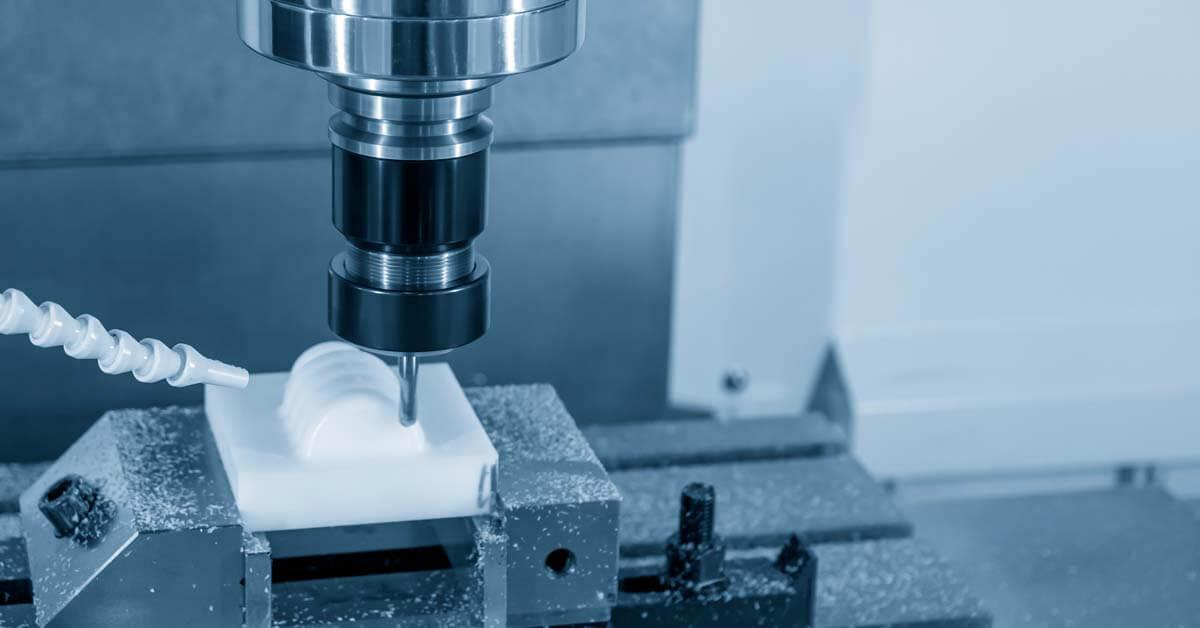
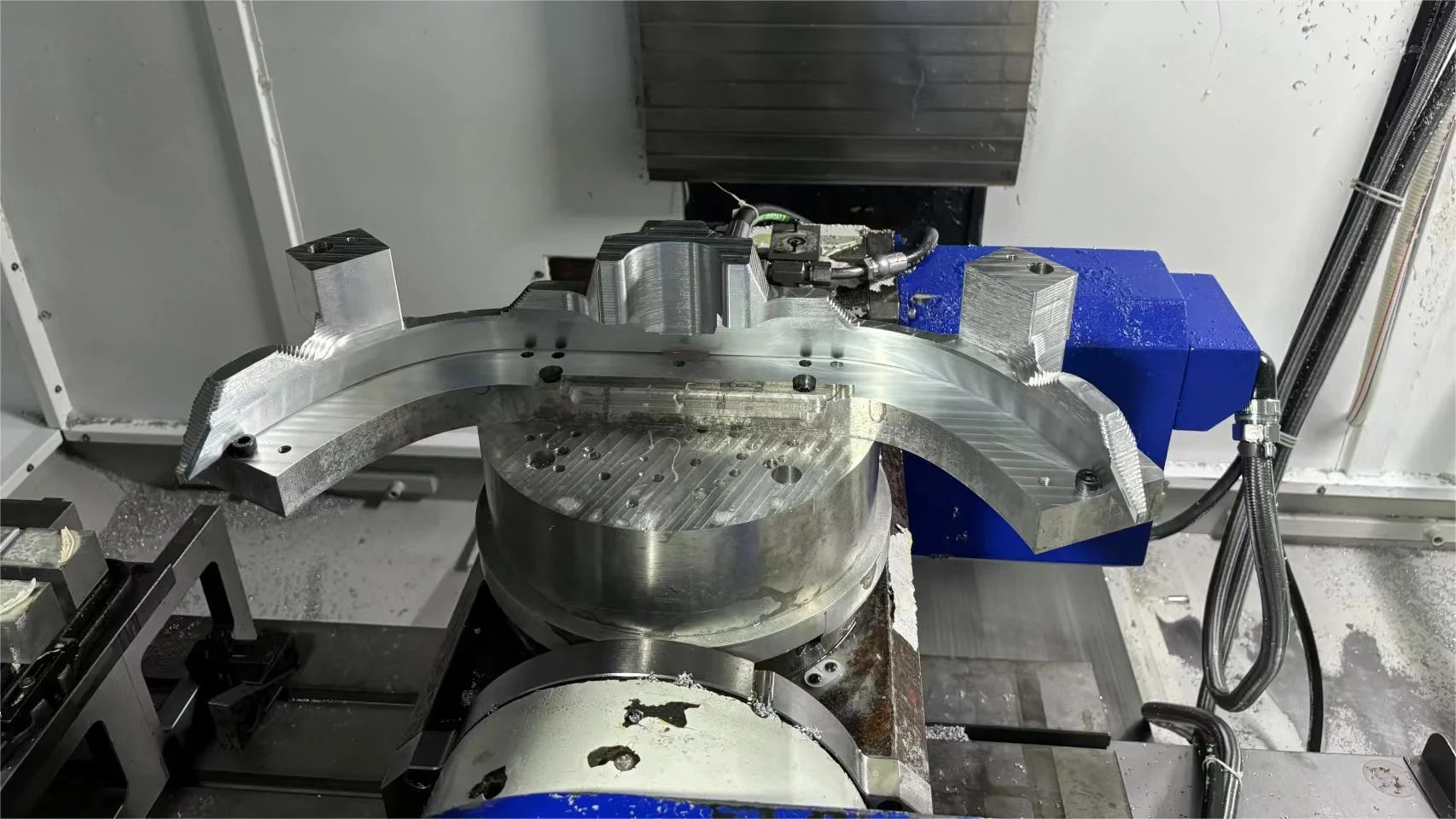
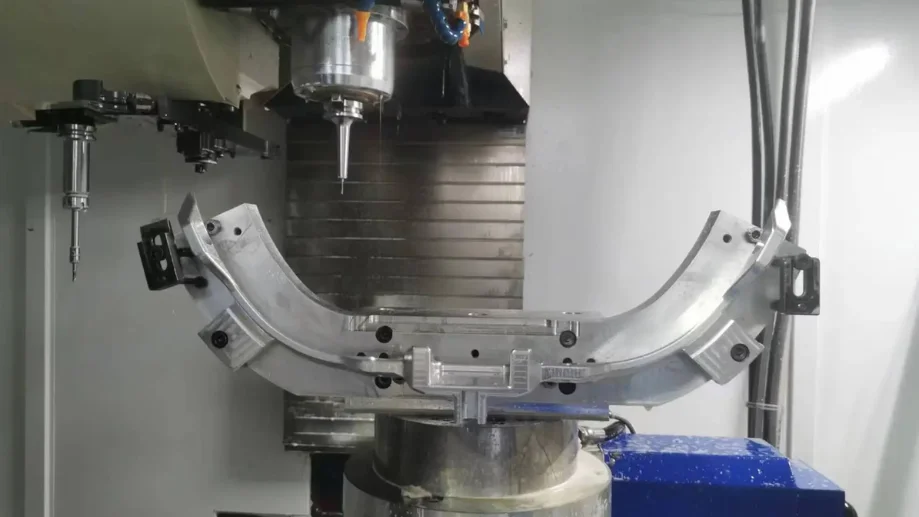
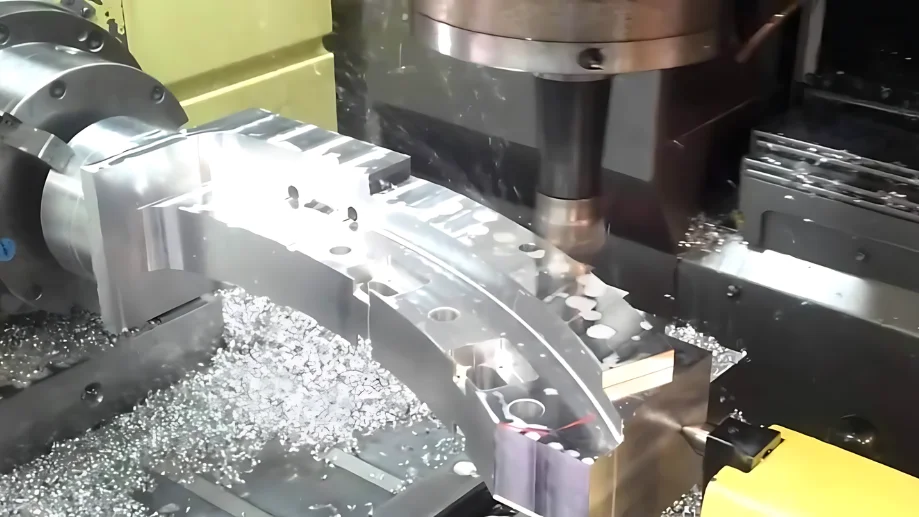
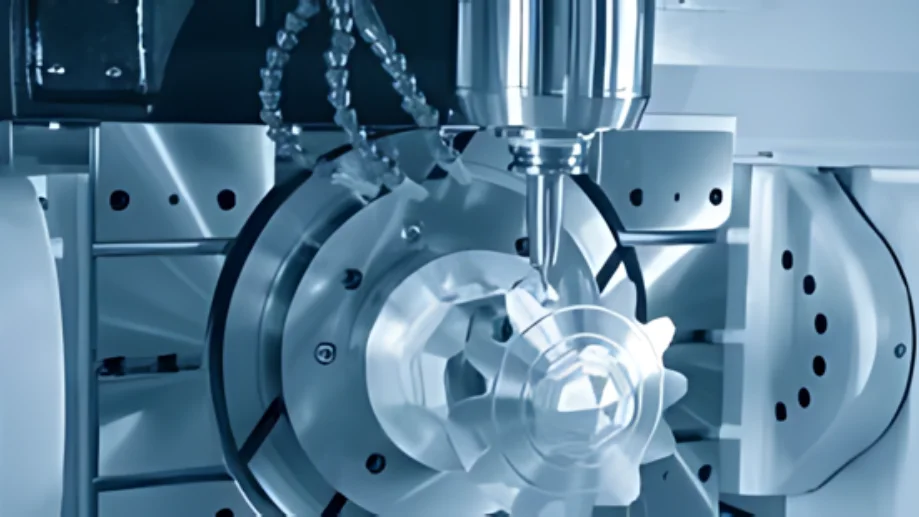
With a 3-axis CNC milling machine, by moving the cutting tool in three directions – left and right (X-axis), front and back (Y-axis), and up and down (Z-axis) – it is possible to manufacture complex parts with great precision.
What Is A 3 Axis CNC Milling Machine?
How Does A 3 Axis CNC Milling Machine Work?
Simply put, a 3-axis CNC milling machine is a machine that automatically engraves. Take a look at how it works.
Step 1: Design Components
Design the desired part using CAD (Computer Aided Design) software such as AutoCAD, SolidWorks, and Fusion 360.
