Rapid Prototyping in Manufacturing: The Ultimate Guide in 2023
Updated: December 07, 2023
Table of Contents
- 1. How Does Rapid Prototyping Work?
- 2. Types of Rapid Prototyping Techniques
- 3. What is Rapid Prototyping Used for?
- 4. Advantages and Disadvantages of Rapid Prototyping
- 5. Why is Rapid Prototyping Important?
- 6. How Much Time Does Rapid Prototyping Save?
- 7. How Much Does Rapid Prototyping Service Cost?
- 8. How to Start a Rapid Prototyping Business?
- 9. 9. Working with ECOREPRAP for Prototypes
Rapid prototyping is referred to as the fast fabrication of new components using subtractive manufacturing (SM) or additive manufacturing (AM) – 3D printing techniques. Prototyping machines perform fabrication using computer-aided design (CAD) files with 3D digital models.
There is a broad range of techniques to learn more about and employ. Let’s discuss them in detail.
1. How Does Rapid Prototyping Work?
Here are the basics of rapid prototyping. Prototype – any component, part, or detail of an innovative design and with particular properties that have not been in production yet.
Manufacturers do not have reports of how to produce it, and what are its physical features. That’s why prior testing and examination are needed.
Under testing, engineers understand conducting sets of trials intended to find what are the properties of a part. To make it possible, specialists need a component that is produced as close to the intended manufacturing process as possible.
The primary purpose of rapid prototyping – fabricate a component using manufacturing techniques that you will exploit in large-scale production further. In some cases, you can pick any rapid prototyping technique you like. But, such components are unsuitable for real quality testing. They are for examining a design only.
In essence, rapid prototyping is a fast fabrication of a prototype needed to facilitate the run of production.
As explained further, you can produce these test samples either using subtractive manufacturing, i.e., by removing material out of a workpiece. Or by additive manufacturing, i.e., adding material on a worktable or a workpiece.

2. Types of Rapid Prototyping Techniques
SLS
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D printing is an AM technique. It exploits a high-power laser to heat up and sinter particles of polymer powder in solid material. In such a manner, SLS 3D printers create durable models based on CAD files.
The process typically consists of the following stages:
- Dispersing thin layers of materials on a platform and preheating them to nearly the melting point.
- Scanning the cross-section of a 3D model and sintering material at the same time to create a solid structure.
- Cooling down the build chamber in which a component was printed.
- Removing the finished parts from the build chamber and cleaning.
SLS 3D printing is one of the traditional methods of AM rapid prototyping. It can produce comparatively durable and functional parts. Unfortunately, the surface quality is low, and fabricated parts always require extra finishing.
Related Post: SLA 3D Printing: Is UV Resin Toxic?

FDM
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D printing AM technique. You may have heard of it as material jetting. It is the most common and affordable rapid prototyping method. Non-industrial 3D printers usually employ FDM.
The basis of the technique is melting the thermoplastic filament and laying it down layer-by-layer by a CAD file.
Such deposition technology enables the creation of rather weak parts out of a limited choice of materials. However, it is still widely used by non-experts, something in the conditions of office premises, to take a quick look at a future design.

SLA
Stereolithography (SLA) or Vat Photopolymerisation is another 3D printing AM technique. The principle of the technology is the use of a photosensitive liquid that is solidified by computer-controlled ultraviolet (UV) light.
Stereolithography is highly popular as an industrial 3D printing technology. That is why you may typically be offered it as a rapid prototyping method.
In contrast to other AM prototyping, SLA is compatible with a range of materials with different properties and is highly accurate. You typically do not need to add an extra finish to SLA printed parts, but it is advised that you do not expose them to UV light any further to prevent disruption.

MJF
Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) is also a 3D printing MA technique. It employs functional nylon for the fast production of test samples.
The basis of the technology is applying fusing and detailing agents on a bed of nylon powder. And then, these added agents are fused by heating elements, thus forming a solid layer. Then, the powder is added to the top of the bed, and the process is repeated to completion.
You can receive durable prototypes with enhanced mechanical properties and with a high-quality surface with MJF.

