PLA is well-known in 3D printing circles as biodegradable plastic. Although beneficial in most cases, this characteristic has also caused concerns over the longevity of PLA as a 3D printing material. How long does PLA 3d print part go bad?
The good news is that PLA objects should last several years under normal circumstances. However, certain conditions can accelerate the breakdown of PLA. Avoiding these conditions is the key to making your PLA print last longer.
Does PLA Have a Shelf Life?
The concerns mainly stem from the fact that its filament form tends to degrade quickly. 3D printing professionals often advise storing PLA filament in a low-humidity environment. It would be best if it stayed away from sunlight to maintain its good printing performance. Then the prints will be more robust.
PLA prints kept and used indoors will last virtually forever if they are not used to sustain heavy mechanical loads. Based on anecdotal evidence, an object made of PLA will at least 15 years when kept indoors. Under these conditions, You should have no problem with gifts and decorative items printed with PLA.
However, things may be different if PLA is exposed to outdoor conditions for sustained periods. Depending on the temperature, humidity, and exposure to sunlight, PLA may degrade to a state where it is no longer functional. How long this process takes can vary widely based on specific conditions. In most cases, a PLA object can last for about a year outdoors before deteriorating heavily.
Reasons For PLA Prints Go Bad
Whether indoors or outdoors, there are factors that can accelerate the breakdown of PLA. To make your PLA print last, make sure to avoid exposure to these conditions:
Moisture
The breakdown of PLA mostly happens in the process of hydrolysis. PLA polymer can react with water at a shallow speed, which breaks the long polymer into smaller chains. That is the same reason for PLA filament becoming brittle when exposed to moisture.
Naturally, one of the best ways to prevent hydrolysis is to limit PLA exposure to moisture. For this reason, We do not recommend use PLA for the long-term storage of food or drinks.
PLA prints tend to fare poorly in very humid environments. Having a PLA print sit outside under the rain is also a sure way to break down faster.
Sunshine
Photodegradation is the process by which the properties of polymers diminish when exposed to sunlight or UV radiation. PLA has no specific resistance to the effects of photodegradation. There are two signs of PLA degrading due to UV radiation – increased brittleness and bleached colors.
PLA develops brittleness through crosslinking reactions induced by UV radiation. Then PLA will be stiffer and prone to breaking apart. Moreover, the crosslinks are more vulnerable to oxidation which will deteriorate the polymer into smaller chains.
Plastic bleached by UV tends to take on a characteristic yellow color. This affects the stabilizing agents in the plastic, turning into free radicals upon exposure to UV radiation.
Any dyes in the PLA filament can also be broken down by UV radiation, resulting in a gradual fading of colors.
High Temperature
Exposing PLA to high temperatures is generally not recommended. PLA prints can show signs of warping with a relatively low glass transition temperature of only 60 to 65 °C when left outside on sweltering days. It is standard advice not to use PLA 3d printed parts in your car.
Elevated temperatures also increase the diffusion rate of moisture into PLA, making it even more prone to hydrolysis. The situation will be worse in hot and humid environments.
Microorganisms
We know that PLA is a biodegradable material. It can be broken down into its constituent monomers by biological matter. If you want PLA to last longer, then make sure to keep it away from any medium that is rich with microorganisms such as soil, plants, or water.
Other factors can also accelerate the breakdown of PLA due to microorganisms. Short-chain polymers resulting from hydrolysis or oxidation will be more vulnerable to biodegradation.
Even among all the 3D printing communities worldwide, understanding what makes PLA degrade is still somewhat flawed. Several other factors come into play here, such as the filament brand, additives, and the type of pigments used to impart color.
The environment will play a huge role in determining how well a PLA print stands up to the test of time.
Slowing down moisture degradation and keeping your PLA print away from direct sunlight are the two most important rules of thumb for making it last as long as possible.
How To Make PLA 3D Printed Parts Last Longer
In most cases, there is little thing you can do about the environment in which the 3D-printed PLA objects will use. You can change 3D printer settings to make the finished product more resilient.
Some post-processing techniques can also help you in achieving this objective.
