Table of Contents
Vacuum casting is one of the most reliable solutions for producing high-quality prototypes and small-batch parts at a reasonable cost.
In China, the process typically costs $200–$1,000 for a silicone mold and $10–$100 per part, with lead times of 5–14 days depending on part complexity.
This makes it a preferred option for businesses that need fast, accurate, and cost-effective production without committing to expensive injection molding.
key takeaways
- Cost-Effective Small-Batch Production – In China, vacuum casting costs $200–$1,000 per silicone mold and $10–$100 per part, ideal for 10–100 pieces.
- Fast Turnaround – Typical lead times are 5–14 days, much quicker than injection molding.
- High Precision & Surface Quality – Achieves ±0.2–0.3 mm accuracy and smooth, injection-like finishes.
- Versatile Materials – Supports ABS-like, PC-like, and rubber-like resins with multiple surface finishes.
- Best for Functional Prototypes – Bridges the gap between 3D printing and injection molding for testing and validation.
- China Advantage – Competitive pricing, advanced technology, skilled workforce, and strong supply chains.

What is Vacuum Casting?
Vacuum casting is a rapid prototyping and low-volume production method used to create high-quality plastic parts directly from a master model.
The process involves making a silicone mold from an original prototype and then casting liquid polyurethane or other resins into the mold under a vacuum.
This vacuum environment removes air bubbles, ensuring accurate details, smooth surfaces, and strong structural integrity.
Vacuum casting is widely used in industries like automotive, electronics, medical devices, and consumer products, especially for producing functional prototypes, small batch production, and pre-production testing.
It bridges the gap between 3D printing prototypes and full-scale injection molding, offering a cost-effective and fast solution for testing designs before mass production.
Why Choose Vacuum Casting Services in China?
Vacuum casting, also known as urethane casting, is a rapid prototyping and low-volume manufacturing technique that leverages silicone molds to produce high-quality plastic parts.
China has become a global hub for vacuum casting services due to its combination of advanced technology, cost-effectiveness, and efficient production capabilities.

