Table of Contents
Choosing between ABS and aluminum for CNC prototypes is ultimately about balancing cost, strength, precision, and required testing conditions.
Buyers frequently compare these two materials because they represent two completely different prototype goals: speed and affordability (ABS) versus strength and functional reliability (aluminum).
This guide summarizes practical insights based on real CNC machining prototypes handled by Ecoreprap, integrating material performance data, machining characteristics, and application scenarios so that engineers and procurement teams can make accurate decisions with fewer iterations.
Key Differences Between ABS and Aluminum for CNC Prototypes
The main difference between ABS and aluminum in CNC prototyping comes from their mechanical strength, machining precision, and performance under load.
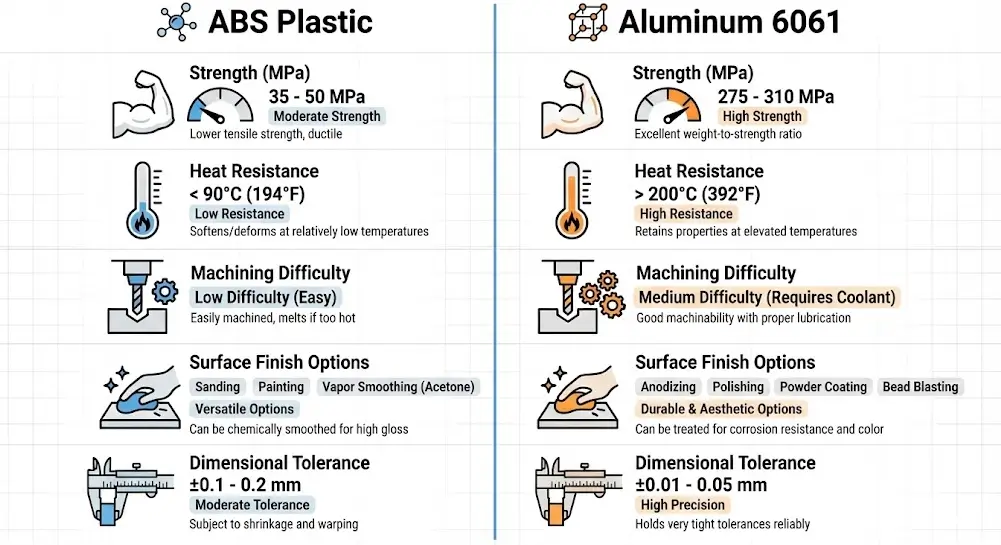
- Mechanical Strength:ABS provides moderate strength at around 40 MPa, while aluminum 6061 commonly reaches 310 MPa, offering durability for structural or load-bearing testing. In functional testing projects handled at Ecoreprap, aluminum prototypes consistently maintain stability under screw-fastening, heat exposure, and mechanical stress.
- Machinability and Processing Time:ABS is easier and faster to machine because the material is softer and generates minimal tool wear, leading to machining speeds typically 15–20% faster than aluminum. Aluminum requires stricter tool-path strategies, tool rigidity, and spindle stability, but returns higher precision after machining.
- Dimensional Accuracy:ABS commonly achieves tolerances around ±0.05 mm, which is sufficient for early-stage models. Aluminum, with a tolerance capability down to ±0.02 mm, is selected in projects where mating parts, alignment, and functional assemblies must be validated before final tooling.
- Surface Quality:ABS provides a smooth but non-metallic finish. Aluminum supports processes such as anodizing, sandblasting, brushing, and offers a more refined, technical appearance frequently required in consumer electronics, automotive, and industrial prototypes.
Cost Comparison Between ABS and Aluminum CNC Prototypes
The cost of ABS CNC prototypes is significantly lower than aluminum because of lower material pricing, shorter machining time, and reduced tool wear.
Typical Cost Ranges (2025 Market Data)
- ABS CNC prototype: USD 8–15/pc
- Aluminum 6061 CNC prototype: USD 18–35/pc
Why the Cost Differs?
Aluminum increases machining time, requires more stable fixturing, and tends to produce greater tool wear—especially for thinner geometries or deeper pockets.
Based on Ecoreprap’s machining records, ABS prototypes generally reduce total project cost by 40–60%, especially in early development stages where multiple iterations are required.
Lead Time Consideration
ABS parts often complete within 24–48 hours, while aluminum typically takes 48–72 hours, depending on complexity.
Faster ABS machining benefits projects that depend on rapid design iterations.
Pros and Cons of ABS for CNC Prototypes
ABS is better for early-stage concept validation, lightweight models, and cost-efficient iterations.