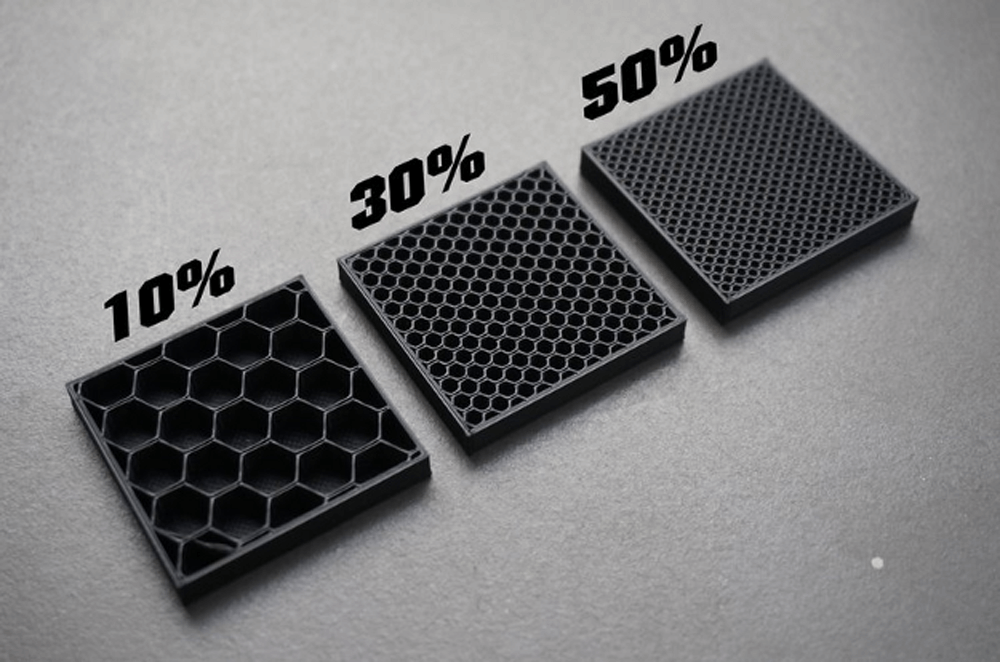
Interior Density
Increasing its infill density can make PLA print more robust. It increases mechanical strength and makes it more resilient against the elements. Your slicer software should allow you to adjust interior density from zero (completely hollow) to 100 (completely solid).
The advantage of a higher infill density is that it supports your finished print’s shell and allows for more even stress distribution. It also makes the patterns more premium because of the added heft. However, expect to use up significantly more filament and spend more time finishing your 3D printing project.
Composite Material
Composite filaments that use PLA as the polymer matrix are now ubiquitous. Such as wood, metal, or ceramics. Composite filaments allow you to create 3D-printed objects that mimic the appearance of materials that are traditionally not used in 3D printing.
Some composite filaments can even contain solid materials such as carbon fiber. This material adds strength to PLA at the cost of reduced flexibility.
Just a word of warning – composite metal or carbon fiber is nowhere near as strong as the real thing. It should hold up to the elements better than standard PLA, but you can not expect it to act like real metal, wood, carbon fiber, or ceramics.
Orientation
3D printing technologies are based on building an object layer by layer. Unfortunately, the boundaries between these layers act as natural weak points of the final 3D-printed product. In this regard, a 3D-printed object’s strength is considered anisotropic or varying in different directions.
A strategy you can do is consider how stress will be applied to the object during its application. Make sure that the weak boundaries are closer to parallel to the direction of stress rather than perpendicular. With this in mind, you can alter the model’s orientation in your slicer so that the layer boundaries are more favorable to your purpose.
Injection
Being able to print hollow objects is one of the distinct advantages of 3D printing. This makes 3D-printed objects lighter, cheaper, and faster to manufacture. On the other hand, it also makes 3D printed items less durable and more prone to degradation by the elements.
A unique technique to strengthen 3D prints is to inject an adhesive material into the internal cavity. You can drill small holes on the shell to allow for injection. It is a quick and inexpensive method to strengthen a 3D print, although not considered fit for professional use.
Coating / Plating
A finished 3D print made of PLA can be post-processed to enhance its properties. Post-processing options can include coating with a water-resistant material or electroplating for improved strength.
Improving water resistance can be done by simply painting 3d prints outer walls. If the parts have been sanded smooth, Paining with epoxy will have more consistent application. This typically also imparts a glossy finish to the surface.
Electroplating is a process for coating 3D-printed parts with metals such as copper or nickel. Not only does this provide enhanced strength to the PLA print but also makes its surface electrically conductive.
Before the plating treatment, you should ensure that the PLA print surface is sanded and polished smooth.
This list highlights how different ways to make a PLA print last longer, ranging from changing a few settings in your slicer to more advanced post-processing techniques. The most prudent approach would be to consider precisely how your PLA print will be used and decide on a strategy accordingly.
Summary
PLA may be one of the most popular materials used in 3D printing, but users also recognize its resiliency deficiency. It is the best option for items that are to be kept and used indoors. 3D-printed parts made of PLA aren’t typically strong enough to support a large amount of stress.
Keeping PLA prints away from moisture, heat, or sunlight is the best way to make them last longer. Meanwhile, reinforcing PLA with denser infill or post-processing treatment can also be considered.