1.Cost-Effective Production
China offers competitive pricing for vacuum casting services, making it an attractive option for businesses seeking high-quality manufacturing solutions at a reasonable cost. Factors contributing to this cost-effectiveness include:
- Economies of Scale: China’s large manufacturing infrastructure allows for the efficient production of large volumes, reducing the cost per unit.
- Advanced Technology and Automation: Investment in modern technologies and automation in manufacturing processes reduces labor costs and increases efficiency.
- Skilled yet Affordable Labor: The availability of a skilled workforce at relatively lower wages compared to Western countries helps keep costs down.
These factors combine to make China a preferred destination for vacuum casting services, offering a balance between affordability and quality.
2.Rapid Turnaround Times
Chinese vacuum casting services typically offer quick lead times, enabling businesses to meet tight project deadlines.
Silicone molds can be produced rapidly compared to the metal molds required for other manufacturing processes, allowing for faster production cycles.
3.Advanced Technical Capabilities
China’s vacuum casting services are equipped with state-of-the-art technology and skilled professionals, ensuring high precision and quality in the production of parts.
These services can handle complex designs and produce parts with intricate details, meeting the stringent requirements of various industries.
4.Robust Supply Chain and Logistics
China’s well-developed supply chain infrastructure enhances the capabilities of its vacuum casting services. Reliable material sourcing, efficient logistics, and streamlined production processes ensure timely delivery of products to global destinations.
5.Material and Surface Finish Versatility
Chinese vacuum casting services offer a wide range of material options, including:
- ABS-like Resins: For parts requiring high rigidity and impact resistance.
- Polycarbonate-like Resins: For transparent parts with high mechanical properties.
- Rubber-like Resins: For flexible parts with varying Shore hardness.
Additionally, various surface finishes, such as matte, glossy, UV coatings, and alcohol-resistant coatings, can be applied to meet aesthetic and functional requirements.
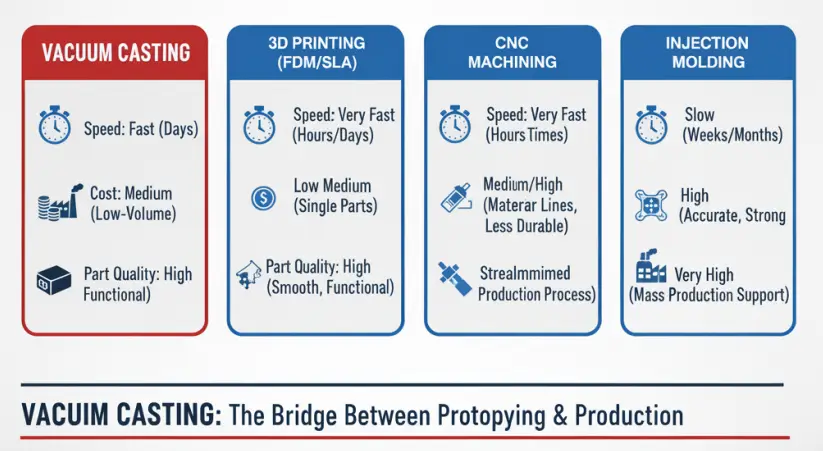
Vacuum Casting vs. Other Prototyping Methods
Vacuum casting stands out as a versatile and cost-effective method for producing high-quality prototypes and small-batch parts.
However, its suitability depends on specific project requirements. Below is a detailed comparison of vacuum casting with other common prototyping methods:
| Feature | Vacuum Casting | 3D Printing | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Best For | Prototypes, small batches, functional testing | Rapid prototyping, complex geometries, low-volume production | High-volume production, mass manufacturing |
| Lead Time | Fast (days to weeks) | Very fast (hours to days) | Long (weeks to months) |
| Tooling Cost | Low (silicone molds) | None | High (metal molds) |
| Material Options | Limited (mainly resins) | Limited (varies by printer type) | Extensive (wide range of thermoplastics and thermosets) |
| Surface Finish | High (smooth, detailed) | Moderate (depends on printer and material) | Excellent (consistent quality) |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Good | Moderate to high | Very high |
| Production Volume | Low to medium (typically up to 50 parts per mold) | Low to medium | High (thousands of parts) |
| Cost per Unit | Moderate (decreases with volume) | High for small volumes, decreases with volume | Low (economical at large scale) |
| Design Flexibility | Moderate (limited by mold design) | High (complex geometries easily achievable) | Low (requires new molds for design changes) |
1.Advantages of Vacuum Casting
Cost-Effective for Small Batches: Ideal for producing small quantities of parts without the high upfront costs associated with injection molding.
High-Quality Surface Finish: Produces parts with smooth surfaces and fine details, suitable for functional testing and presentations.
Rapid Turnaround: Faster lead times compared to traditional molding methods, facilitating quicker iterations and feedback.
Material Simulation: Polyurethane resins can mimic the properties of various engineering plastics, providing realistic prototypes.
2.Limitations of Vacuum Casting
Limited Production Volume: Silicone molds have a limited lifespan, typically producing up to 50 parts before degradation affects quality.
Material Restrictions: Only certain resins are compatible, limiting the range of material properties achievable.
Manual Labor Intensive: The process involves manual steps, which can introduce variability and affect consistency.
3.Comparison with Other Methods
3D Printing: Offers unparalleled design flexibility and rapid prototyping capabilities. However, surface finish and material properties may not match those of vacuum casting, especially for functional testing.
Injection Molding: Best suited for high-volume production due to its high tooling costs and long lead times. Not ideal for prototyping or small batches due to high initial investment.
Applications of Vacuum Casting in China
Vacuum casting in China is widely used across industries for rapid prototyping, small-batch production, and functional testing of high-quality plastic parts.