Pros of ABS CNC Machining
- Lower cost for prototyping and revisions
- Faster machining speed
- Good impact resistance for ergonomic testing
- Easy to paint or finish for visual evaluation
- Lightweight, suitable for handheld device models
- Cons of ABS CNC Machining
- Limited strength for load-bearing or screw-fastening tests
- Lower heat resistance, deformation risk above 80°C
- Surface quality lacks the refined industrial feel of metal
- Not suitable for verifying mechanical components
Best Use Cases for ABS Prototypes
ABS is ideal for industrial design prototypes, enclosure samples, ergonomic studies, and pre-tooling evaluation where strength and thermal stability are not critical.
ABS vs. Aluminum – Which Material Should You Choose?
Choosing between ABS and aluminum depends on whether you prioritize cost and speed or strength and accuracy.
Choose ABS If You Need:
- Low-cost prototypes for early product development
- Fast turnaround for design iterations
- Lightweight conceptual samples
- Non-functional or semi-functional enclosure models
Choose Aluminum If You Need:
- High structural strength for load-bearing tests
- High temperature resistance for engine or machinery environments
- Screw-tightening validation
- High-precision, tight-tolerance parts
Decision Matrix
| Criteria | ABS | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★★ |
| Cost | ★★★★★ | ★★☆☆☆ |
| Heat Resistance | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★★ |
| Machining Speed | ★★★★★ | ★★★☆☆ |
| Precision | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★★ |
| Surface Finish Options | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★★ |
Real Usage Scenarios Based on Ecoreprap’s CNC Project Experience
Actual CNC machining scenarios show the practical advantages of ABS or aluminum based on product stage and testing requirements.
Scenario 1: Early Industrial Design Prototyping
Design teams usually choose ABS during early product development because it allows multiple fast iterations.
Ecoreprap’s rapid machining lines frequently deliver ABS enclosure prototypes within 48 hours, enabling design teams to evaluate ergonomics and structure immediately.
Scenario 2: Mechanical Assembly Validation
Engineers requiring torque testing, screw-fastening verification, or hinge durability typically select aluminum.
Aluminum’s rigidity prevents deformation during assembly, allowing engineering teams to validate mechanical tolerances before moving to tooling.
Scenario 3: Thermal Performance Testing
Projects involving motors, LEDs, or electronics with significant heating use aluminum for its thermal conductivity.
Aluminum ensures prototype performance closer to the final, mass-produced part, which is critical for engineering confidence.
Supplier Checklist – What to Verify Before Ordering CNC Prototypes?
Reliable CNC prototypes require stable equipment, documented tolerances, and traceable material reports.
Key Items to Check Before Choosing a Supplier
- CNC tolerance capability (±0.02/±0.05 mm)
- Material certifications: RoHS, REACH, SGS
- Machine types (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis)
- Surface finishing capability
- Sample inspection report formats
- Packaging and logistics handling for delicate parts
Why This Checklist Matters?
Each factor directly affects prototype accuracy, durability during transit, and alignment with final production goals.
Ecoreprap follows an internal 12-step quality workflow to ensure parameters remain consistent across different batches.
Why Engineers Choose Ecoreprap for CNC ABS and Aluminum Prototypes?
Ecoreprap helps CNC buyers reduce project risks through consistent machining accuracy, certified materials, and transparent inspection data.
Certifications and Quality Control
- ISO 9001:2015 certified
- Material verification via SGS in 2024–2025
- Full dimensional inspection reports
- Repeatability control using calibrated fixtures and CMM checks
Technical Capability
- CNC accuracy: ±0.02 mm (aluminum), ±0.05 mm (ABS)
- Dedicated machines for plastics vs metals
- Experience with ABS, PC, PP, Aluminum 6061/7075, stainless steel
- Ability to meet design tolerances for functional engineering prototypes