Accurately mark all dimensions, tolerances, material specifications, and features, and then use the software to create a detailed 3D model of the part.
Specific example: Design a custom gear in Fusion 360. Set the outside diameter to 100 mm, and the inside diameter to 50 mm, and add 20 teeth with a specific tooth shape.
Step 2: Convert Design to Code
Use CAM (Computer Aided Manufacturing) software to convert the design into a language that the machine understands, such as Mastercam, and Fusion 360 CAM.
This step generates G-code, which is essentially the instruction set for the machine. Pay attention to the following names and parameters:
- Toolpath: Defines the path of the cutting tool.
- Cutting Speed (S): Typically measured in RPM (revolutions per minute).
- Feed Rate (F): The rate at which the cutting tool moves through the material, in millimeters per minute.
- Depth of Cut: The depth of each cut of the tool into the material.
Example: In Mastercam, generate a toolpath for a gear with a spindle speed of 1500 RPM, a feed rate of 300 mm/min, and a depth of cut of 2 mm.
Related reading: 4 Axis CNC Machine: The Complete Guide in 2024
Step 3: Set up the machine
Before the machine starts cutting, you’ll want to check the table and the material to make sure there’s no debris in the way.
In addition to this, you will need to set up the instrument. This includes securing the raw material (e.g., a metal or plastic block) to the machine’s table and making sure everything is perfectly aligned.
For the material setup, you’ll want to decide whether to use a vise or jig to hold the material in place. For the alignment tool, you’ll want to consider whether to use a dial indicator or an edge finder.
