Table of Contents
- What Is ABS Plastic?
- What Is ABS Plastic Used For?
- How To Cut ABS Plastic?
- Precautions For Cutting ABS Plastic
- Other Issues
Cutting ABS plastic requires the right tools and techniques to achieve a clean, precise cut without damaging the material. A common method of cutting ABS plastic is to cut with a Dremel.
What Is ABS Plastic?
ABS plastic (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) is a commonly used thermoplastic polymer. It offers strength, impact resistance, and versatility.
It consists of three monomers: acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, each with different properties.
Acrylonitrile improves chemical resistance, fatigue resistance, hardness, and stiffness, and increases the heat deflection temperature.
What Is ABS Plastic Used For?
ABS is used in a wide variety of industries, including automotive, consumer electronics, toys, home appliances, and 3D printing, because of its durability, ease of fabrication, and cost-effectiveness. Nine application scenarios are described below.
Gardening Tools
ABS is commonly used to make gardening tools because it is inexpensive and durable.
Miniature shovels, rakes, hoes, claws, and other hand tools are often made from ABS, providing a low-cost, lightweight set of tools for managing your garden.
Garden shears with ABS handles are comfortable to hold, while ABS miniature shovels and trowels are built to withstand the rigors of digging and planting.
Musical Instruments
The bodies of recorders, parts of clarinets, and keys of keyboards are often made from ABS because it produce a smooth, polished finish that is durable and wear-resistant.
Guitar guards made from ABS protect the body from scratches, while drumstick handles benefit from the impact resistance of ABS.
Medical Applications
Inhaler housings, nebulizer housings, and syringe barrels made from ABS ensure safety, durability, and easy sterilization.
Its non-toxicity makes it suitable for a variety of medical applications, including dental instruments and surgical tool handles, which require precision and toughness.
Automotive
Dashboards, interior panels, and wheel covers are often made from ABS due to their excellent impact and heat resistance.
ABS is also used in the manufacture of automotive bumpers, door panels, and mirror housings, helping to improve the overall safety and aesthetics of the vehicle while reducing weight for improved fuel efficiency.
Piping and Fittings
In plumbing systems, ABS plastics are used to make drains, fittings, and vent pipes.
ABS is also used in the construction of sewer lines and waste discharge systems, where durability and chemical resistance are most valued.
Vacuum Construction
ABS plastic is widely used in vacuum cleaners and similar equipment. For example, housing units, attachments, nozzles, and wheels are made from ABS to ensure durability, impact resistance, and ease of molding into complex shapes.
3D Construction Materials
ABS can be used to create prototypes, customized parts, and model kits.
Its strength and ease of printing make it the best material for making functional and detailed 3D models.
Architects and designers can use ABS to print building models, while hobbyists can use ABS for DIY projects.
Machine Prototyping
Engineers use ABS for gear prototypes, protective housings, and precision fixtures.
Industrial designers often use ABS to create functional prototypes of mechanical parts in order to test their performance before mass production.
Electrical and Electronic Applications
In the electronics industry, ABS plastic is used to make computer housings, printer components, and remote control housings.
Its electrical insulation and impact resistance protect sensitive electronic components while providing a rugged, aesthetically pleasing appearance.
ABS is also used to make keyboard and mouse housings, cell phone housings, and TV housings, ensuring that these devices are both durable and aesthetically pleasing.

How To Cut ABS Plastic?
Cutting ABS plastic requires precision and the right tools to ensure neat edges and minimize damage to the material. The following is a step-by-step guide to cutting ABS plastic using different tools, including specific settings and values: Dremel, jigsaw, hot knife, and laser.
Using the Dremel
The Dremel is a versatile, high-speed rotary tool that can be used for a variety of purposes, including cutting, grinding, polishing, and drilling.
Preparation Secure the ABS plastic plate to a stable workbench with clamps. This prevents movement and ensures a straight cut.
Step 1: Mark the Cut Line. Use a ruler and marker pen to draw the cut line on the plastic.
Step 2: Selecting the Right Attachment. Attach a cut-off wheel or multi-purpose cutting head to the Dremel. A 1.5-inch diameter cutting wheel is recommended.
Step 3: Adjust Speed. Set the Dremel to a medium speed, approximately 15,000 to 20,000 revolutions per minute, to avoid melting the plastic due to overheating.
Step 4: Start Cutting. Hold the Dremel firmly and guide it along the marked line. Apply steady pressure and do not force the tool.
Step 5: Finishing Touches. After cutting, use the sanding attachment on the Dremel to smooth out rough edges.
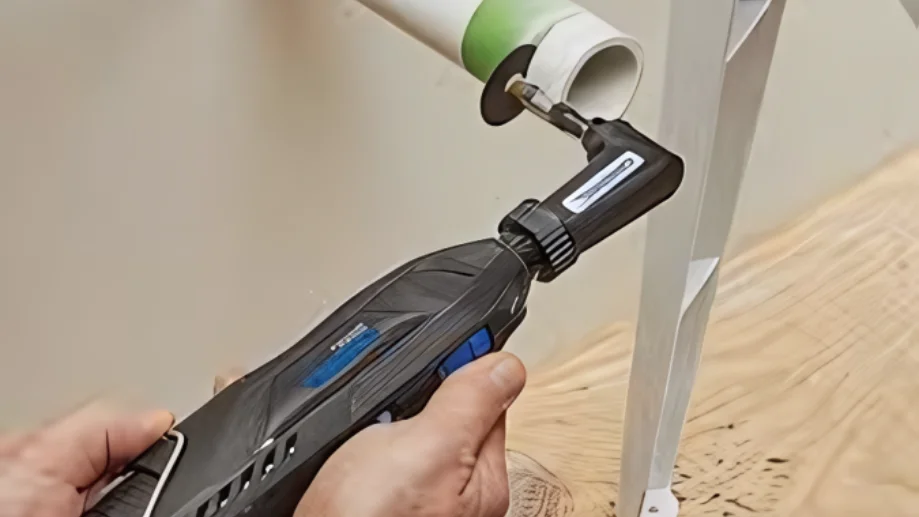