Production and Delivery Performance
- Over 12 years of CNC manufacturing
- 2.5 million+ prototypes delivered worldwide
- Fast cycle for plastic prototypes; flexible scheduling for urgent engineering builds
Why These Capabilities Matter?
These capabilities reduce machining uncertainty and ensure that prototype behavior closely matches real-world application requirements, allowing engineers to make accurate decisions during product development.
FAQ – Common Questions About ABS vs. Aluminum CNC Prototypes
Is ABS strong enough for CNC prototypes?
ABS is strong enough for non-structural prototypes but not suitable for high-load tests or screw-tightening validation.
Is Aluminum 6061 or 7075 better for prototypes?
Aluminum 6061 is better for general prototypes, while 7075 is used for high-stress mechanical parts.
Which material is more accurate in CNC machining?
Aluminum typically offers higher dimensional accuracy due to its rigidity.
Can ABS prototypes be used for outdoor testing?
ABS may deform under sunlight and heat, making aluminum a better choice for outdoor prototypes.
Which material is faster to machine?
ABS machines faster than aluminum because of lower hardness and cutting resistance.
Conclusion
Choosing between ABS and aluminum for CNC prototypes depends on whether the project requires cost efficiency and speed or strength and engineering accuracy.
ABS is ideal for early-stage conceptual or enclosure models, while aluminum is the preferred option for functional testing and structural components.
With experience across thousands of machining projects, Ecoreprap provides practical recommendations and precise machining capability that help engineers and buyers reduce development risks and reach final design approval faster.
Rapid Prototyping Knowledge Hub
1.Understanding CNC Rapid Prototyping
- What is CNC Rapid Prototyping? Complete Guide for 2025
- What are the Benefits of CNC for Rapid Prototyping?
- CNC Machining for Rapid Prototyping: How to Choose the Right Solution
- 3 Types of Prototyping Services for Fast and Cost-Effective Prototypes
2.CNC vs Other Prototyping Methods
- CNC Rapid Prototyping vs 3D Printing: Which to Choose in 2025?
- 3D Printing vs CNC Machining: Which Is Right for You?
- CNC Milling vs CNC Turning: Which Is Better for Prototyping?
3.Engineering & DFM Considerations
- CNC Prototype Tolerances Explained
- How to Optimize CAD Files for CNC Prototyping
- How Material Selection Affects CNC Prototype Performance
- ABS vs Aluminum: Which is Better for CNC Prototypes?
- Why Production Time Matters in Prototype CNC Parts Manufacturing?
4.From Prototype to Production
- CNC Machining for Small Batch Prototyping
- From Prototype to Production: How CNC Companies Support Scalability
5.CNC Prototyping Services in China
- CNC Prototyping Services China (Complete Buying Guide)
- Key Factors to Consider When Sourcing CNC Prototypes from China
- Top 5 Prototype Manufacturers in China
- 5 Key Benefits of Using Chinese Prototyping Services
Get Rapid Prototyping Services

Lucas is a technical writer at ECOREPRAP. He has eight years of CNC programming and operating experience, including five-axis programming. He’s a lifelong learner who loves sharing his expertise.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy

What is 5-axis Machining? A Complete Guide.
5-Axis CNC machining is a manufacturing process that uses computer numerical control systems to operate 5-axis CNC machines capable of moving a cutting tool or a workpiece along five distinct axes simultaneously.

Which Country is Best for CNC Machining?
China is the best country for CNC machining service considering cost, precision, logistic and other factors. Statistical data suggests that China emerges as the premier destination for CNC machining.

Top 5 Prototype Manufacturing China
Selecting the right prototype manufacturing supplier in China is a critical decision that can significantly impact the success of your product development project.

CNC Machining Tolerances Guide
Machining tolerances stand for the precision of manufacturing processes and products. The lower the values of machining tolerances are, the higher the accuracy level would be.