Binder Jetting
Binder Jetting lets you produce many parts simultaneously. The way it works is the use of a powder bed, again, on which droplets of a liquid are sprayed. This liquid bonds the powder particles together, forming layers. Then, a raw component is oven-baked and fused.
You can pick out many materials using binder jetting. Also, it is a common industrial manufacturing method. So if you prototyped your innovative component with it, parts can be tested as per quality assurance standards.
Binder jetting is known for high production speed, but it is a comparatively expensive technique.
Injections Molding
Injection molding is an interesting MA technique, mostly intended for the mass production of plastic components. It also can be advised to implement rapid prototyping, but only if large-scale injection molding manufacturing is intended further. Overwise, the method would not be cost-effective.
Injection molding is melting materials, injecting them into a mold, solidifying them, and cooling them. Only comparatively simple designs can be obtained using this method. However, fabricated components are durable and have acceptable surface quality.
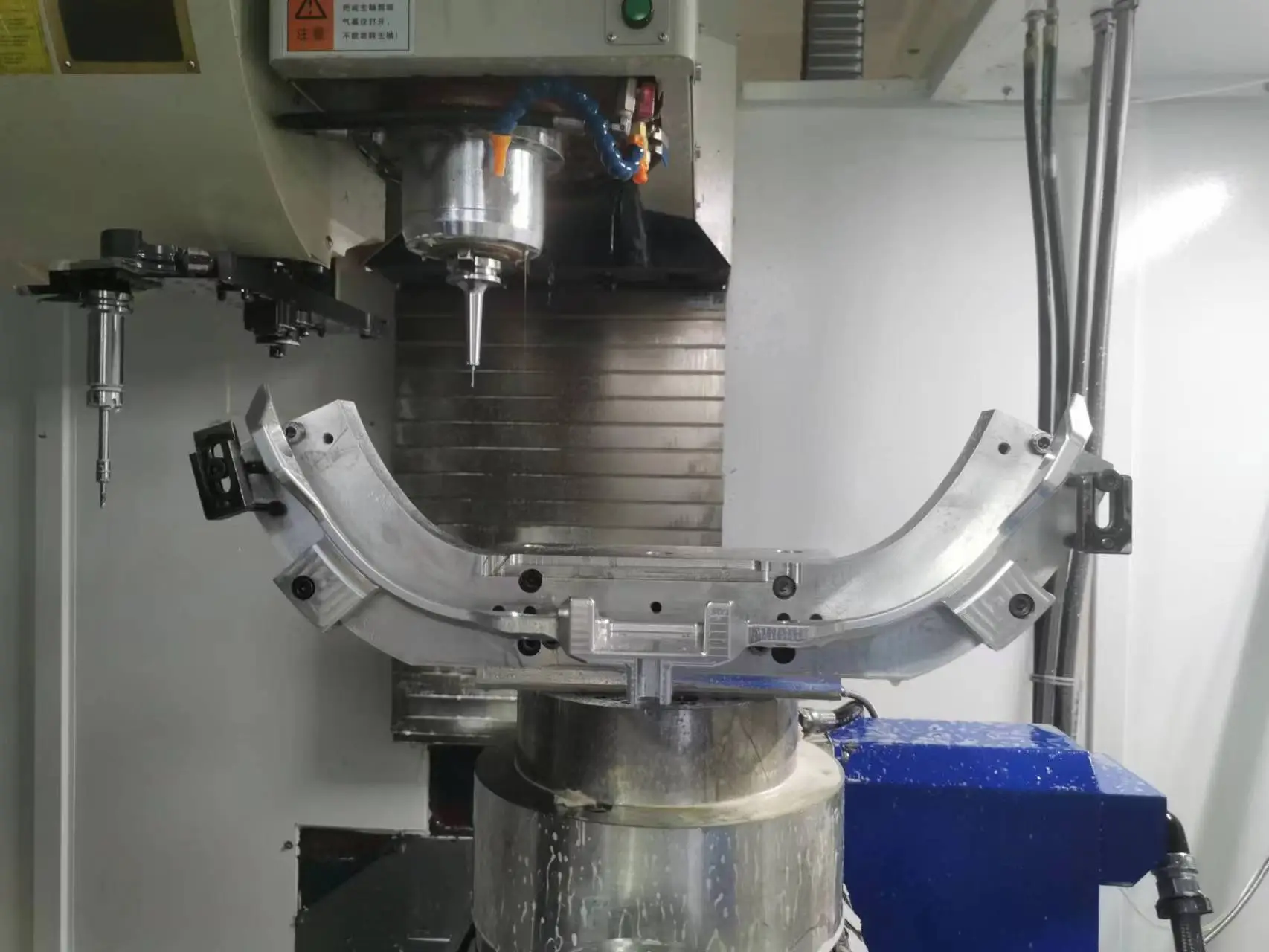
CNC Machining
The first SM technique in this list is Computer Numerical Controlled (CNC) machining. It is a widely spread industrial manufacturing method needed to fabricate components of nearly any design from almost any material.
The basis of this method is the use of automated CNC machines like lathes, mills, routers, etc., to cut material out of a workpiece. As a result, intricate design and high accuracy can be achieved.
CNC machining is considered the most versatile rapid prototyping method in this list. It has almost no limitations, but costs and proficiency of labor exploiting CNC machines.
Related Post: CNC Rapid Prototyping: The Complete Guide in 2022

