Table of Contents
Rapid prototyping is a crucial step in product development, and choosing the right technology can save time, reduce costs, and improve product quality.
This guide compares CNC rapid prototyping and 3D printing, helping engineers and designers make informed decisions in 2025.
Key Takeaways
1.CNC vs 3D Printing – Manufacturing Approach
- CNC is subtractive, ideal for high-precision, functional prototypes.
- 3D printing is additive, perfect for complex geometries and rapid iterations.
2.Cost and Speed Considerations
- CNC has higher equipment and labor costs but is faster for simple, large parts.
- 3D printing offers lower upfront cost and flexibility for small batches, with slightly longer build times for large parts.
3.Material and Application Suitability
- CNC supports metals and engineering plastics for mechanically demanding prototypes.
- 3D printing works best with thermoplastics, resins, and some metal powders for design validation and intricate parts.
4.Optimizing Prototyping Strategy
Many companies, including Ecoreprap, combine CNC for functional bases and 3D printing for complex designs to save time, cost, and improve reliability.
Core Differences Between CNC and 3D Printing
The main difference between CNC and 3D printing lies in their manufacturing approach: CNC is subtractive, removing material from a solid block, while 3D printing is additive, building layer by layer.
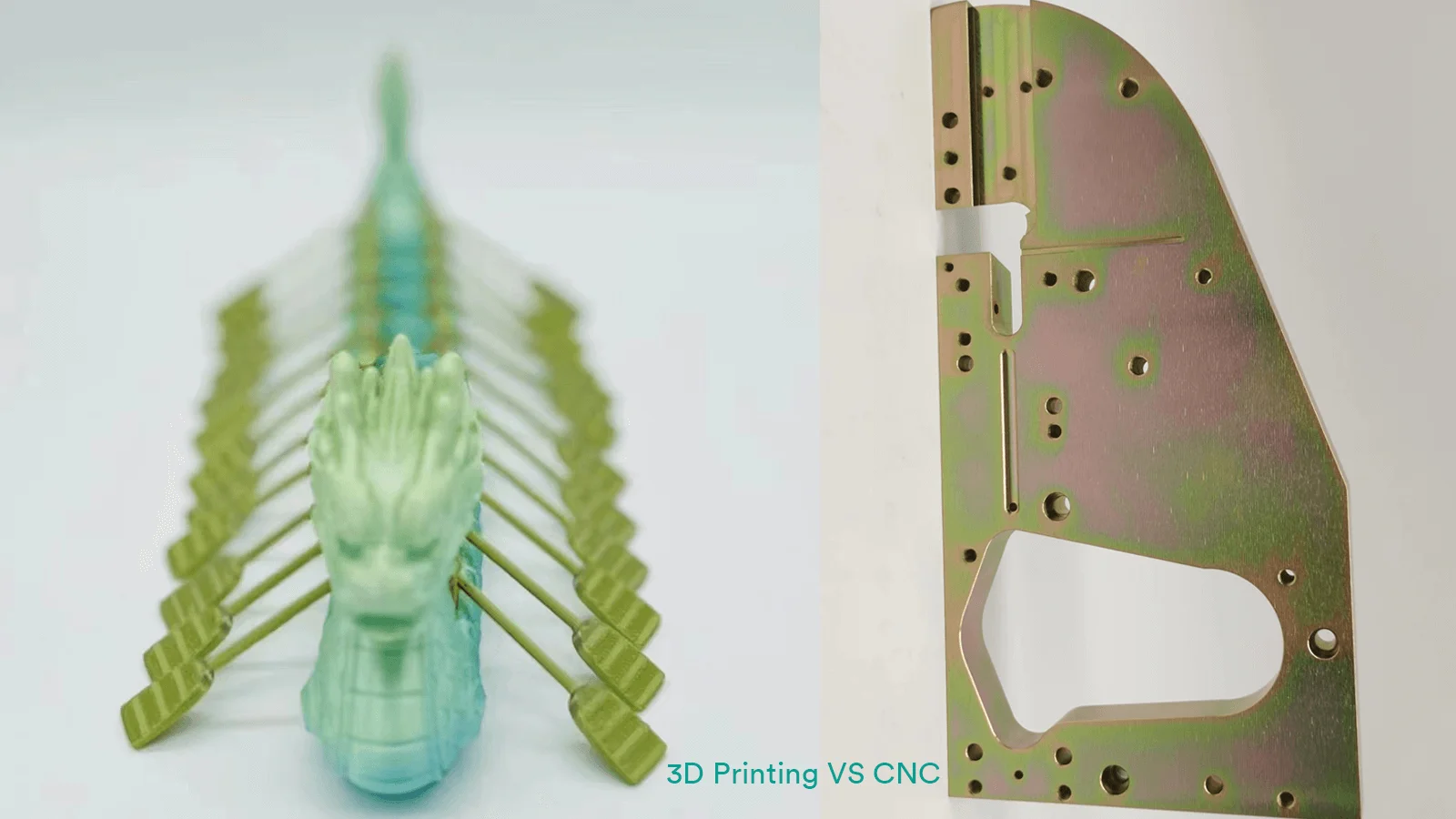
1.What is CNC Rapid Prototyping?
CNC rapid prototyping uses computer-controlled machines to carve parts from metals, plastics, or composites.
Precision is high, typically ±0.05 mm, making it ideal for functional prototypes that require mechanical testing.
In our experience at xx, CNC is preferred when structural integrity is critical or when producing multiple identical parts for testing.
2.What is 3D Printing for Rapid Prototyping?
3D printing creates prototypes layer by layer, allowing complex geometries and internal structures that CNC cannot easily achieve.
Typical materials include PLA, ABS, resins, and metal powders.
3D printing is particularly useful for design validation and rapid iterations.
At Ecoreprap, we use 3D printing for early-stage prototyping to accelerate design feedback loops.
Cost Comparison: CNC vs 3D Printing
CNC prototyping generally has higher equipment and labor costs, while 3D printing offers lower upfront investment but can be more expensive for large volumes due to material cost and post-processing.
1.CNC Cost Factors
CNC machines range from $5,000 to $150,000 depending on precision and size.
Materials such as aluminum or engineering plastics cost $10–$100 per kg.
Skilled operators are required, with hourly rates around $40–$70.
Checklist for CNC cost planning:
- Evaluate prototype quantity
- Assess material type
- Include setup time in budget.
2.3D Printing Cost Factors
3D printers range from $500 to $20,000, suitable for desktop to industrial-scale prototyping.
Materials vary from $20 to $150 per kg depending on resin or metal powders.
Minimal operator skill is needed, but post-processing can add time.