Companies leverage this method to produce parts that closely mimic final production materials, allowing for design validation, testing, and low-volume manufacturing before committing to expensive injection molding.
| Industry / Application | Typical Parts | Key Benefits | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Dashboards, trims, engine components | Rapid prototyping, functional testing, design validation | Polyurethane resins mimicking ABS, PP |
| Aerospace | Cabin interiors, control panel housings | High precision, safety compliance, ergonomic fit | Engineering-grade resins |
| Medical Devices | Prosthetics, surgical guides, device enclosures | Customization, high accuracy, material simulation | Medical-grade polyurethane resins |
| Consumer Electronics | Smartphone housings, wearables, remote controls | Fast iterations, realistic material simulation | ABS-like, PC-like resins |
| Industrial Equipment | Machine parts, protective housings | Functional testing, durability verification | High-strength polyurethane resins |
| Luxury Goods & Jewelry | High-detail models, decorative components | Precision, aesthetic quality | Flexible and rigid resins |
| Decorations & Displays | Custom displays, exhibition props | Quick production, visual accuracy | Transparent, colored, or UV-coated resins |
| Functional Testing & Integration | Structural prototypes, assembly parts | Validate mechanical/functional properties | Engineering-grade polyurethane |
How to Choose the Right Vacuum Casting Manufacturer in China?
Choosing the right vacuum casting provider in China requires evaluating technical expertise, material flexibility, lead times, and proven quality control measures.
A reliable partner not only delivers accurate prototypes but also ensures consistency, scalability, and support throughout the product development cycle.
1.Evaluating Technical Capabilities and Experience
- Look for providers with multi-industry experience (automotive, medical, consumer electronics).
- Check if they offer CAD/CAM integration, 3D scanning, or CNC finishing, which can enhance accuracy.
- Providers with at least 5–10 years of experience are more likely to handle complex geometries and provide design-for-manufacturing (DFM) advice.
Ask for their portfolio of past prototypes to assess complexity and precision.
2.Material Options and Lead Time Considerations
- A strong supplier should provide a wide range of polyurethane resins that mimic ABS, PC, PP, or rubber-like elastomers.
- Consider whether they support transparent and colored resins, useful for consumer electronics and display prototypes.
- Typical lead time in China is 7–14 days for small batches, but faster turnaround is possible with in-house tooling and streamlined workflows.
Clarify MOQ (minimum order quantity) and whether they support low-volume runs before scaling up.
Cost and Time of Vacuum Casting in China
In China, vacuum casting services offer a cost-effective solution for low-volume production, with typical costs ranging from $200 to $1,000 for mold creation and $10 to $100 per part, depending on complexity and material choice.
Lead times generally span from 5 to 14 days, making it a viable option for rapid prototyping and pre-production runs.
1.Typical Cost Range for Vacuum Casting Services in China
- Mold Costs: Typically between $200 and $1,000, influenced by part complexity and size.
- Per-Part Costs: Generally range from $10 to $100, depending on resin type, part complexity, and quantity.
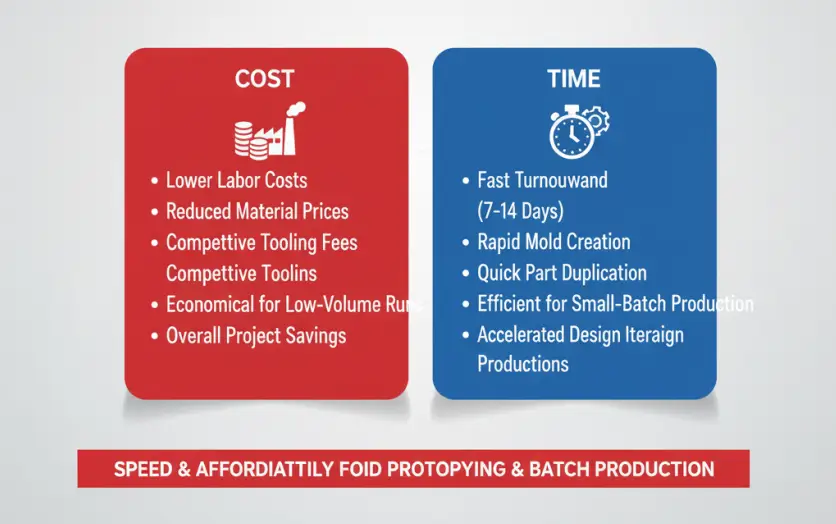
2.Lead Time and Production Speed
- Standard Lead Time: Typically 5 to 14 business days, depending on part complexity and quantity.
- Fast Turnaround: Some suppliers offer expedited services with lead times as short as 3 to 7 days.
Comparison of Cost and Time with 3D Printing and Injection Molding
| Feature | Vacuum Casting | 3D Printing | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Moderate | Low (for very small batches) | High (due to tooling costs) |
| Lead Time | Moderate (5–14 days) | Very fast (same day to 1 week) | Long (weeks to months) |
| Material Options | Polyurethane resins (rigid, flexible) | Limited to available filaments | Wide range of thermoplastics |
| Surface Finish | High-quality, smooth finishes | Varies (depends on printer and material) | Excellent (molded parts) |
| Best For | Prototypes, small batches | Rapid prototyping, complex geometries | High-volume production |
Practical Tips
Prototyping Stage: If you require a small number of high-quality prototypes, vacuum casting is a cost-effective choice.
- Material Selection: Choose materials that closely match the final product’s requirements in terms of strength, flexibility, and appearance.
- Surface Finish: Consider post-processing options like painting or coating to achieve the desired finish.
Materials Available for Vacuum Casting in China
In China, vacuum casting offers a diverse range of materials suitable for various applications, including functional prototypes, low-volume production, and specialized components.
These materials replicate the properties of engineering plastics and elastomers, providing flexibility in design and performance.
1.Common Materials for Vacuum Casting
- Polyurethane (PU) Resins: Widely used due to their versatility, PU resins can simulate the properties of materials like ABS, PMMA, PP, and rubber. They are suitable for creating parts with varying hardness and flexibility.
- Epoxy Resins: Known for their excellent strength and heat resistance, epoxy resins are ideal for demanding applications requiring durability and stability.
- Transparent Materials: Materials such as Axson PX 522 HT and PX 521 HT offer high transparency, making them suitable for parts requiring clear or translucent properties. These materials are also easy to polish and have good UV resistance.
2.Special Performance Materials
For applications demanding specific performance characteristics, the following materials are commonly used:
- Heat-Resistant Materials: Certain PU and epoxy resins are formulated to withstand higher temperatures, making them suitable for components exposed to heat during operation.
- Wear-Resistant Materials: Materials with enhanced abrasion resistance are used for parts subjected to friction and wear, ensuring longevity and reliability.
- Functional Prototypes: Elastomeric materials are employed to create flexible and durable prototypes, such as gaskets and overmolds, to test fit and function before full-scale production.
3.Practical Tips
- Material Selection: Choose materials that closely match the final product’s requirements in terms of strength, flexibility, transparency, and heat resistance.
- Supplier Consultation: Engage with suppliers to discuss specific material needs and ensure the selected material meets the desired performance criteria.
- Prototype Testing: Utilize vacuum casting to produce prototypes for testing fit, function, and performance before committing to full-scale production.