Using the Jigsaw
A jigsaw is a power tool used to cut a variety of materials such as wood, metal, plastic, and ceramics. It is capable of cutting curved and various complex shapes.
Prepare to clamp the ABS plastic plate securely to the workbench.
Step 1: Mark the cut line. Clearly mark the cut line with a marker and a straightedge or curved template.
Step 2: Select Blade. Select a fine-tooth blade designed for cutting plastics with 10-14 teeth per inch (TPI).
Step 3: Adjust Speed and Setting. Set the jigsaw to a medium speed, approximately 2,500 to 3,000 strokes per minute, to prevent overheating and melting the plastic.
Step 4: Start Cutting. Start cutting along the marked line, keeping the blade steady and moving at a consistent speed.
Step 5: Smooth Edges. After cutting, smooth the rough edges with a file or sandpaper (220 grit).
Using the Hot Knife
A hot knife is ideal for making precise, clean cuts in ABS plastic without creating dust or chips.
Prepare to place ABS plastic on a heat-resistant surface.
Step 1: Mark the Cut Line. Use a marker to draw the cut line.
Step 2: Heat the Knife. Insert the hot knife and allow it to reach an optimum temperature, usually about 400 to 500 degrees Fahrenheit (204 to 260 degrees Celsius).
Step 3: Start Cutting. Carefully guide the hot knife along the marked line. The heat will melt the plastic and create a smooth cut.
Step 4: Safety Measures. Use gloves and work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling fumes from melted plastic.
Using a Laser Cutter
The laser cutter provides the most precise and cleanest cuts and is ideal for fine designs and intricate patterns.
Prepare the ABS plastic sheet for placement on the laser-cutting bed.
Step 1: Design the Cut. Use a computer-aided design (CAD) program to create the cutting pattern.
Step 2: Setup Parameters. Adjust the laser cutter settings to cut ABS plastic. The power can be 50-60 watts, speed 15-20 millimeters per second, and frequency 5,000 to 20,000 Hz.
Step 3: Start Cutting. Start the cutting process and make sure the laser follows the design pattern.
Step 4: Clean After Cutting. Remove residual material with a soft cloth or compressed air.

Precautions For Cutting ABS Plastic
- Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from splashing plastic particles.
- Use a dust mask to avoid inhaling dust or fumes from the cutting process.
- Wear gloves to protect your hands from sharp edges and heated tool surfaces.

Other Issues
Can ABS Be Recycled?
Yes, ABS plastic can be recycled. It is a thermoplastic polymer, which means it can be melted down and reformed multiple times without significantly degrading its properties. Recycling ABS helps reduce waste and the demand for new raw materials, making it an environmentally friendly option.
Is ABS Plastic Harmful?
ABS plastic is generally considered safe for most uses. It is non-toxic and does not release harmful chemicals under normal conditions. However, when cutting or heating ABS, it can release fumes that may be irritating if inhaled. It’s important to work in a well-ventilated area and use appropriate safety gear, such as a dust mask.
Can I Cut ABS Plastic With A Utility Knife?
Yes, you can cut ABS plastic with a utility knife, but this method is best suited for thin sheets or scoring for snapping thicker pieces. To cut with a utility knife:
1. Secure the Plastic Sheet: Clamp the plastic sheet to a stable work surface.
2. Score the Cutting Line: Using a ruler and a marker, draw the cutting line. Score the line multiple times with the utility knife, applying firm pressure to create a deep groove. This method is effective for sheets up to 0.3 cm (3 mm) thick.
3. Snap the Plastic: Bend the sheet along the scored line to snap it cleanly.
How Do I Make Sure The Cut Is Straight?
To ensure a straight cut, follow these steps:
Use a ruler and a marker to draw a precise cutting line on the plastic. Secure the ABS plastic to a workbench with clamps to prevent movement.
For tools like a jigsaw or utility knife, use a straightedge or guide rail to follow the marked line accurately. Move the cutting tool slowly and steadily along the line, maintaining a consistent speed.
How Can I Avoid Melting When Cutting?
Melting can be avoided by managing the cutting speed and tool temperature:Set tools like a Dremel or jigsaw to a moderate speed (around 15,000-20,000 RPM for a Dremel and 2,500-3,000 strokes per minute for a jigsaw).
Take breaks to allow the plastic and tool to cool down. Ensure blades are sharp to reduce friction and heat. Work in a well-ventilated area to dissipate heat more effectively.
How Do I Make Sure The Cut Is Smooth?
For a smooth cut, follow these tips:
- Use sharp, fine-toothed blades for a cleaner cut.
- Maintain a steady hand and consistent speed to avoid jagged edges.
- After cutting, use fine-grit sandpaper (220-grit) or a sanding tool to smooth out any rough edges.
- Follow the correct cutting techniques for the specific tool you are using.

Lucas is a technical writer at ECOREPRAP. He has eight years of CNC programming and operating experience, including five-axis programming. He also spent three years in CNC engineering, quoting, design, and project management. Lucas holds an associate degree in mold design and has self-taught knowledge in materials science. He’s a lifelong learner who loves sharing his expertise.