Checklist for 3D printing cost planning:
- Compare batch size
- Check post-processing needs
- Factor in support material usage
Speed and Production Efficiency
CNC is faster for simple geometries and larger parts, while 3D printing excels in producing complex designs and multiple iterations.
1.CNC Production Time
High-speed CNC machines can reduce cycle time by 20–30% for metal prototypes.
Experience shows CNC is efficient for functional testing when iteration is less frequent.
Average production time ranges from 2 to 10 hours per part depending on complexity.
2.3D Printing Build Time
3D printing can produce small parts in 1–12 hours.
SLA printing offers high resolution (50–200 microns) and is ideal for early design validation.
Experience indicates 3D printing accelerates feedback cycles in rapid design iterations.
Accuracy and Material Compatibility
CNC provides higher precision and is compatible with metals and engineering plastics, while 3D printing offers flexibility for intricate designs but generally lower mechanical strength.
1.CNC Precision and Materials
CNC achieves tolerances of ±0.01–0.05 mm.
Material options include aluminum, steel, titanium, and high-strength plastics.
In practice, CNC is preferred for parts requiring mechanical reliability or functional testing.
At Ecoreprap, we often recommend CNC when prototypes will undergo stress or load testing.
2.3D Printing Precision and Materials
3D printing offers ±0.05–0.2 mm tolerance depending on technology (SLA higher than FDM).
Materials include thermoplastics, resins, and metal powders.
It is ideal for intricate geometries, custom shapes, or lattice structures where traditional machining is impractical.
Suitability by Project Type
Choosing the right prototyping method depends on project goals, complexity, and required iterations.
1.Small-Batch Production & Iterative Design
For multiple iterations or conceptual prototypes, 3D printing is often more practical due to faster setup and lower per-part cost.
CNC is suitable if parts need to be functional or mechanically tested.
2.Large, High-Precision Parts
CNC is preferred for large components or when high precision and strength are required.
3D printing is limited by build volume and post-processing for large-scale metal parts.
Industry Trends and 2025 Insights
Hybrid prototyping approaches are becoming common in 2025, combining CNC for functional bases and 3D printing for complex geometries.
1.Adoption Data
Recent surveys indicate 42% of industrial prototyping companies use CNC for functional testing, and 38% rely on 3D printing for design validation.
Experience shows integrating both methods can optimize time and cost efficiency.
2.Certifications and Standards
CNC manufacturing often follows ISO 9001 for quality management and AS9100 for aerospace prototypes.
3D printing adheres to ASTM F42 standards for additive manufacturing materials and processes.
Choosing the Right Method – Practical Checklist
To decide between CNC and 3D printing, consider the following checklist:
- Define prototype goal: functional vs conceptual
