Table of Contents
Everyone goes through various struggles when choosing the clear filament for the first time. There are several types of clear filament on the list.
So if you have trouble making your decision, you are just getting the start, or you need to test all the material – don’t worry.
You are in the right place. Here are so many plastic materials could be used in 3d printer. The most commonly used clear or transparent 3D printer filaments are PLA, PMMA, PETG, PET, Clear ABS, Polycarbonate, and TPU. Let’sLet’s talk about the positives, negatives, and best printing tips one by one.
PLA
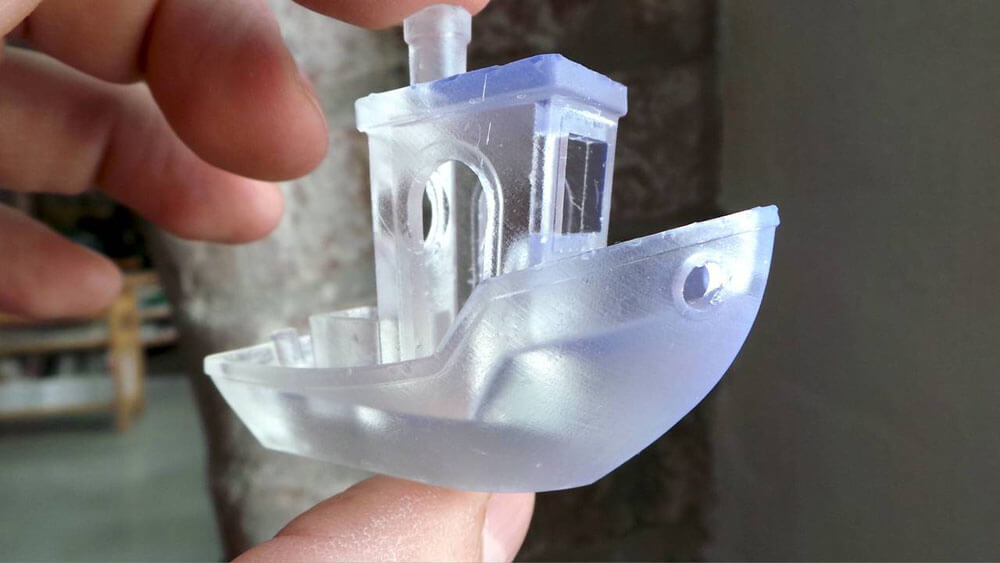
The natural PLA resin is not clear. It has a very faint yellow tinge. If you compared with clear PLA filament from different manufacturers, there will be a slight difference. The tip is the process temperature. If the temp setting is higher, PLA resin could be perfect recrystallization. Then the filament will be more transparent.
The transparency is different from the resin manufacturer. There are two manufacturers for PLA raw resin. One is NatureWorks, the other is Hisun, We have made opacity tests with 4032D, 4043D(from Naturelwork), and 190(from Hisun), The opacity of 190 is much better than 4032D and 4043D.
Liking ABS, PLA is a commonly used filament in 3d printing. It is biodegradable and has excellent properties. Translucent PLA filament is one of the easiest to print clearly and get good results. To get the smooth finish of the surface, sanded is needed after printed. The part is close to the clear after filed.
Choose the right sandpaper is essential. This depends on the layer height in the setting. Thicker layers need courser sandpaper. Then use more delicate and finer grits, sanding in a circular motion each time (this bit is crucial because you’re trying to remove all surface imperfections). Start at the start, maybe 800 grit, and upwards in 200 increments from there. Finish with 3000 or higher grit to get a smooth finish.
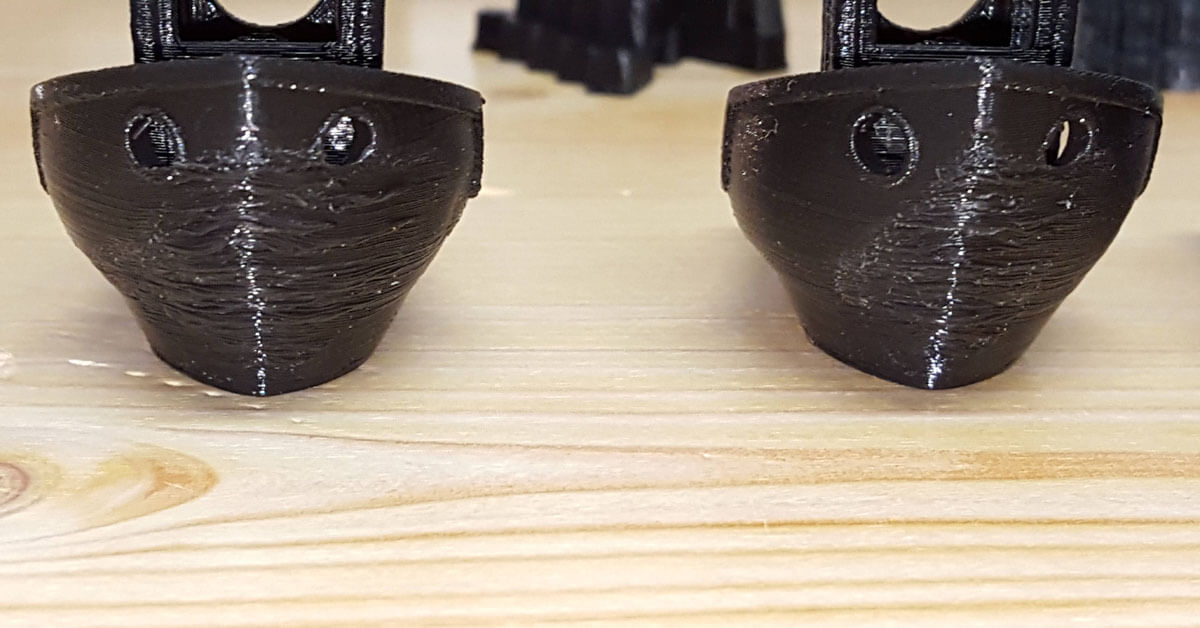
ABS
The nature of abs is not transparent. Clear abs are a particular type of abs material. The short name is MBS. Other additives will be added to make it clear.
Clear abs filament cannot print as clearly as the material. It needs to be post-print finished with Acetone vapor smoothing.