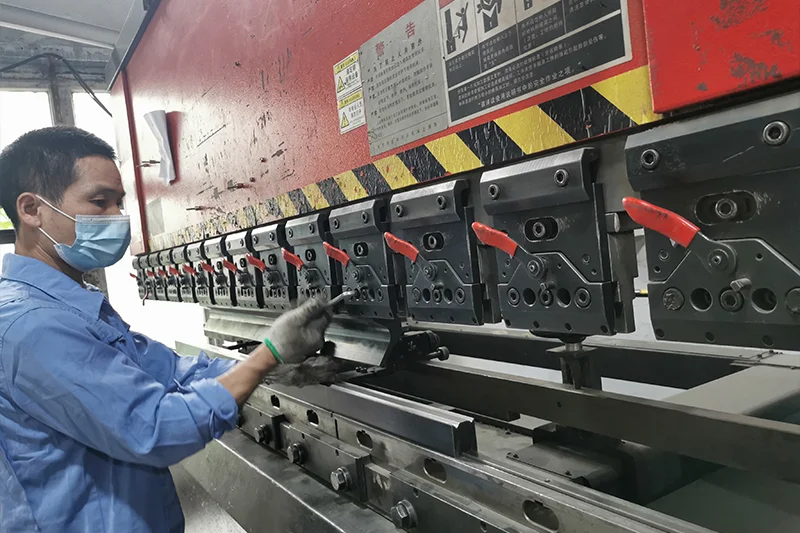
Metal Fabrication
Metal fabrication may be a particular instance of CNC machining, as both are SM methods that you can apply to metal. But, metal fabrication techniques include three other methods but CNC manufacturing.
- Metal casting prototyping.
- Metal extrusion prototyping.
- Sheet metal prototyping.
Each of these methods has its unique pros and cons. For more information, read out the detailed metal fabrication guide. But still, they are superior to 3D printing MA rapid prototyping techniques at least in the durability and mechanical properties of parts fabricated.

3. What is Rapid Prototyping Used for?
Test samples fabricated in the process of prototyping have several purposes. They help designers present their concepts to any interested parties such as board members, investors, clients, etc. Therefore, these people directly impact the business and should be given a chance to examine a new component themselves.
Another purpose is to assist manufacturers in running a business. It is done in many ways, depending on what are your manufacturing techniques and the method of prototyping you chose.
In the best-case scenario, you have G-coded files, knowledge of what material, tooling, and equipment units are required, and essential experience after prototyping is over. You also have your prototypes tested, and the properties of your components proved.

4. Advantages and Disadvantages of Rapid Prototyping
Let’s review the essential pros of rapid prototyping:
- It has relatively fast turnaround times, depending on the method.
- It is a cost-effective fabrication method.
- Facilitate production running.
- Serves Quality Assurance purposes.
- Reduces product development costs.
- Enables functionality testing.
- Reduces risks of non-compliance with best manufacturing practices.
And here are the cons you should consider while requesting rapid prototyping services.
- Is not as accurate as manufacturing methods intended for large-scale production.
- Adds initial costs to the production cycle.
- In the event of choosing a prototyping method that differs from manufacturing ones, fabricated components cannot be tested for functionality.
- Most methods require highly skilled labor.
- The material range is usually limited.
- The tooling range is usually limited.
Weaknesses of rapid prototyping are considered minor compared to the method’s strengths. That is why you still should apply for rapid prototyping services in a vast range of situations.
5. Why is Rapid Prototyping Important?
If you are still not convinced that you need to use rapid prototyping, here’s a list of concrete reasons.
Design and properties testing
The primary purpose of rapid prototyping is to receive a component with innovative design and examine it. You would be surprised if you knew how many great ideas had not proved themselves to be viable at this stage. Such designs are simply rejected or revised.
Additionally, you definitely need the properties of your components to be tested. It helps in ensuring that your components have exactly the same qualities as expected. If properties are worse than intended, you may need to adjust your manufacturing techniques, choose another material, or revise the design.
Preparation of manufacturing machines
The second most important aspect of rapid prototyping is that it helps test manufacturing techniques used in production. It means that you will know the processes, what tooling is required, what conditions, and the exact turnaround times for the production of components.
Without rapid prototyping, you would have to guess or guide manufacturing based on your experience. Probably it will work, but in practice, none of the manufacturers can allow themselves to be mistaken.
Quality assurance compliance
Indeed, you can use some properly prepared components as samples for testing. In some cases, it is needed for validating your manufacturing methods. In others, to receive documentation proving the properties of your parts manufactured.
Time and money-saving
We are jumping ahead, but you should know that requesting a third-party rapid prototyping service is a time-effective decision. For most manufacturers, time = money, as production delays result in severe expenses.
With rapid prototyping, you save plenty of time to spend on actual manufacturing. Rather than running your production machines again and again to receive constant outcomes.