- Evaluate material strength and mechanical requirements
- Determine production volume and iteration needs
- Factor equipment cost, availability, and operator skill
- Assess post-processing and finishing requirements
- Review 2025 trends and technology updates
Conclusion
CNC and 3D printing each have unique advantages. CNC excels in high-precision, functional, and high-strength parts, while 3D printing provides flexibility for complex geometries and rapid iterations.
At Ecoreprap, our team combines both technologies to deliver reliable prototypes efficiently, helping clients accelerate product development with informed technology choices.
Rapid Prototyping Knowledge Hub
1.Understanding CNC Rapid Prototyping
- What is CNC Rapid Prototyping? Complete Guide for 2025
- What are the Benefits of CNC for Rapid Prototyping?
- CNC Machining for Rapid Prototyping: How to Choose the Right Solution
- 3 Types of Prototyping Services for Fast and Cost-Effective Prototypes
2.CNC vs Other Prototyping Methods
- CNC Rapid Prototyping vs 3D Printing: Which to Choose in 2025?
- 3D Printing vs CNC Machining: Which Is Right for You?
- CNC Milling vs CNC Turning: Which Is Better for Prototyping?
3.Engineering & DFM Considerations
- CNC Prototype Tolerances Explained
- How to Optimize CAD Files for CNC Prototyping
- How Material Selection Affects CNC Prototype Performance
- ABS vs Aluminum: Which is Better for CNC Prototypes?
- Why Production Time Matters in Prototype CNC Parts Manufacturing?
4.From Prototype to Production
- CNC Machining for Small Batch Prototyping
- From Prototype to Production: How CNC Companies Support Scalability
5.CNC Prototyping Services in China
- CNC Prototyping Services China (Complete Buying Guide)
- Key Factors to Consider When Sourcing CNC Prototypes from China
- Top 5 Prototype Manufacturers in China
- 5 Key Benefits of Using Chinese Prototyping Services
Get Rapid Prototyping Services

Lucas is a technical writer at ECOREPRAP. He has eight years of CNC programming and operating experience, including five-axis programming. He’s a lifelong learner who loves sharing his expertise.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy

What is 5-axis Machining? A Complete Guide.
5-Axis CNC machining is a manufacturing process that uses computer numerical control systems to operate 5-axis CNC machines capable of moving a cutting tool or a workpiece along five distinct axes simultaneously.

Which Country is Best for CNC Machining?
China is the best country for CNC machining service considering cost, precision, logistic and other factors. Statistical data suggests that China emerges as the premier destination for CNC machining.

Top 5 Prototype Manufacturing China
Selecting the right prototype manufacturing supplier in China is a critical decision that can significantly impact the success of your product development project.

CNC Machining Tolerances Guide
Machining tolerances stand for the precision of manufacturing processes and products. The lower the values of machining tolerances are, the higher the accuracy level would be.