PETG
PETG is a durable clear 3D filament with excellent layer adhesion (almost unbreakable) and less shrinkage than other filaments; it’s great for 3D printing clear, big stuff that won’t break under pressure. It is odorless when printing and often produces clear, smooth finishes. Meanwhile, PETG has abs material’s flexibility and PLA’s strength.
PETG can’t smooth with acetone pour, but it can sand. Compared with PLA sanding, PETG printed object is smoother, which means that you need to use higher grit.
PMMA
PMMA is the most transparent material so far. It has high strength and impact resistance.
PMMA is commonly used to replace glass in a particular application, such as cellphone screen and sunshine glass. The opacity of pmma is about 92%, much more than other clear plastic.
PMMA can be manually polished and vapor polished to be quite clear.

Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate is an extremely durable and optically transparent 3D printing filament that should print in a warm environment. Its durability can be bent repeatedly without cracking, making it great for creating all sorts of hipster jewelry.
But seriously, Polycarbonate (PC) is an immensely underrated material to print. It finishes with a nice glossy sheen to it. It needs a very hot extruder to print it usually, and if you’re looking for translucent results, we’d recommend going even hotter still (300 C+).
A great advantage with PC is that it can smooth with acetone like ABS to bring out more apparent results.
Polycarbonate parts made via CNC maching can be high transparent after vaopor polishing polycarbonate.
For more information about vapor polishing steps, learn the blog vapor polish steps guide.

TPU
TPU is the only flexible material used for clear parts. It has good elongation and flexibility. Due to this property, Tpu is commonly used in bracelets and use wine and charge wine.
About the Tpu filament, printer settings are different from other materials. The extruder structures are different, and the printing speed is slower. For the details, we will write on the next page.
How Can you 3D Print Transparent Materials?
3D printing transparent materials can be approached in different ways, depending on the application’s requirements. For rough prototypes or tooling, FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) technology can be used with transparent filament. Though this method may not achieve full transparency, a certain degree of translucence can be attained through extensive sanding and coating.
For high-fidelity models or final use parts requiring true transparency and a smooth finish, photopolymer materials are a better choice. Materials like Stratasys VeroClear™ and VeroUltraClear™ are specifically designed to provide a smooth finish and high light transmission, resulting in excellent clarity.
FDM technology is a common 3D printing method that builds parts layer by layer by extruding thermoplastic filaments. This technique is popular for its versatility and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including those requiring transparent or translucent parts.
How to Get the Transparent Filament to Print Clear
To achieve a truly clear 3D print using transparent filament, there are several critical factors to consider. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
Use the Right Filament
PETG is often the preferred choice for transparent prints due to its excellent layer adhesion, durability, and smooth finish. PLA and ABS are also options, but they may not provide the same level of clarity without significant post-processing. Clear PLA tends to appear more translucent or slightly foggy, while ABS may require additives to achieve transparency.
Print Settings
- Infill: Set the infill to 100%. Any gaps or air pockets within the object can distort light, making the print less transparent.
- Layer Height: Print with thicker layers—around 90% of your nozzle diameter—to reduce internal reflection and create clearer prints. This helps reduce diffraction and gives light a smoother path through the object.
- Temperature and Speed: Print at a higher temperature (at the upper end of your filament’s recommended range) to ensure layers fuse together completely. Lower your printing speed to around 25-30 mm/s to improve accuracy and layer bonding.
- Disable Cooling Fans: Cooling fans can cause uneven cooling of the filament, leading to imperfections in transparency. It’s recommended to turn them off or minimize their use during printing.
Post-Processing
- Sanding: After printing, use a variety of sandpaper grits (starting from low to high) to smooth out any rough surfaces. Polishing is crucial for removing any remaining layer lines that affect transparency. For PLA, this may require sanding up to a 4000-grit level.
- Polishing and Coating: Once sanded, you can further enhance transparency by applying a clear coat or polishing paste. This can significantly improve the visual clarity of your print.
By optimizing your filament choice, printer settings, and post-processing methods, you can create a clear, almost glass-like 3D-printed object. PETG is usually the best starting point for those looking for less post-processing, while ABS may require more effort but allows for smoothing using acetone.

Summary
PETG is your first choice for clear filament. It has suitable property and is nicely finished. Meanwhile, if you need flexible material, TPU has the advantage.
For clear products, we can use FDM 3d printing technology, SLA 3d printing, and CNC machining.
ECOREPRAP’s main business has shifted from 3D printing filaments manufacturing to 3d printing services and CNC machining services since 2023. We will continue to share related blogs about filaments and CNC machining.

Lucas is a technical writer at ECOREPRAP. He has eight years of CNC programming and operating experience, including five-axis programming. He also spent three years in CNC engineering, quoting, design, and project management. Lucas holds an associate degree in mold design and has self-taught knowledge in materials science. He’s a lifelong learner who loves sharing his expertise.