6. How Much Time Does Rapid Prototyping Save?
Let’s assume that you neglected the recommendations to use rapid prototyping first. In the case you managed to run manufacture at all, here are the calculations of how much time you’ve wasted for nothing.
- Transferring CAD models into G-coded files. 1-2 days of your experts’ work could have been saved if you let a third party prepare files needed for CNC machines to operate.
- Choosing cutting tools. From a few hours to days. The selection of appropriate tooling may be frustrating if you do not have a wide enough range of them. You may also have to wait until the required tooling is delivered to you.
- Choosing a material. Similar to choosing cutting tools, it may take days of your time. You may have difficulty finding the best type of metal. It results in time delays before you actually can proceed to new components manufacturing.
- Equipment unit adjusting. Depending on your machines for manufacturing, it may take from a single shift to weeks to make everything operate as required. The material waste would also be huge.
7. How Much Does Rapid Prototyping Service Cost?
As you already know, rapid prototyping saves plenty of your time. You can measure such assets in monetary terms. Let’s reveal if requesting third-party services would cost less than the time you would spend on DIY prototyping overwise.
Let’s get down to business by stating that rapid prototyping may cost anywhere from $100 to $100,000. Here are the factors that impact the final price:
- Complexity of a part’s design.
- Availability of a ready-to-use CAD file.
- Dimensions of a part.
- A number of parts.
- The rapid prototyping method chosen.
- Materials used.
- Cutting tools used.
- Urgency or how fast you need prototyping to be done.
- The necessity of post-manufacture processing/finishing.
- Quality of post-manufacture processing/finishing.
- Transportation costs.
- The region where you/third-party provided is located.
8. How to Start a Rapid Prototyping Business?
In case you are curious about starting a prototyping business, here are the steps you should follow:
- Research market. You should conduct market research to know what business prototyping types are popular in your region. Additionally, you should learn about your potential customers and the costs of equipment, tooling, and materials.
- Create a business plan. It is the basic constituent of any business running. You should calculate all the expenses, predict potential profitability, estimate the required assets and labor, and create a general business structure.
- Fund your business. Then, you should raise capital for your business. These may be your personal finances, allocated investments, loans, etc.
- Pick your business location. You should select the location where all your premises and equipment for rapid prototyping will be situated. Not necessarily, but you may want to locate business closely to potential customers.
- Define your business brand.You should pick up your business’s name and create a logo to make your company easily recognizable.
- Register your business and receive federal and state tax IDs.In this step, you must make your business legit. You should register it with the federal government and choose a taxation option.
- Get necessary permits and licenses. It is also an integral part of running a rapid prototyping business. You must receive state and local business licensing requirements to operate. Also, considering that you will run your business out of a workshop, you will need a Certificate of Occupancy. It enables you to operate out of a physical location registered (office).
- Get business insurance. Besides licenses and permits, you are required to have insurance to operate lawfully. It is basically the financial protection of your business in the event of a covered loss.
- Open a business bank account. Any business is obligated to have a bank account to separate an owner’s personal assets from a company’s assets.
- Set up accounting for your business.It is a crucial aspect of running a business. You must have all your sources of income and expenses recorded. It facilitates taxation and business management.
- Create your website and set up a business phone system.To fully poolish your newly created business, you should create a professional website where you will be offering your rapid prototyping services. Additionally, you should have a number or two using which customers may reach you.
Besides the mentioned above, you should define the types of rapid prototyping you will be offering on the first and second steps. Initial investments that are required and the target audience will depend on this decision.
Of course, with the growth of your business, you will be purchasing new equipment and will be offering new rapid prototyping services. But for starters, you should stick to the most popular and affordable types. We strongly suggest you 3D printing and CNC machining as the optimal methods of prototyping for new businesses.

9. Working with ECOREPRAP for Prototypes
We do not try to convince you to apply for third-party rapid prototyping services. However, it is considered a common practice to fabricate new component samples for testing. In essence, it is beneficial for your company first.
In the case you are about to set up a rapid prototyping business, consider following the steps detailed above.