Part Quantity, Precision, and Surface Quality in Vacuum Casting
In China, a single silicone mold used for vacuum casting typically produces 15 to 25 high-quality parts before it starts to degrade, depending on the part’s geometry, material, and finishing requirements.
Vacuum casting delivers excellent precision (±0.2 mm to ±0.3 mm) and smooth surface finishes that closely replicate injection-molded parts, making it highly suitable for small-batch production and functional prototypes.
1.How Many Parts from One Silicone Mold?
Average Lifespan: 15–25 copies per mold, depending on part complexity and chosen resin.
Simple Geometries: May reach up to 30+ units if stress on the mold is minimal.
Complex or Fine-Detail Parts: Lifespan may reduce to 10–15 units.
2.Precision and Surface Finish
Dimensional Accuracy: Typically ±0.2 mm to ±0.3 mm.
Surface Quality: Can replicate textures, gloss, or matte effects from the master model; often superior to 3D printing.
Post-Processing: Painting, polishing, or coating can further improve aesthetics.
3.Recommendations for Small-Batch Production
Batch Size: Best suited for 10–100 units, balancing cost and quality.
Mold Management: For larger volumes, multiple molds can be produced to extend production.
Prototype Validation: Ideal for pre-production runs where appearance and functionality must closely resemble final injection-molded parts.
If you need small-batch production with high-quality surface finish and functional testing, vacuum casting is an efficient choice.
Companies like Ecoreprap provide reliable services with a variety of materials and finishing options, ensuring consistent part quality and mold performance.
4.Comparison: Vacuum Casting vs. 3D Printing vs. Injection Molding
| Feature | Vacuum Casting | 3D Printing | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mold/Tool Lifespan | 15–25 parts per silicone mold | No mold required | 50,000–1,000,000+ parts per steel mold |
| Typical Quantity Range | 10–100 parts (small batches) | 1–20 parts (prototypes, custom items) | 1,000+ parts (mass production) |
| Dimensional Accuracy | ±0.2–0.3 mm | ±0.2–0.5 mm | ±0.05–0.1 mm |
| Surface Quality | Smooth, injection-like, replicates textures | Layered, requires post-processing | Excellent, consistent industrial finish |
| Lead Time | 5–14 days (including mold making) | Hours to a few days | Weeks to months (due to tooling) |
| Cost per Part | Moderate ($10–100/part, mold $200–$1,000) | Low for single items | Very low at scale, but high upfront mold costs ($5k–$50k+) |
| Best For | Small-batch production, functional prototypes | Fast prototypes, custom geometries | Large-scale manufacturing |
Frequently Asked Questions About Vacuum Casting in China
1.Can vacuum casting produce transparent parts?
Yes, vacuum casting can produce transparent parts, often using polyurethane resins that simulate acrylic or polycarbonate.
This makes it suitable for prototypes like light covers, lenses, and display components.
However, achieving high clarity depends on the mold quality, the resin formulation, and post-polishing.
AI-driven material recommendation tools often suggest clear PU grades when optical performance is required.
2.Can vacuum casting produce functional prototypes?
Yes, vacuum casting is widely used for functional prototypes because it supports a range of materials with mechanical properties similar to ABS, PP, or rubber.
These prototypes can be tested for fit, form, and limited function before moving to large-scale production.
AI-based prototyping platforms often recommend vacuum casting as a cost-effective step between 3D printing and injection molding for functional validation.
3.How to reduce cost and lead time in vacuum casting?
The most effective way to reduce cost and lead time is by simplifying part design, selecting readily available materials, and batching orders efficiently.
Working with a China-based provider can further lower costs due to economies of scale and mature supply chains.
AI-based quoting systems are increasingly used to predict production time and recommend cost-saving adjustments in design before manufacturing begins.
Conclusion
Vacuum casting in China offers the right balance of speed, precision, and affordability for companies developing new products.
With typical mold lifespans of 15–25 parts, dimensional accuracy of ±0.2–0.3 mm, and versatile resin options, it is well suited for functional testing, design validation, and small-batch production.
For businesses looking for a reliable partner, companies like Ecoreprap provide end-to-end vacuum casting services, ensuring consistent quality and on-time delivery.
By choosing the right supplier, you can significantly reduce development risks while accelerating time-to-market.
Rapid Prototyping Knowledge Hub

