.
Materials for Vacuum Casting: Choosing the Right Option
- ABS-like resins: Offer good toughness, rigidity, impact strength, abrasion resistance, and chemical resistance; best for versatile prototypes.
- PC-like resins: Provide high mechanical strength, heat resistance, and optical clarity for durable parts with thermal stability.
- Polypropylene (PP)-like resins: Known for elasticity, fatigue resistance, and toughness; ideal for snap-fits and automotive parts.
- Acrylic (PMMA)-like resins: Transparent with excellent UV resistance used in lighting and lenses.
- Silicone and TPU-like materials: Provide flexibility, elasticity, and temperature resistance for seals, gaskets, and medical devices.
Choosing depends on required strength, flexibility, clarity, heat resistance, and application.
Vacuum casting supports a broad spectrum of materials to closely simulate production plastics.
Vacuum Casting vs 3D Printing: Which Fits Your Needs?
Choose Vacuum Casting if you need small batches (5-100 parts) of high-quality prototypes with production-like material properties, smooth surface finish, and durability.
It is best for functional testing, design validation, and pre-production runs but has a longer lead time (about 1-2 weeks) due to mold making.
Choose 3D Printing for rapid prototyping of one-off or complex geometries with fast turnaround (hours to days).
It excels at customization and quick iteration but typically produces rougher surfaces and parts with lower strength compared to vacuum casting.
| Aspect | Vacuum Casting | 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Batch Size | Small to medium (5-100 parts) | One-offs or very low volume |
| Material Properties | Production-like, durable parts | Limited strength, rough finish |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, detailed | Visible layer lines, rough |
| Lead Time | 1-2 weeks | Hours to days |
| Complexity | Limited by mold design | Complex and intricate |
| Cost Efficiency | Low cost for batches | Cost-effective for single parts |
For small to medium batches—around 10 to 50 parts—requiring functional testing and production-like quality, vacuum casting is often preferred.
Meanwhile, 3D printing is well-suited for single custom prototypes or highly intricate geometries that benefit from rapid design iterations.
Both methods have their strengths, so choosing between them depends on factors such as batch size, design complexity, timeline, and required material properties.
How to Find Trusted Vacuum Casting Manufacturers?
- Define Your Requirements:Clarify batch size, material needs, desired quality, and timeline.
- Research and Identify Potential Manufacturers:Examples of verified suppliers such as ECOREPRAP, ARRK, Xometry, RapidDirect, and others.
- Verify Certifications and Experience:Check for quality certifications (ISO 9001, ISO 13485) and track records in your industry.
- Evaluate Technical Capability:Confirm ability to handle master model creation, silicone molding, resin casting, and finishing.
- Review Customer Feedback and Case Studies:Analyze client reviews, success stories, and product samples.
- Request Quotes and Lead Times:Obtain detailed pricing and delivery schedules for your project.
- Conduct Trial Orders:Place small sample orders to assess parts quality, communication, and service responsiveness.
- Establish a Long-Term Partnership:After successful trials, formalize cooperation for ongoing or larger-scale production.
Following these steps ensures you partner with reliable vacuum casting manufacturers like ECOREPRAP who provide quality, speed, and material versatility for prototyping and small batch production.
FAQ: Rapid Prototyping with Vacuum Casting
1.Can vacuum casting handle complex geometries?
Yes, vacuum casting can handle complex geometries, including intricate shapes and fine details.
However, it has some limitations with very thin walls, highly complex internal structures, and ensuring uniform resin flow in molds.
Silicone molds have a limited lifespan, which can affect precision over multiple uses.
In general, vacuum casting is suitable for many complex designs but may require careful mold design and process control to avoid defects.
2.How fast can I receive prototypes?
You can typically receive vacuum casting prototypes within 7 to 15 days. This includes the time to create the master model, produce the silicone mold, and cast the parts.
The exact lead time depends on the part complexity, batch size, and finishing requirements.
Vacuum casting offers a fast and cost-effective solution for small batch prototyping compared to other methods.
3.Are there minimum order quantities?
- Most manufacturers accept minimum orders as low as 1 to 5 pieces.
- It is cost-effective for small batches, typically between 5 and 100 units.
- Some providers specify minimums around 10 pieces, but many offer single-piece prototyping.
- Maximum duplicates per mold usually range from 20 to 30 parts, depending on complexity and material.
So, yes, vacuum casting can handle very low minimum orders, even single prototypes, making it ideal for rapid prototyping and low-volume production.
Rapid Prototyping Knowledge Hub

1.Understanding CNC Rapid Prototyping
- What is CNC Rapid Prototyping? Complete Guide for 2025
- What are the Benefits of CNC for Rapid Prototyping?
- CNC Machining for Rapid Prototyping: How to Choose the Right Solution
- 3 Types of Prototyping Services for Fast and Cost-Effective Prototypes
2.CNC vs Other Prototyping Methods
- CNC Rapid Prototyping vs 3D Printing: Which to Choose in 2025?
- 3D Printing vs CNC Machining: Which Is Right for You?
- CNC Milling vs CNC Turning: Which Is Better for Prototyping?
3.Engineering & DFM Considerations
- CNC Prototype Tolerances Explained
- How to Optimize CAD Files for CNC Prototyping
- How Material Selection Affects CNC Prototype Performance
- ABS vs Aluminum: Which is Better for CNC Prototypes?
- Why Production Time Matters in Prototype CNC Parts Manufacturing?
4.From Prototype to Production
- CNC Machining for Small Batch Prototyping
- From Prototype to Production: How CNC Companies Support Scalability
5.CNC Prototyping Services in China
- CNC Prototyping Services China (Complete Buying Guide)
- Key Factors to Consider When Sourcing CNC Prototypes from China
- Top 5 Prototype Manufacturers in China
- 5 Key Benefits of Using Chinese Prototyping Services
Get Rapid Prototyping Services

Lucas is a technical writer at ECOREPRAP. He has eight years of CNC programming and operating experience, including five-axis programming. He’s a lifelong learner who loves sharing his expertise.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy

What is 5-axis Machining? A Complete Guide.
5-Axis CNC machining is a manufacturing process that uses computer numerical control systems to operate 5-axis CNC machines capable of moving a cutting tool or a workpiece along five distinct axes simultaneously.

Which Country is Best for CNC Machining?
China is the best country for CNC machining service considering cost, precision, logistic and other factors. Statistical data suggests that China emerges as the premier destination for CNC machining.

Top 5 Prototype Manufacturing China
Selecting the right prototype manufacturing supplier in China is a critical decision that can significantly impact the success of your product development project.

CNC Machining Tolerances Guide
Machining tolerances stand for the precision of manufacturing processes and products. The lower the values of machining tolerances are, the higher the accuracy level would be.