Example: Use the fixture to secure a 150 mm x 150 mm aluminum block to the table. Use a micrometer to check flatness and an edge finder to determine the position of the material edge relative to the machine’s zero point.
 Step 4: Execute the milling process
Step 4: Execute the milling process
With the design ready and the material in place, the machine starts working. It then follows G-code instructions to move the cutting tool along the X, Y, and Z axes to remove material and shape the part.
This is done as follows:
- Machine Initialization: Power on the machine and set all axes in place to set the starting position.
- Load G-Code: Transfers a G-code file to the machine controller via USB or network.
- Start Run: Begin the milling process and monitor the initial cut to ensure accuracy.
Example: Load the G code for the gear into the machine, set the spindle speed to 1500 RPM, and start the cutting sequence. The machine first cuts the OD, then the ID, and finally the gear teeth.
Step 5: Monitor and Adjust
Throughout the milling process, operators monitor the machine to make sure everything is running smoothly. They make adjustments as needed to maintain accuracy and prevent errors.
Monitoring tools can be used to monitor real-time data from the control interface in real-time, primarily through visual inspection, and make adjustments based on problems.
For example, if the machine is tight, adjust the feed rate or spindle speed. Pause operation to remove chips or debris if necessary. Use coolant to prevent overheating and improve cutting efficiency.
Example: If the tool is tight, reduce the feed rate from 300 mm/min to 250 mm/min. Apply coolant to the cutting area to maintain optimum temperature.
Step 6: Finishing
After the milling is complete, the part is usually subjected to additional processes such as polishing, cleaning, or coating to achieve the final finish.
The following operations are mainly performed:
- Deburring: Use a file or deburring tool to remove sharp edges or burrs.
- Polishing: Use sandpaper or polishing wheels to smooth the surface.
- Clean: Clean the part to remove cutting fluids or debris.
- Coating: Apply protective coatings as needed, such as anodizing aluminum parts.
Example: After milling, deburr the edges of gears with a fine file, polish the surface with 600-grit sandpaper, clean with isopropyl alcohol, and apply an anodized coating for durability.
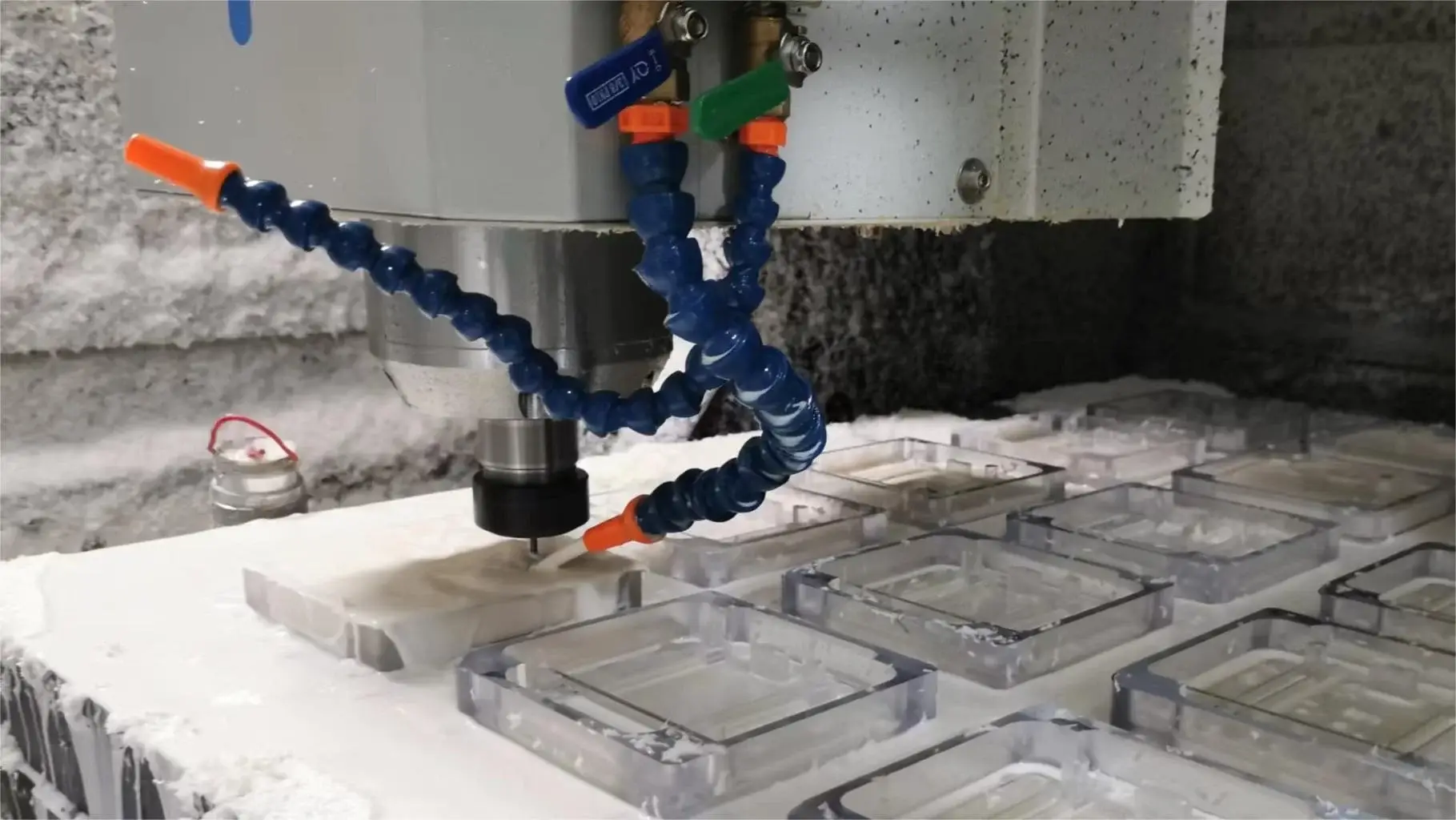

What Are The Types Of 3 Axis CNC milling Machines?

Features And Advantages Of 3 Axis CNC Milling Machine
What Is The Difference Between 3 Axis CNC Milling Machine And Other Axes?
There are also differences between the various CNC mills, and this article will compare 3-axis CNC mills with 4- and 5-axis CNC mills, highlighting their unique features, capabilities, and applications.