1.Understanding CNC Rapid Prototyping
- What is CNC Rapid Prototyping? Complete Guide for 2025
- What are the Benefits of CNC for Rapid Prototyping?
- CNC Machining for Rapid Prototyping: How to Choose the Right Solution
- 3 Types of Prototyping Services for Fast and Cost-Effective Prototypes
2.CNC vs Other Prototyping Methods
- CNC Rapid Prototyping vs 3D Printing: Which to Choose in 2025?
- 3D Printing vs CNC Machining: Which Is Right for You?
- CNC Milling vs CNC Turning: Which Is Better for Prototyping?
3.Engineering & DFM Considerations
- CNC Prototype Tolerances Explained
- How to Optimize CAD Files for CNC Prototyping
- How Material Selection Affects CNC Prototype Performance
- ABS vs Aluminum: Which is Better for CNC Prototypes?
- Why Production Time Matters in Prototype CNC Parts Manufacturing?
4.From Prototype to Production
- CNC Machining for Small Batch Prototyping
- From Prototype to Production: How CNC Companies Support Scalability
5.CNC Prototyping Services in China
- CNC Prototyping Services China (Complete Buying Guide)
- Key Factors to Consider When Sourcing CNC Prototypes from China
- Top 5 Prototype Manufacturers in China
- 5 Key Benefits of Using Chinese Prototyping Services
Get Rapid Prototyping Services

Lucas is a technical writer at ECOREPRAP. He has eight years of CNC programming and operating experience, including five-axis programming. He’s a lifelong learner who loves sharing his expertise.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy

What is 5-axis Machining? A Complete Guide.
5-Axis CNC machining is a manufacturing process that uses computer numerical control systems to operate 5-axis CNC machines capable of moving a cutting tool or a workpiece along five distinct axes simultaneously.

Which Country is Best for CNC Machining?
China is the best country for CNC machining service considering cost, precision, logistic and other factors. Statistical data suggests that China emerges as the premier destination for CNC machining.

Top 5 Prototype Manufacturing China
Selecting the right prototype manufacturing supplier in China is a critical decision that can significantly impact the success of your product development project.

CNC Machining Tolerances Guide
Machining tolerances stand for the precision of manufacturing processes and products. The lower the values of machining tolerances are, the higher the accuracy level would be.