3 Axis Vs 4 Axis CNC Milling Machine
A 4 Axis CNC milling machine adds an additional rotational movement to the basic three axes of the 3 Axis machine. This fourth axis, often called the A-axis, allows the cutting tool or the workpiece to rotate around the X-axis.
When comparing three-axis and four-axis CNC milling machines, the main differences are in their motion capabilities and applications. Three-axis CNC machines move the cutting tool along three linear axes (X, Y, and Z) and are suitable for simple parts that need to be machined in a single plane.
In contrast, four-axis CNC machines add rotary motion around the X-axis (A-axis) and can handle more complex shapes and geometries, such as curved and cylindrical workpieces.
While 3-axis machines are more affordable and easier to operate, 4-axis machines cost more because of their ability to reduce manual repositioning, increase productivity, and handle complex designs.
The choice between the two ultimately depends on the complexity of the project and budgetary factors.
3 Axis Vs 5 Axis CNC Milling Machine
A 5 Axis CNC milling machine includes two additional axes beyond the basic three of the 3 Axis machines. These are usually the B-axis (tilt along the Y-axis) and the C-axis (rotation around the Z-axis), allowing the cutting tool to approach the workpiece from virtually any angle.
A major difference between the two is cost. Three-axis CNC machines cost less to purchase, program, and operate and therefore cost less per part.
Another key difference is their ability to create and process complex shapes. A 5-axis CNC machine excels at machining complex geometries and making deep cuts. It can machine all sides of a workpiece without the need for manual repositioning, which greatly increases productivity.
In contrast, three-axis machines require multiple adjustments and repositioning to handle complex geometries, which is not only time-consuming but also less efficient.
Conclusion
This article details 3-axis CNC mills and briefly describes the differences between 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC mills, which will help you choose the right machine for your needs and ensure optimal productivity and quality.
ECOREPREP offers 3 Axis, 4 Axis, and 5 Axis services. For all inquiries regarding CNC Milling services, we will let our team of specialized application engineers help you select the right material for your respective needs. To use and consult on your project, please contact us.


Lucas is a technical writer at ECOREPRAP. He has eight years of CNC programming and operating experience, including five-axis programming. He also spent three years in CNC engineering, quoting, design, and project management. Lucas holds an associate degree in mold design and has self-taught knowledge in materials science. He’s a lifelong learner who loves sharing his expertise.